Green S Theorem
Found 7 free book(s)The residue theorem and its applications
people.math.harvard.eduTheorem 1.1 (Complex Green Formula) f ∈ C1(D), D ⊂ C, γ = δD. Z γ f(z)dz = Z D ∂f ∂z dz ∧ dz . Proof. Green’s theorem applied twice (to the real part with the vector field (u,−v) and to the imaginary part with
Line Integrals and Green’s Theorem Jeremy Orlo
math.mit.eduLine Integrals and Green’s Theorem Jeremy Orlo 1 Vector Fields (or vector valued functions) Vector notation. In 18.04 we will mostly use the notation (v) = (a;b) for vectors. The other common notation (v) = ai + bj runs the risk of i being confused with i = p 1 {especially if I forget to make i boldfaced. De nition.
3 Contour integrals and Cauchy’s Theorem
www.math.columbia.edu3.2 Cauchy’s theorem Suppose now that Cis a simple closed curve which is the boundary @Dof a region in C. We want to apply Green’s theorem to the integral
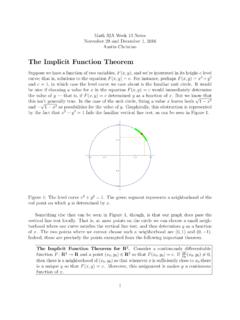
The Implicit Function Theorem - UCLA Mathematics
www.math.ucla.eduThe Implicit Function Theorem Suppose we have a function of two variables, F(x;y), and we’re interested in its height-c level ... The green segment represents a neighborhood of the red point on which y is determined by x. ... Here’s an example (due to Lincoln Chayes) to test our understand-ing.
GREEN’S FUNCTION FOR LAPLACIAN - University of Michigan
math.lsa.umich.eduGREEN’S FUNCTION FOR LAPLACIAN 3 finally we arrive at 1 = 2πRΓ′(R) this gives that Γ′(R) = 1 2πR, therefore Γ(R) = 1 2π lnR. In other wards, an application of divergence theorem also gives us the same answer as above, with the constant c1 = 1 2π.
The Stokes Theorem. (Sect. 16.7) The curl of a vector field ...
users.math.msu.eduVerify Stokes’ Theorem for the field F = hx2,2x,z2i on the ellipse S = {(x,y,z) : 4x2 + y2 6 4, z = 0}. Solution: We compute both sides in I C F·dr = ZZ S (∇×F)·n dσ. S x y z C - 2 - 1 1 2 We start computing the circulation integral on the ellipse x2 + y2 22 = 1. We need to choose a counterclockwise parametrization, hence the normal to ...
4 Green’s Functions - Stanford University
web.stanford.eduThat is, the Green’s function for a domain Ω ‰ Rn is the function defined as G(x;y) = Φ(y ¡x)¡hx(y) x;y 2 Ω;x 6= y; where Φ is the fundamental solution of Laplace’s equation and for each x 2 Ω, hx is a solution of (4.5). We leave it as an exercise to verify that G(x;y) satisfies (4.2) in the sense of distributions. Conclusion: If ...