Search results with tag "Probabilities"
Risk-Neutral Probabilities
people.stern.nyu.eduRisk-Neutral Probabilities 6 Examples of Risk-Neutral Pricing With the risk-neutral probabilities, the price of an asset is its expected payoff multiplied by the riskless zero price, i.e., discounted at the riskless rate: call option: Class Problem: Price the put option with payoffs K u =2.71 and K d =0 using the risk-neutral probabilities. €
CONTINUOUS-TIME MARKOV CHAINS - Columbia University
www.columbia.eduThe conditional probabilities P(X(s+t) = j|X(s) = i) are called the transition probabil-ities. We will consider the special case of stationary transition probabilities (sometimes referred to as homogeneous transition probabilities), occurring when
CHAPTER 2 Estimating Probabilities
www.cs.cmu.edujoint probabilities over any subset of the variables, given their joint distribution. This is accomplished by operating on the probabilities for the relevant rows in the table. For example, we can calculate: The probability that any single variable will take on any specific value. For example, we can calculate that the probability P(Gender ...
Joint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities
markirwin.netJoint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities The three axioms for probability don’t discuss how to create probabilities for combined events such as P[A \ B] or for the likelihood of an event A given that you know event B occurs. Example: Let A be the event it rains today and B be the event that it rains tomorrow.
CS 547 Lecture 9: Conditional Probabilities and the ...
pages.cs.wisc.eduCS 547 Lecture 9: Conditional Probabilities and the Memoryless Property Daniel Myers Joint Probabilities For two events, E and F, the joint probability, written P(EF), is the the probability that both events occur. For example, let E be “the probability that a die roll is even” and F be “the probability that a die roll is greater than 3”.
Introduction to Hidden Markov Models
cse.buffalo.edu• Transition probabilities and initial probabilities are calculated from language model. • Observations and observation probabilities are as before. a m h e r s t b v f o • Here we have to determine the best sequence of hidden states, the one that most likely produced word image. • This is an application of Decoding problem.
Tabl e: Cumulative Binomial probabilities [ ] n ( ) P X c ...
www.math.hawaii.eduTable: Cumulative Binomial probabilities ( continued ) 2 p c 0.05 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.50 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 0.95
Better Predicted Probabilities - Stata
www.stata.como Inverse probability weighting o Propensity score methods o Expected loss o Discrete-time survival functions Many authors state that invalid predicted probabilities are the principal disadvantage of LPMs (e.g., Westin 1973, Long 1997, Hellevik 2007, …
15 Markov Chains: Limiting Probabilities
www.math.ucdavis.edu15 MARKOV CHAINS: LIMITING PROBABILITIES 170 This is an irreducible chain, with invariant distribution π0 = π1 = π2 = 1 3 (as it is very easy to check). Moreover P2 = 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 , P3 = I, P4 = P, etc. Although the chain does spend 1/3 of the time at each state, the transition
Forecasting the Supply of Human Resources - Jiwaji University
www.jiwaji.eduA transition matrix, or Markov matrix, can be used to model the internal flow of human resources. These matrices simply show as probabilities the average rate of historical movement from one job to another. To determine the probabilities of job incumbents remaining in their jobs for the forecasting period. Example -
Predicted probabilities and marginal effects after ...
www.princeton.eduPredicted probabilities after logit/probit: estimating the probability that the outcome variable = 1, setting a predictor to specific value
1 Probability, Conditional Probability and Bayes Formula
www2.isye.gatech.eduThe multiplication rule tells us how to find probabilities for composite event (A¢B). The probability of (A¢B) is used in the general addition rule for finding the probability of (A[B). Rule Notation Definitions The conditional probability of A given B is the probability of event A, if event B occurred. P(AjB)
CHAPTER A - Stanford University
web.stanford.edustates are represented as nodes in the graph, and the transitions, with their probabil-ities, as edges. The transitions are probabilities: the values of arcs leaving a given. 2 APPENDIX A•HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS state must sum to 1. FigureA.1b shows a Markov chain for assigning a probabil-
Probability of Default Ratings and Loss Given Default ...
care-mendoza.nd.educase that firms with above average firm-wide expected LGDs have lower default probabilities than other firms with the same CFR. Based on this reasoning, given a CFR and an expected firm-wide LGD rate, PDRs are derived in a straightforward manner via idealized loss and default tables. (See Appendix 1.)
