Search results with tag "Buoyancy"
Barge Stability Guidelines - Maritime New Zealand
www.maritimenz.govt.nzbuoyancy may be considered to act. (The force of) buoyancy always acts vertically upwards. Metacentre (M) is a point in space where the vertical line upwards through the centre of buoyancy (B) of the ‘inclined’ vessel cuts through the vertical line upwards through the centre of buoyancy (B) of the ‘upright’ vessel. Metacentric height (GM)
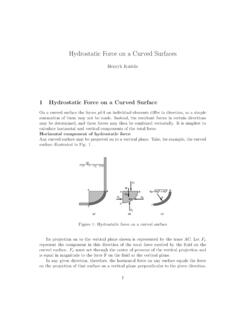
Force on a Curved Surface due to Hydrostatic Pressure
site.iugaza.edu.psBuoyancy When a body is submerged or floating in a static fluid, the resultant force exerted on it by the fluid is called the buoyancy force. Buoyancy Force= ! ! and this force will act vertically upward through the centroid of the volume of fluid displaced, known as the center of buoyancy. Archimedes’ principle
Personal buoyancy equipment on inland and inshore waters …
www.hse.gov.ukbuoyancy before entering the water. It is vital that the lifejacket/buoyancy aid is the correct type for the water conditions where the work is to be carried out. Even if a lifejacket/buoyancy aid complies with a BS EN Standard, it does not mean that it is suitable for use in all water or work conditions. BS EN 394:1994 Lifejackets and personal
To determine the Metacentric height of a floating body (i ...
scetcivil.weebly.comAccording to Archimedes Principle, FB = weight of volume of liquid displace by the body. CENTER OF GRAVITY (C) It is the point where is weight of the body is acting. CENTER IF BUOYANCY (B O AND B) It is the point to which force of Buoyancy is acting. Center of Buoyancy is center if gravity of volume of liquid displace by the body. Or in 2D case ...
Lecture6 Hydrostatic Force on curved Surfaces
fluid.itcmp.pwr.wroc.plas the buoyancy. This buoyancy force can be computed using the same principles used to compute hydrostatic forces on surfaces. The results are the two laws of buoyancy discovered by Archimedes in the third century B.C.: 1. a body immersed in a fluid experiences a vertical buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces.
FE Review Course Fluid Mechanics
www.lsu.eduF buoyancy = g fluid " submerged For curved surface, separate the pressure force into horizontal and vertical part. The horizontal part becomes plane surface and the vertical force becomes weight. If an object is submerged in several different fluids, must calculate the buoyancy in each of them, then add together. When using buoyancy in
10. Buoyancy-driven flow
www.me.unm.edu10.7. Stability of horizontal layers T = T 1 T = T 2 x y y = h T 1 < T 2 (hot above cold) – stable (and stably stratified) horizontal thermal layer, heat transfer – by conduction only T 1 > T 2 (cold above hot) – for some DT, unstable stratification leads to convection? Buoyancy
COURSE OBJECTIVES CHAPTER 4 4. STABILITY
www.usna.edubuoyancy is located at the centroid of the underwater volume of the ship. When the ship is heeled over by an external moment the underwater shape changes and thus the centroid moves. Where the center of buoyancy moves with respect to the center of gravity defines the stability characteristics of the ship as the ship is heeled over.
Natural Convection - Simon Fraser University
www.sfu.cathe body. This is known as Archimedes’ principle. We all encounter the feeling of “weight loss” in water which is caused by the buoyancy force. Other examples are hot balloon rising, and the chimney effect. Note that the buoyancy force needs the …
Chapter 3 Fluid Statics
www.civilittee-hu.comBuoyancy, Flotation & Stability Archimedes’ Principle The resultant fluid force acting on a body that is completely Submerged or floating in a fluid is called the buoyant force. Buoyancy is due to the fluid displaced by a body V D is the displaced or “Submerged ”Volume F BD
COURSE OBJECTIVES CHAPTER 10 10. SUBMARINES AND …
www.usna.eduthe reserve buoyancy above the waterline. That is, by changing the vessel’s draft, its submerged volume is altered to reflect any changes to its displacement due weight removals or additions, changes in water density, or as a passing wave causing excess buoyancy. Unfortunately, a submerged submarine is given no such luxury. The crew must actively
Guidelines on the Calibration of Non-Automatic Weighing ...
www.euramet.org4.2 Test load and indication 4 4.3 Test loads 7 4.4 Indications 9 5 MEASUREMENT METHODS 11 ... A ADVICE FOR ESTIMATION OF AIR DENSITY 37 ... E INFORMATION ON AIR BUOYANCY 54 E1 Density of standard weights 54 E2 Examples for air buoyancy in general 54
Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy - CSU, Chico
physics.csuchico.eduArchimedes’ Principle 2. Examples Involving Buoyant Force Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy . Ranking Task Exercises in Physics 108 Properties of Matter, Heat-Thermodynamics, Waves Blocks Suspended in Liquids at Different Depths—Buoyant Force 101
STABILITY OF A FLOATING BODY Principle
user.engineering.uiowa.educoncept of buoyancy, metacenter, and metacentric height. It is also an experimental verification of the theory presented in the textbook. The center of the buoyancy (C, the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid) of a floating body depends on the shape of the body and on the position in which it is floating.
