Joint Probability Density
Found 10 free book(s)Conditional Joint Distributions
web.stanford.eduA joint probability density functiongives the relative likelihood of more than one continuous random variable each taking on a specific value. < £ < £ = ò ò 2 1 2 1 P(1 2, 1 2) , ( , ) a a b b a X a b Y b f X Y x y dy dx Joint Probability Density Function 0 y x 900 900 0 900 900
Chapter 5: JOINT PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Part 1 ...
homepage.stat.uiowa.edudescribed with a joint probability mass function. If Xand Yare continuous, this distribution can be described with a joint probability density function. Example: Plastic covers for CDs (Discrete joint pmf) Measurements for the length and width of a rectangular plastic covers for CDs are rounded to the nearest mm(so they are discrete).
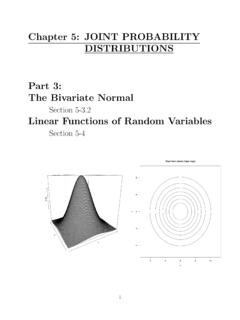
Chapter 5: JOINT PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Part 3: The ...
homepage.stat.uiowa.eduBivariate Normal Probability Density Function ... tour plot of the joint distribution looks like con-centric circles (or ellipses, if they have di erent variances) with major/minor axes that are par-allel/perpendicular to the x-axis: The center of each circle or …
LECTURE NOTES on PROBABILITY and STATISTICS Eusebius …
users.encs.concordia.caJoint distributions 150 Marginal density functions 153 Independent continuous random variables 158 Conditional distributions 161 Expectation 163 Variance 169 Covariance 175 Markov’s inequality 181 ... The probability of a sequence to contain precisely two Heads is …
Condit Density - Department of Statistics and Data Science
www.stat.yale.eduThe joint density for (X;Y) equals f(x;y) = (2ˇ) 1 exp (x2 + y2)=2. To nd the conditional density for Xgiven R= r, rst I’ll nd the joint density for Xand R, then I’ll calculate its Xmarginal, and then I’ll divide to get the conditional density. A simpler method is described at the end of the Example. We need to calculate Pfx 0 X x 0 + ;r ...
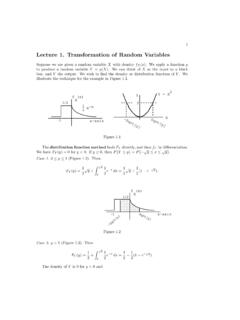
Lecture1.TransformationofRandomVariables
faculty.math.illinois.edu1. The joint density of two random variables X 1 and X 2 is f(x 1,x 2)=2e−x 1e−x 2, where 0 <x 1 <x 2 <∞;f(x 1,x 2) = 0 elsewhere. Consider the transformation Y 1 =2X 1,Y 2 = X 2 −X 1. Find the joint density of Y 1 and Y 2,and conclude thatY 1 and Y 2 are independent. 2. Repeat Problem 1 with the following new data. The joint density is ...
Probability, Statistics, and Random Processes for ...
www.sze.hu4.2 The Probability Density Function 148 4.3 The Expected Value of X 155 4.4 Important Continuous Random Variables 163 4.5 Functions of a Random Variable 174 4.6 The Markov and Chebyshev Inequalities 181 ... 5.3 The Joint cdf of X and Y 242 5.4 The Joint pdf of Two Continuous Random Variables 248
Exam 1 Practice Questions I - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.edualways X minutes late, where X is an exponential random variable with probability density function f. X (x) = λe −λx. Suppose that you arrive at the bus stop precisely at noon. (a) Compute the probability that you have to wait for more than five minutes for the bus to arrive. (b) Suppose that you have already waiting for 10 minutes.
Strict-Sense and Wide-Sense Stationarity Autocorrelation ...
isl.stanford.edu+sint with probability 1 4 −sint with probability 1 4 +cost with probability 1 4 −cost with probability 1 4 E(X(t)) = 0 and RX(t1,t2) = 1 2 cos(t2 −t1), thus X(t) is WSS But X(0) and X(π 4) do not have the same pmf (different ranges), so the first order pmf is not stationary, and the process is not SSS
Lecture 5: Estimation
www.gs.washington.eduThe likelihood is the probability of the data given the parameter and represents the data now available. The prior is the probability of the parameter and represents what was