Chapter 1 Poisson Processes - NYU Courant
www.math.nyu.eduIf we have a Markov Chain {Xn} on a state space X, with transition probabil-ities Π(x,dy), and a Poisson Process N(t) with intensity λ, we can combine the two to define a continuous time Markov process x(t) with X as state space by the formula x(t) = XN(t) The transition probabilities of this Markov process are given by
An Introduction to the Kalman Filter - Welcome to the UNC ...
www.cs.unc.eduThe probability of an outcome favoring either or is given by. (2.1) If the probability of two outcomes is independent (one does not affect the other) then the probability of both occurring is the product of their individual probabilities:. (2.2) For example, if the probability of seeing a “heads” on a coin flip is 1/2, then the
Decision Making under Uncertain and Risky Situations
www.soa.orgprobabilities; hence, determining the consequences of our choices. The origin of decision theory is derived from economics by using the utility function of payoffs. It suggests that decisions be made by computing the utility and probability, the ranges of options, and also lays down strategies for good decisions [3].
A Review of Basic Statistical Concepts - SAGE Publications Inc
www.sagepub.comarguments from probabilities may be pretty useful. In contrast, some modern nonstatisticians might agree with what the first author’s father, Bill Pelham, used to say about statistics and probability theory: “Figures . 2 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS can’t lie, but liars sure can figure.” His hunch, and his fear, was that “you
Joint and Marginal Distributions - University of Arizona
www.math.arizona.eduAs with univariate random variables, we compute probabilities by adding the appropriate entries in the table. P{(X,Y) ∈ A} = X (x,y)∈A f (X,Y )(x,y). Exercise 2. Find 1. P{X = Y} 2. P{X +Y ≤ 3}. 3. P{XY = 0}. ... The joint cumulative distribution function is right continuous in each variable. It has limits at −∞ and
Single Maths B Probability & Statistics: Exercises & Solutions
www.maths.dur.ac.ukno chance of winning. What do you think of Joe’s advice? SOLUTION: Assume that the sample space consists of a win for each of the 16 different horses. Joe’s probabilities for these sum to 1.3 (rather than unity), so Joe is incoherent, albeit profitable! Additionally, even “Dobbin” has a non-negative probability of winning. 6. QUESTION:
INSTRUCTIONS: Applying the AHRQ Quality Indicators to ...
www.ahrq.govcalculate and sum the probabilities to obtain the counts of expected events (see box above). Another commonly used measure is: Observed to Expected (O/E) ratio = observed rate / expected rate. If a hospital’s observed rate for an indicator is higher than its expected rate (an O/E ratio greater than 1),
LECTURE 1 INTRO TO GENETICS - University of Alberta
sites.ualberta.caAutosomal Dominant probabilities: Daughters 50% normal 50% affected Sons 50% normal 50% affected Neurofibromatosis - Café au lait spots In Neurofibromatosis - A large plexiform neurofibroma - Caused by a mutation in the NF1 gene on chromosome 17. - This is one of the largest genes in the genome.
Table of Poisson L Probabilities For a given value of ...
faculty.wwu.edul x 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 5.0 0 0.0166 0.0150 0.0136 0.0123 0.0111 0.0101 0.0091 0.0082 0.0074 0.0067 1 0.0679 0.0630 0.0583 0.0540 0.0500 0.0462 0.0427 ...
Guidelines for Wind Resource Assessment: Best Practices ...
www.adb.org3 Illustration of Exceedance Probabilities 10 A2.1 Process for Estimation of Annual Energy Production 26. v Foreword Wind energy enjoys a unique place in climate change mitigation. It is the most mature and the most cost-e ective solution to reducing global greenhouse gas
Lecture 3 Scoring Matrices Position Specific Scoring ...
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov(transition probabilities) Transition probability in two steps P2 (a,b) (Matrix square) ... Scoring matrices discussed so far are used in pairwise sequence alignment (previous class) . Can be used to; • estimate the evolutionary distance between a pair of proteins.
