Reactions Of Alcohols
Found 10 free book(s)10 Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, Amines, and
www.pearsonhighered.com10.1 Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Alcohols: Forming Alkyl Halides 461 the S N2 Reaction of primary alcohols Primary alcohols cannot undergo S N1 reactions because primary carbocations are too unstable to be formed, even when the reaction is heated (Section 9.3).
Chapter 3 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
www.angelo.eduChapter 3 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers 13 25 Reactions of Alcohols 26 Dehydration of Alcohols to Produce Alkenes • Heating alcohols in concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) at 180°C removes the OH group and a H from an adjacent carbon to produce an alkene, with water as a by-product. Since water is “removed”
10.2 REACTIONS OF ALCOHOLS WITH HYDROGEN HALIDES
www.saplinglearning.com10.2 REACTIONS OF ALCOHOLS WITH HYDROGEN HALIDES 441 (10.10a) Once the alcohol is protonated, the reaction is an S N1reaction with H 2O as the leaving group. When a primary alcohol is the starting material, the reaction occurs as a concerted displace-
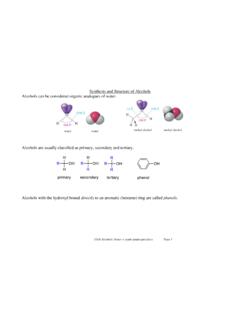
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols
as.vanderbilt.edu17.7 Some reactions of alcohols A. Reactions involving the C-O bond Dehydration to alkenes: E1 mechanism (reactivity: 3° > 2° >> 1°) requires strong acid catalyst (H 2SO 4) water is a much better leaving group than HO-usually follows Zaitzev’s rule OH H 3CCCH 2CH 3 CH 3 H 2SO 4 H 2O, 3THF C H 3C H 3C C CH H H2C C H 23-H 2O 95 Dehydration ...
Oxidation Reactions of Sugars
butane.chem.uiuc.eduhalf reactions. Oxidation Reactions of Sugars Oxidation of Alcohol Groups Alcohols are organic molecules with the C-OH functional group and sugars always have many of these groups. Oxidizing agents, such as chromium trioxide, convert the C-OH group of alcohols into the C=O group of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols
crab.rutgers.eduCh10 Alcohols; Struct + synth (landscape).docx Page 18 Other Selected Organometallic Reactions Corey-House Reaction This is a good synthetic way to join two alkyl groups together. A lithium dialkylcuprate reacts with an alkyl halide. The lithium dialkylcuprate is formed using the alkylithium reagent and copper (I) iodide.
Reactions of Alcohols - Rutgers University
crab.rutgers.eduDehydration Reactions of Alcohols Dehydration of alcohols requires an acidic catalyst to convert the hydroxyl into a good leaving group – this is an equilibrium reaction. It is possible to force the equilibrium to the right (alkene) by removing one or both of the products.
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOLS
www.ntci.on.ca6. Acid-Base Reactions • Like water, alcohols can act as an acid or base, depending on what it is reacting with. • When they react as an acid, the alkyl oxide ion (R-CH2O-) is formed. ethanol + sodium ethoxide ion + sodium ion + hydrogen 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 Na 2 CH3CH2O-+ 2 Na+ + H2
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
sites.tufts.edu6 Ionic Reactions - Overview 6.1 General Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A deprotonation step is required to complete the reaction when the nucelophile was a neutral atom that bore a proton Example showing deprotonation 4: 6.2 Carbocation Stability Order of Carbocation Stability: 3 >2 >1 >Methyl 6.3 actorsF A ecting the Rates of S N1 and S ...
Chapter a I to ChemICal reaCtIons - Mark Bishop
preparatorychemistry.com4.1 Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations 127 A chemical equation is a shorthand description of a chemical reaction. The following equation describes the burning of hydrogen gas to form liquid water.