Chap 2
Found 10 free book(s)Chap 2. Basic Encryption and Decryption - Apprendre en ligne
www.apprendre-en-ligne.netChap 2. Basic Encryption and Decryption H. Lee Kwang Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science, KAIST Objectives • Concepts of encryption • Cryptanalysis: how encryption systems are “broken”
Chap. 1 Introduction to Biochemistry Reading Assignment
www.uwyo.eduChap. 2. "Water" Reading Assignment: pp. 26-49. Problem Assignment: 1-5, 7, 8, 11, 13, 15 and 16 I. Introduction. While modern biochemistry tends to …
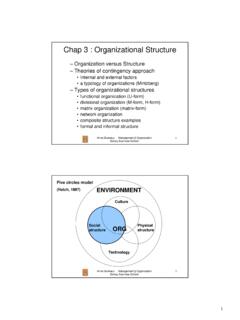
Chap 3 : Organizational Structure
www2.ulb.ac.beChap 3 : Organizational Structure – Organization versus Structure – Theories of contingency approach • Internal and external factors • a typology of organizations (Mintzberg) – Types of organizational structures • functional organization (U-form) • …
Chap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly MULTIPLE ...
academic.udayton.eduChap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly These questions may include topics that were not covered in class and may not be on the exam. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1)A monopolistically competitive firm has _____ power to set the price of its product because _____.
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
kean.edu4 ©2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 9-19 Joints 0 2 0 0 ©2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 9-20 Joints
5 Numerical Differentiation
www2.math.umd.edu2 f00(ξ)(x 1 −x 0). Here, we simplify the notation and assume that ξ ∈ (x 0,x 1). If we now let x 1 = x 0 +h, then f0(x 0) = f(x 0 +h)−f(x 0) h − h 2 f00(ξ), which is the (first-order) forward differencing approximation of f0(x 0), (5.3). Example 5.2 We repeat the previous example in the case n = 2 and k = 0. This time Q 2(x) = f(x ...
Spectral and Algebraic Graph Theory
cs-www.cs.yale.edu1 Introduction 2 2 Eigenvalues and Optimization: The Courant-Fischer Theorem21 3 The Laplacian and Graph Drawing27 4 Adjacency matrices, Eigenvalue Interlacing, and the Perron-Frobenius Theorem32 5 Comparing Graphs39 II The Zoo of Graphs46 6 Fundamental Graphs47 7 Cayley Graphs 55 8 Eigenvalues of Random Graphs63 9 Strongly Regular Graphs73 i
6 Numerical Integration
www2.math.umd.edu6.1 Basic Concepts D. Levy For the purpose of the present discussion we can think of the upper and lower Dar-boux sums (6.1), (6.2), as two approximations of the integral (assuming that the …
Introduction to Operating Systems
pages.cs.wisc.eduFigure 2.4: Running The Memory Program Multiple Times The program does a couple of things. First, it allocates some memory (line a1). Then, it prints out the address of the memory (a2), and then puts the number zero into the first slot of the newly allocated memory (a3). Finally, it loops, delaying for a second and incrementing the value
Denial of Service Attacks - Pennsylvania State University
s2.ist.psu.eduFigure 2 Low-rate Intermittent Flooding Host Based Attacks Besides misusing network protocols, attackers can also launch DoS attacks via exploiting vulnerabilities in target’s applications and systems. Different from network based attacks, this type of attacks are application specific, i.e., exploiting particular algorithms (Crosby et al. 2003),