Solute
Found 8 free book(s)Chapter 3 Molar Mass Calculation of Molar Masses
people.uwec.eduSolute: the component of a solution that is dissolved in another substance Solvent: the medium in which a solute dissolved to form a solution Aqueous: any solution in which water is the solvent Chapter 5 The properties and behavior of solutions often depend not only on the type of solute but also on the concentration of the solute.
Practical 3: Production of a dilution series of a solute ...
filestore.aqa.org.ukAS and A-level Biology practicals: Equipment set up Practical 3: Production of a dilution series of a solute to produce a calibration curve with which to
0.5 mole/liter x 180 grams/mole x 1 liter = 90 g molecules ...
www.deanza.educompare to the grams of solute in the 0.5M glucose solution? 0.5 mole/liter x 342 grams/mole x 1 liter = 171 g = almost twice as many grams How many molecules of sucrose in that 1 liter of 0.5M sucrose solution? How does that compare to the amount of solute in the 0.5M glucose solution?
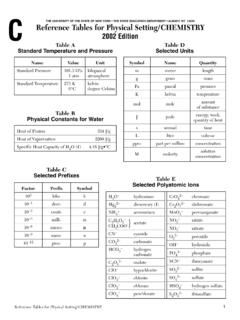
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK • THE STATE ...
www.p12.nysed.govSolute per 100 g of H 2 O (g) 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 KI NaNO 3 NH 3 HCl NaCl KNO 3 NH 4Cl KCl SO 2 KClO 3 Table G Solubility Curves Ions That Form Soluble Compounds Exceptions Group 1 ions (Li+, Na+, etc.) ammonium (NH 4 +) nitrate (NO 3 –) acetate (C 2 H 3 O 2 – or CH 3 COO–) hydrogen carbonate (HCO 3 ...
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
orise.orau.govhypotonic: the area with lower concentration of solute (more water) water • essential for cells • water moves across the cell membrane by osmosis it depends on the concentration of water inside and outside the cell . follow the water. cell swells “salt sucks” cell shrinks .
Adsorption Basics: Part 1 - AIChE
www.aiche.orgprocess, the solid is called the adsorbent and the solute is known as the adsorbate. Commercial adsorbents are highly porous, with pore sur-face areas ranging from about 100 to 1,200 m2/g. The large surface area allows a large amount of adsorption relative to the weight of the adsorbent, well in excess of its own weight in some cases.
Why? MODEL 1: Movement of Water – a type of diffusion.
www.dvusd.orgsolution contains more solute per unit volume compared to a 1M solution, i.e. is more concentrated. Target Responses 1. Complete the following table: Left side of membrane Right side of membrane Number of water molecules 24 15 Number of sugar molecules 6 15 Ratio of water to sugar 4:1 1:1 2. a. What is the solvent in the diagram? water b.
Laboratory Math II: Solutions and Dilutions
www.training.nih.govsolute particles ” per unit volume, or ions per volume. So, normality is the number of moles of active ions per liter in a solution. Acid and base concentrations are often expressed in normality. Slide 4 . Making a Solution: What You Need to Know