Column Chromatography
Found 8 free book(s)Experiment 6 — Thin-Layer Chromatography
www.amherst.eduIn column chromatography, the sample is carried down a column of silica or alumina by solvent, and the separate components of the mixture are captured as they elutes from (exit) the column. This can be done by allowing the solvent to flow …
Teaching notes: Chromatography - AQA
filestore.aqa.org.ukcolumn gas chromatography (GC) – a column is packed with a solid or with a solid coated by a liquid, and a gas is passed through the column under pressure at high temperature. Separation depends on the balance between solubility in the moving phase AT a, i and k PS 1.2, 3.2 and 4.1 Students could use thin-layer chromatography to identify ...
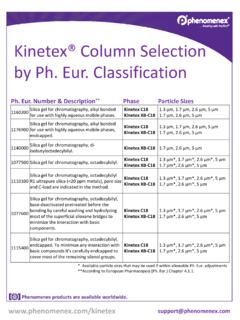
Kinetex® Column Selection by USP Listing - .NET Framework
phenomenex.blob.core.windows.netSilica gel for chromatography, alkyl bonded for use with highly aqueous mobile phases, endcapped. Kinetex C18 Kinetex XB-C18 1.3 µm, 1.7 µm, 2.6 µm, 5 µm 1.7 µm, 2.6 µm, 5 µm 1140000 Silica gel for chromatography, di-isobutyloctadecylsilyl. Kinetex XB-C18 1.7 µm, 2.6 µm, 5 µm 1077500 Silica gel for chromatography, octadecylsilyl.
Affinity Chromatography: Principles and Applications
cdn.intechopen.comAffinity Chromatography 8 pore size. Often, the optimal pore size takes in to account the ability of the affinity ligand to interact with the biomolecule as well as the surf ace area of the column since increasing pore
Introduction to Liquid Chromatography
www.chem.tamu.eduWhat is Chromatography? Separation of a mixture into individual components. The separation uses a Column (stationary phase) and Solvent (mobile phase). The components are separated from each other based on differences in affinity for the mobile or stationary phase. The goal of the separation is to have the best
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy
cires1.colorado.eduGas Chromatography In general, chromatography is used to separate mixtures of chemicals into individual components. Once isolated, the components can be evaluated individually. In all chromatography, separation occurs when the sample mixture is introduced (injected) into a mobile phase. In liquid chromatography (LC), the mobile phase is a solvent.
Size Exclusion Chromatography
wolfson.huji.ac.ilBiomolecules are purified using chromatography techniques that separate them according to differences in their specific properties, as shown in Figure I.1. Property Technique Size Size exclusion chromatography (SEC), also called gel filtration (GF) Hydrophobicity Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) Reversed phase chromatography (RPC)
Chromatography
www.soinc.orgchromatography uses liquids which may incorporate hydrophilic, insoluble molecules. ... mixture through a column of absorbent material. Thin-layer Chromatography uses an absorbent material on flat glass or plastic plates. This is a simple and rapid method to check the purity of an organic compound. It is used to detect pesticide or