Rotor Winding
Found 7 free book(s)Types of Electric Motors - The University of Alabama in ...
www.ece.uah.edu1. Brush wear: Since they need brushes to connect the rotor winding. Brush wear occurs, and it increases dramatically in low‐pressure environmet. So they cannot be used in artificial hearts.If used on aircraft, the brushes would need repltlacement after one hour of operation. 2.
ARTICLE 430 - MOTORS, MOTOR CIRCUITS AND …
arlweb.msha.govmarked with a code letter designating the locked rotor KVA per horsepower on 60 cycles. (5) Part-winding-start motors shall be marked with a code letter designating the locked-rotor KVA per horsepower that is based upon the locked-rotor current for the full winding of the motor.
GER-4212 - GE Generator Rotor Design, Operational Issues ...
www.ge.comradiates from the rotor follows the magnetic cir-cuit across the air gap, through the stator core and then back across the air gap into the rotor to complete the loop. Simply stated, the primary function of the field winding is to provide the path for the DC current needed to magnetize the field. However, reach-ing this goal is not so simple.
3-Phase Induction Motors - UNLV
www.egr.unlv.edurotor magnetic field and stator magnetic field and make the stator field rotating. The rotor will constantly be turning to align its magnetic field with that of the stator field. • The 3-phase set of currents, each of equal magnitude and with a phase difference of 120o, flow in the stator windings and generate a rotating
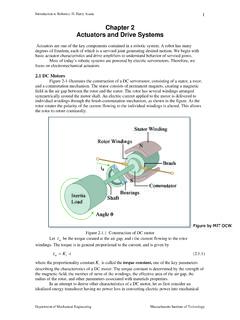
Chapter 2 Actuators and Drive Systems - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.edumagnets, thicker winding wires, and a larger rotor diameter has a larger motor constant. A motor with a larger motor constant, however, has a larger damping, as the negative slope of the torque-speed characteristics becomes steeper, as illustrated in Figure 2.1.3. Km τm-Km 2 Pout maxωm maxωm 2 1 m u maxτ ωm
Stepper motor basics - FAULHABER
www.faulhaber.comturing of both the stator and the rotor. The rotor, made of a ferromagnetic material (e.g. iron) has several teeth, which can be attracted to the stator poles. Once the stator coils are cyclically energized, the teeth of the rotor will be attracted and will tend to align themselves with the magnetized stator poles, thus resulting in
Handbook Softstarter Handbook - ABB
library.e.abb.comtor winding and the main frequency. At 50 Hz, a motor will run at a speed related to a constant of 6000 divided by the number of poles and for a 60 Hz motor the constant is 7200. To calculate the speed of a motor, the following formula can be used: n = 2 x f x 60 p n = speed f = net frequency 4