Review Notes for IB Standard Level Math
www.nlcsmaths.com6.15 Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions . . . . . . . . . .111 6.15.1 Explicitly Listed Probabilities ...
std normal table - University of Arizona
www.math.arizona.eduStandard Normal Cumulative Probability Table Cumulative probabilities for POSITIVE z-values are shown in the following table: Title: std normal table.xls Created Date:
Modeling Default Risk - Moody's Analytics
www.moodysanalytics.comDec 18, 2003 · Cross default clauses in debt contracts usually ensure that the default probabilities for each of the classes of debt for a firm are the same. That is, the default probability of the firm determines the default probability for all …
Equally Likely outcomes - University of Notre Dame
www3.nd.eduYou can do a little research on the probabilities of all types of poker hands here Example(more respectable than lotteries & poker) A box ready for shipment contains 100 light bulbs, 10 of which are defective. The quality control test is to take a random sample of 5 light bulbs, without replacement, from the box.
probably chance
www.ncert.nic.inActivity 3. Find the probabilities of getting a 3 when throwing a die a certain number of times. Also, show how it changes as the number of trials increases. Now let us consider some other examples. Example 1 : A coin is tossed 1000 times with the following frequencies: Head : 455, Tail : 545 Compute the probability for each event.
STAT 400 Discussion 09 Solutions Spring 2018 - GitHub Pages
daviddalpiaz.github.ioPZ. 10. A machine operation produces widgets whose diameters are normally distributed, with a ... and the standard deviation shifted to 0.10 inches, while the distribution of the ... Using Cumulative Binomial Probabilities table or a computer: P ( X ³ 7 ) = 1 – P
Lecture 2: Markov Decision Processes - David Silver
www.davidsilver.ukState Transition Matrix For a Markov state s and successor state s0, the state transition probability is de ned by P ss0= P S t+1 = s 0jS t = s State transition matrix Pde nes transition probabilities from all states s to all successor states s0, to P = from 2 6 4 P 11::: P 1n... P n1::: P nn 3 7 5 where each row of the matrix sums to 1.
Matrices of transition probabilities
faculty.uml.eduMarkov chain. Absorbing states and absorbing Markov chains A state i is called absorbing if pi,i = 1, that is, if the chain must stay in state i forever once it has visited that state. Equivalently, pi,j = 0 for all j i. In our random walk example, states 1 and 4 are absorb-ing; states 2 and 3 are not.
INTRODUCTION TO BINARY LOGISTIC REGRESSION
wp.asc.ohio-state.eduthe distribution of logged odds is symmetrical around 0. The same size increase or decrease in the probabilities has the same absolute value in logged odds. It is important to point out that the difference between the logged odds is not constant. For example, 2.197-1.386=.811 while 1.386-.847=.539. What does this mean? The logit
Conditional Probability
www3.nd.eduCalculating Conditional Probabilities (b) What is the probability that the day chosen was a Sunny day, P(S)? The sample space is still the 30 days under discussion. It was sunny on 9 + 1 = 10 of them so P(S) = 10 30 ˇ33%. (c) What is P G S? P G S = P(G\S) P(S). Hence we need to calculate P(G\S). Here the sample space is still
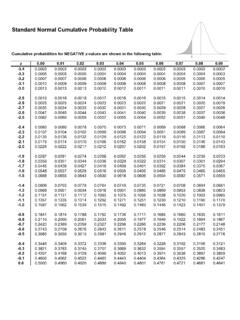
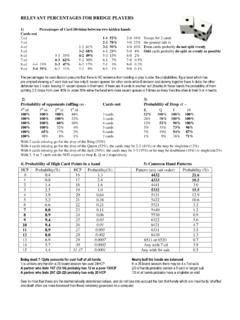
RELEVANT PERCENTAGES FOR BRIDGE PLAYERS
www.bridgewebs.comThe percentages for card division presume that there is NO evidence from bidding or play to alter the probabilities. Eg a hand which has pre-empted showing a 7 card club suit has only 6 ‘vacant spaces’ for other cards while if declarer and dummy together have 4 clubs the other defender has 2 clubs leaving 11 vacant spaces in that hand.
