Angular Momentum And Central Forces
Found 7 free book(s)4. Central Forces - University of Cambridge
www.damtp.cam.ac.ukWe already saw in Section 2.2.2 that angular momentum is conserved in a central potential. The proof is straightforward: dL dt = mx⇥x¨ = x⇥rV =0 where the final equality follows because rV is parallel to x. The conservation of angular momentum has an important consequence: all motion takes place in a plane.
8.09(F14) Chapter 1: A Review of ... - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.edumotion and central force scattering, and the basic ideas of canonical transformations. This ... Often when using Lwe can avoid discussing forces of constraint (for example, the force normal to the surface). ... which is equivalent to the relation between angular momentum and torque perpendicular to
Angular Momentum and Central Forces
alan.ece.gatech.educentral field) has conserved physical observables such as energy, angular momentum, etc. – In a central force problem there is no external torque acting on the system • “The law of conservation of angular momentum is a statement about the rotational symmetry of a …
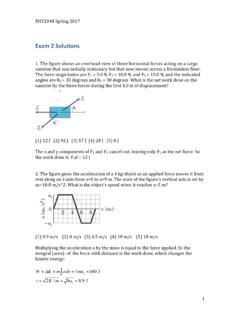
Exam 2 Solutions - Department of Physics
www.phys.ufl.edu11. A disk rotates about its central axis starting from rest and accelerates with constant angular acceleration. At one time it is rotating at 10 rev/s; 50 revolutions later, its angular speed is 25 rev/s. Calculate the angular acceleration in rev/s^2. (1) 5.25 (2) 1.0 (3) 6.25 (4) 15.0 (5) 0.15 ω 2 2−ω 1 2=2αΔθ α= ω 2 2−ω 1 2 2Δθ =
AP Physics 1 and 2 Exam Questions - College Board
secure-media.collegeboard.orgLearning Objective (5.E.2.1): The student is able to describe or calculate the angular momentum and rotational inertia of a system in terms of the locations and velocities of objects that make up the system. Students are expected to do qualitative …
Classical Mechanics: A Critical Introduction
www.physics.upenn.eduthe forces which act on a given object. Most people require a considerable amount of practice before they can make a correct list. One must learn to distinguish between the forces acting on a thing and the forces which it exerts on other things, and one must learn the di …
Lecture Notes on Classical Mechanics (A Work in Progress)
courses.physics.ucsd.eduLecture Notes on Classical Mechanics (A Work in Progress) Daniel Arovas Department of Physics University of California, San Diego May 8, 2013