Relativistic Quantum
Found 8 free book(s)M O D E R N QUANTUM MECHANICS
kgut.ac.ir8 • Relativistic Quantum Mechanics 8.1 Paths to Relativistic Quantum Mechanics 486 8.2 The Dirac Equation 494 8.3 Symmetries of the Dirac Equation 501 8.4 Solving with a Central Potential 506 8.5 Relativistic Quantum Field Theory 514 vii 486 A • Electromagnetic Units 519 A.1 Coulomb's Law, Charge, and Current 519
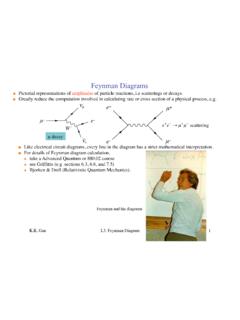
Feynman Diagrams - College of Arts and Sciences
www.asc.ohio-state.edutake a Advanced Quantum or 880.02 course see Griffiths (e.g. sections 6.3, 6.6, and 7.5) Bjorken & Drell (Relativistic Quantum Mechanics). Feynman Diagrams µ decay € e+e−→µ+µ− scattering Feynman and his diagrams
Introduction to Quantum Field Theory
www-thphys.physics.ox.ac.uk2 The Feynman path integral in particle quantum mechanics In this lecture we will recall the Feynman path integral for a system with a single degree of freedom, in preparation for the fleld theory case of many degrees of freedom. Consider a non-relativistic particle of unit mass moving in one dimension.
Introduction to Quantum Field Theory
www.astro.sunysb.eduquantum chromodynamics, followed by the renormalization theory. The second part is dedicated to Topological Field Theories. A topological ... for the relativistic case it is H= c p p2 + (mc)2. In the same logic one can restrict the global eld to a local eld theory
5. Feynman Diagrams - University of Cambridge
www.hep.phy.cam.ac.ukour relativistic theory of Quantum Mechanics. AFeynman diagramrepresents the sum of all time orderings!time +!time =!time Prof. Tina Potter 5. Feynman Diagrams 3. Feynman Diagrams Each Feynman diagram represents a term in the perturbation theory expansion of the matrix element for an interaction.
Quantum Field Theory - DAMTP
www.damtp.cam.ac.uk2.4.1 Relativistic Normalization 31 2.5 Complex Scalar Fields 33 2.6 The Heisenberg Picture 35 2.6.1 Causality 36 2.7 Propagators 38 2.7.1 The Feynman Propagator 38 2.7.2 Green’s Functions 40 2.8 Non-Relativistic Fields 41 2.8.1 Recovering Quantum Mechanics 43 { 1
Quantum Physics II, Lecture Notes 1 - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.eduThis is the equation for a (non-relativistic) particle of mass m moving along the x axis while acted by the potential V (x, t) ∈ R. It is clear from this equation that the wavefunction must be complex: if it were real, the right-hand side of (1.2) would be real while the left-hand side would be imaginary, due to the explicit factor of i. ...
CHAPTER 3 ABSORPTION, EMISSION, REFLECTION, AND …
cimss.ssec.wisc.eduwhere m is the electron mass, v the velocity, r the radius, n the quantum number, and h Planck's constant; and (b) the atoms radiate (absorb) only when the electron makes a transition from one energy state to another state of lower (higher) energy, E n1 - E n2 = hf .