Charged Particles
Found 7 free book(s)Chapter 2 Motion of Charged Particles in Fields
ocw.mit.eduMotion of Charged Particles in Fields Plasmas are complicated because motions of electrons and ions are determined by the electric and magnetic fields but also change the fields by the currents they carry. For now we shall ignore the second part of the problem and assume that Fields are Prescribed.
Chapter 5 Capacitance and Dielectrics
web.mit.eduFigure 5.2.3 Charged particles interacting inside the two plates of a capacitor. Each plate contains twelve charges interacting via Coulomb force, where one plate contains positive charges and the other contains negative charges. Because of their mutual repulsion, the particles in each plate are compelled to maximize the distance
Chapter 2 Coulomb’s Law - Massachusetts Institute of ...
web.mit.eduparticles is approximately . On the other hand, one may show that the gravitational force is only . Thus, gravitational effect can be ... The other object is a small charged sphere that is free to move (we neglect the force of gravity on this sphere). According to Coulomb’s law, these two like charges repel each
CHEMISTRY Module 1 Fundamentals of Chemistry
sites.ntc.doe.govThe particles that orbit the nucleus are electrons. They are very small, with a mass only 1/1835 the mass of a proton or neutron. Each electron is negatively charged, and the charge of one electron is equal in magnitude (but opposite in sign) to the charge of one proton. The number
INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY PARTICLES
nuclphys.sinp.msu.ruIntroduction to elementary particles. Includes bibliographies and index. 1. Particles (Nuclear physics) I. Title. QC793.2.G75 1987 539.7'21 86-25709 ISBN 0-471-60386-4 Printed and bound in the United States of America 20 19 18 17 16 15 14
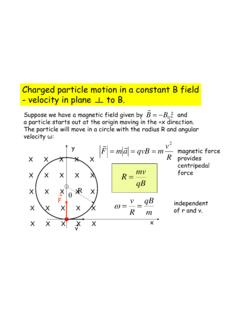
Charged particle motion in a constant B field - velocity ...
www.phys.hawaii.eduA charged particle enters a region with perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. The electric and magnetic forces will cancel if the velocity is just right. Particles with this velocity will go through undeflected. Others will be deflected. E m F qE F qv B r r r r r = =− =− × sin qE qv B qv B 1 r rr rr = θ= B E v r r r =
Synchrotron Radiation - NASA
asd.gsfc.nasa.govParticles of a particular energy E, or Lorentz factor γ, are often expected to have an isotropic distribution of pitch angles and therefore we can work out their average energy loss rate by averaging over such a distribution of pitch angles p(θ)dθ = 1