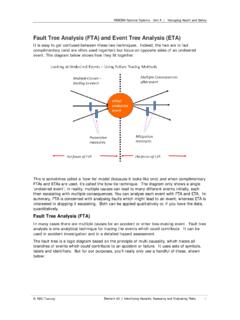
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) and Event Tree Analysis (ETA)
www.icao.intMoving up again, we can now calculate the probability of the top event. These faults are below an AND gate, so we multiply the probabilities, giving 0.21 x 1 x 0.35 = 0.0735. The top of the fully quantified fault tree then looks like this:
10. Momentum Space - Weber State University
physics.weber.edumomentum probabilities just as you would use (x) to calculate position probabil-ities: Probability of nding particle between p 1 and p 2 = Z p 2 p 1 j( p)j2 dp: (10) Of course, this formula doesn’t make sense unless ( p) is properly normalized, so that the integral from 1 to 1equals 1. But as you might guess, this will always
Probability, Expectation Value and Uncertainty
physics.mq.edu.authe measurement cannot be predicted precisely – different possible results could be obtained, each ... After all, a race is only run once, so while it is ... the practical value of this line of thinking. Nevertheless, the ‘probability as frequency’ interpretation of quantum probabilities is the interpretation that is still
Chapter 10 Joint densities - Yale University
www.stat.yale.edudescribe how one might calculate probabilities of the form Pf.X;Y/2Bgfor various sub-sets B of the plane. For example, how could one calculate PfX <Ygor PfX2 CY2 •9gor PfX CY •7g? <10.1> Definition. Say that random variables X and Y have a jointly continuous distribution with joint density function f.¢;¢/if †joint density Pf.X;Y/2BgD ZZ
National Vital Statistics Report
www.cdc.gov57.8%. Probabilities of survival can be calculated at any age by simply dividing the number of survivors at the terminal age by the number at the beginning age. For example, to calculate the probability of surviving from age 20 to age 85, one would divide the number of survivors at age 85 (42,382) by the number of
National Significant Wildland Fire Potential Outlook ...
www.predictiveservices.nifc.govhighest probabilities likely in the South. Below normal temperatures and above normal precipitation are expected across the Pacific Northwest into portions of the northern Rockies and northern Plains. The Great Lakes and Mid-Mississippi Valley are also likely to experience above normal precipitation through March.
Probabilities of Poker Hands with Variations
meteor.geol.iastate.educard hand possible. Other variations include the use of jokers and wild cards. In this paper I will derive the probabilities of being dealt one of the given hands in five-card stud poker and how those probabilities change when jokers and wild cards are included. I will also analyze Texas Hold em and derive the probability of a given hand winning
Probabilities: Expected value
people.cs.pitt.eduProbabilities: Expected value M. Hauskrecht Probability basics Sample space S: space of all possible outcomes Event E: a subset of outcomes Probability: a number in [0,1] we can associate with an an outcome or an event Probability distribution A function p: S [0,1] that assigns a probability to every possible outcome in S L ' L Í L : O ; ∈ ...
Similar queries
Risk-neutral probabilities, Risk-Neutral, Columbia University, Probabilities, Probabil-ities, The probabilities, Memoryless, Predicted probabilities, Transition, Matrices, Probability, Probabil, Default, Default probabilities, Chapter 1 Poisson Processes, An Introduction to the Kalman Filter, Determining, Statistical Concepts, SAGE Publications Inc, Cumulative, Maths B Probability & Statistics: Exercises & Solutions, Of winning, Applying the AHRQ Quality Indicators, LECTURE 1 INTRO TO GENETICS, Transition probabilities, Review Notes for IB Standard Level Math, Std normal table, Standard Normal Cumulative, Cumulative probabilities, Modeling Default Risk, University of Notre Dame, Standard, Matrices of transition probabilities, Markov, Markov chains, INTRODUCTION TO BINARY LOGISTIC REGRESSION, Distribution, Conditional Probability, Calculate, Predicted, After, Chapter 10 Joint densities, Calculate probabilities, Fire Potential Outlook, Probabilities of Poker Hands with Variations, Variations, Hands, Poker






![Tabl e: Cumulative Binomial probabilities [ ] n ( ) P X c ...](/cache/preview/3/0/e/d/f/4/3/1/thumb-30edf4310c295959b164370ee641e1ff.jpg)