How To Calculate The Probabilities
Found 10 free book(s)CHAPTER 2 Estimating Probabilities
www.cs.cmu.eduexample, we can calculate that the probability P(Gender =male)=0:6685 for the joint distribution in Table 1, by summing the four rows for which Gender = male. Similarly, we can calculate the probability P(Wealth = rich)=0:2393 by adding together the probabilities for the four rows cover-ing the cases for which Wealth=rich.
Introduction to Hidden Markov Models
cse.buffalo.edu• Transition probabilities and initial probabilities are calculated from language model. • Observations and observation probabilities are as before. a m h e r s t b v f o • Here we have to determine the best sequence of hidden states, the one that most likely produced word image. • This is an application of Decoding problem.
Chapter 10 Joint densities - Yale University
www.stat.yale.edudescribe how one might calculate probabilities of the form Pf.X;Y/2Bgfor various sub-sets B of the plane. For example, how could one calculate PfX <Ygor PfX2 CY2 •9gor PfX CY •7g? <10.1> Definition. Say that random variables X and Y have a jointly continuous distribution with joint density function f.¢;¢/if †joint density Pf.X;Y/2BgD ZZ
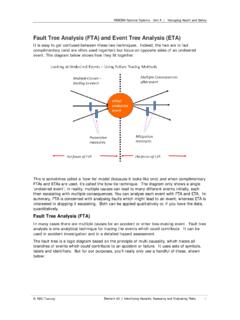
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) and Event Tree Analysis (ETA)
www.icao.intMoving up again, we can now calculate the probability of the top event. These faults are below an AND gate, so we multiply the probabilities, giving 0.21 x 1 x 0.35 = 0.0735. The top of the fully quantified fault tree then looks like this:
Conditional Probability
www3.nd.eduCalculating Conditional Probabilities (b) What is the probability that the day chosen was a Sunny day, P(S)? The sample space is still the 30 days under discussion. It was sunny on 9 + 1 = 10 of them so P(S) = 10 30 ˇ33%. (c) What is P G S? P G S = P(G\S) P(S). Hence we need to calculate P(G\S). Here the sample space is still
Joint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities
markirwin.netJoint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities The three axioms for probability don’t discuss how to create probabilities for combined events such as P[A \ B] or for the likelihood of an event A given that you know event B occurs. Example: Let A be the event it rains today and B be the event that it rains tomorrow.
CS 547 Lecture 9: Conditional Probabilities and the ...
pages.cs.wisc.eduCS 547 Lecture 9: Conditional Probabilities and the Memoryless Property Daniel Myers Joint Probabilities For two events, E and F, the joint probability, written P(EF), is the the probability that both events occur. For example, let E be “the probability that a die roll is even” and F be “the probability that a die roll is greater than 3”.
Review of Probability Theory
cs229.stanford.eduBy using this function one can calculate the probability of any event in F.3 Figure ?? shows a sample CDF function. Properties: 2Technically speaking, not every function is not acceptable as a random variable. From a measure-theoretic perspective, random variables must be Borel-measurable functions. Intuitively, this restriction ensures that
Fundamentals of Probability
78bbm3rv7ks4b6i8j3cuklc1-wpengine.netdna-ssl.comYou can use your TI 83/84 Plus to calculate the Factorial Formula: 1. First input value for total number of objects. 2. Press MATH 3. Use the Arrow Keys to highlight PRB 4. Use Arrow Keys to highlight 4: ! 5. Press ENTER Fundamental Counting Principal (FCP) When repetitions are allowed and the number of ways to fill an open place is not ...
1 Probability, Conditional Probability and Bayes Formula
www2.isye.gatech.eduThe multiplication rule tells us how to find probabilities for composite event (A¢B). The probability of (A¢B) is used in the general addition rule for finding the probability of (A[B). Rule Notation Definitions The conditional probability of A given B is the probability of event A, if event B occurred. P(AjB)