Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Found 8 free book(s)Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Patient’s Guide
www.hepatitis.va.govNon-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) What is NAFLD? NAFLD is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the U.S. It is due to the buildup of fat in the liver not caused by an overuse of alcohol. Fatty liver (steatosis) occurs when the liver has more than 5 -10% of its weight in fat. NAFLD is related to obesity, diabetes and
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Information for Patients
www.hepatitis.va.govNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease or NAFLD is when fat is increased in the liver and there is not a clear cause such as . excessive alcohol use. The fat deposits can cause liver damage. NAFLD is divided into two types: simple fatty liver and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Most people with NAFLD
Nutrition in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
www.health.qld.gov.auMAFLD is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Risk factors include: • Being obese or over weight • Having diabetes • Having high blood cholesterol and triglyceride (a type of blood fat) levels . Are MAFLD and NAFLD the same? • In the past , fatty liver was called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, also known as NAFLD .
ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition in liver disease
www.espen.orgtitis, (iii) non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, (iv) liver cirrhosis, and (v) liver surgery/transplantation. The disease-related recommendations are preceded by general recommendations on the diagnostics of nutritional status in liver patients and on liver complications associated with medical nutrition.
The Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver ...
aasldv2019stg.aasld.orglogically into nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH; Table 2). NAFL is defined as the presence of 5% HS without evidence of hepatocellular injury in the form of hepatocyte bal-looning. NASH is defined as the presence of 5% HS and inflammation with hepatocyte injury (e.g., bal-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Alcoholic Liver Disease and Its ...
pubs.niaaa.nih.govinjury. In other patients, alcoholic fatty liver or alcoholic hepatitis often coexist and may be accompanied by hepatomegaly, an enlarged spleen (i.e., splenomegaly), or both. In cirrhotics with severe alco holic hepatitis, hepatomegaly or spleno megaly may be the dominant feature; in other patients, the signs and symp
BLOOD SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY …
www.nbt.nhs.uk11. Day. C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Evidence-based Gastroenterology. August 2004; 393-403. 12. Dixon et al. NAFLD: predictors of NASH and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology 2001; 121: 91-100 13. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or ...
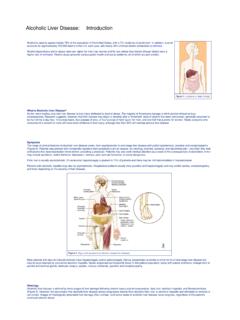
Alcoholic Liver Disease: Introduction - Hopkins Medicine
www.hopkinsmedicine.orgAlcoholic liver disease is defined by three stages of liver damage following chronic heavy alcohol consumption: fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and fibrosis/cirrhosis (Figure 5). However, the assumption that alcoholic liver disease always progresses linearly from alcoholic fatty liver, to alcoholic hepatitis and ultimately to cirrhosis is