The Law of Buoyancy - PDHonline.com
pdhonline.comThe Law of Buoyancy, or by another name, The Law of Flotation, is what the Principle of Archimedes is also called for and known as. Archimedes’ discovery came to change the
Density and Buoyancy Practice Test
d2ct263enury6r.cloudfront.netDensity and Buoyancy Practice Test Multiple Choice ... Archimedes’ principle B) Pascal’s principle C) Bernoulli’s principle D) Newton’s third law of motion 30) A ship stays afloat as long as the buoyant force is A) less than the ship’s weight.
LECTURE NOTES - Institute of Aeronautical Engineering
www.iare.ac.insurfaces. Center of pressure, buoyancy, meta-centre, meta-centric height. Derivations and problems. UNIT-II FLUID KINEMATICS Classes: 09 Description of fluid flow, Stream line, path line and streak lines and stream tube. Classification of flows: Steady and unsteady, uniform and non-uniform, laminar and turbulent, rotational and irrotational flows.
Hydraulics 1: Course notes
personalpages.manchester.ac.ukB4 Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle B5 Hydrostatic force on a curved surface B6 Tutorial: Hydrostatics C Kinematics and continuity C1 Kinematics C2 Conservation of mass: continuity C3 Tutorial: Kinematics and continuity D Energy and momentum: Principles D1 Conservation of energy: Bernoulli's Equation
Mechanical Engineering Principles - Weebly
vinukumar.weebly.com21.4 Archimedes’ principle 233 21.5 Measurement of pressure 235 21.6 Barometers 235 21.7 Absolute and gauge pressure 237 21.8 The manometer 237 21.9 The Bourdon pressure gauge 238 21.10 Vacuum gauges 239 21.11 Hydrostatic pressure on submerged surfaces 240 21.12 Hydrostatic thrust on curved surfaces 241 21.13 Buoyancy 241
Thermal Expansion and Sea Level Rise - University of Maine
cosee.umaine.edulevel rise. This is a consequence of Archimedes' principle of buoyancy. The mass of floating ice (above and below water both) is identical to the mass of the water displaced. If the ice melts into water, its density decreases but is mass is the same, and water level is unchanged. Thermal expansion and glacial melt will have a
What You Need To Know - California State University, Fullerton
physics.fullerton.eduDensity and Buoyancy Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: ... Archimedes Principle Any object that is either partially or completely submerged in a fluid will always feel a buoyant force acting on it. A buoyant force always acts in a direction opposite to that of gravity.
Skill and Practice Worksheets - LPS
sites.lps.org1.3 Speed Problems 1.3 Problem Solving Boxes (template for solving problems) ... 8.2 Buoyancy 8.2 Archimedes Principle 8.3 Boyle’s Law ... 8.3 Pressure-Temperature Relationship 8.3 Charles’ Law 9.1 The Structure of the Atom 9.2 Dot Diagrams Unit 4: 10.2 Power in Flowing Energy 10.2 Efficiency and Energy 11.2 Balancing Chemical Equations 11 ...
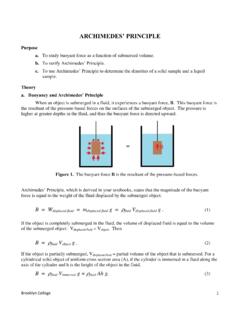
ARCHIMEDES’ PRINCIPLE
depthome.brooklyn.cuny.eduJun 19, 2019 · ARCHIMEDES’ PRINCIPLE Purpose a. To study buoyant force as a function of submersed volume. b. To verify Archimedes’ Principle. c. To use Archimedes’ Principle to determine the densities of a solid sample and a liquid sample. Theory a. Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle When an object is submerged in a fluid, it experiences a buoyant ...
SCIENCE (5 2) - CISCE
cisce.orgArchimedes’ principle, buoyancy and floatation. 5. Heat and Energy (i) Concepts of heat and temperature. Heat as energy, SI unit – joule, 1 cal = 4.186 J exactly. (ii) Anomalous expansion of water; graphs showing variation of volume and density of water with temperature in the 0 to 10 0C range. Hope’s experiment and consequences
DIPLOMA IN FIRE TECHNOLOGY Dip (Fire Technology) - NQF ...
www.tut.ac.zaFluid properties, pressure in fluids, hydrostatic forces, buoyancy, fluid flow, Bernoulli’s equation. (Total notional time: 180 hours) FIRE HYDRAULICS III (FHY316D, FHY316U) 1 X 3-HOUR PAPER (Module custodian: Department of Physics) Fluid flow types, control fluid volume principles and applications, conservation of mass flow and energy, ap-
STABILITY OF FLOATING BODIES - Western University
www.eng.uwo.ca(2) To assess stability, first find the location of the centre of gravity G of the body. (3) Then, find the location of the centre of buoyancy B (centroid of displaced volume). For a regularly shaped body this will be at half the height of the immersed portion of the body. (4) Calculate the distance GB. (5) Calculate MB, using MB = I / VS. Note ...
Smoke-Control Systems CHAPTER 5 - NFPA
www.nfpa.orgTemperature effect of the fire — the energy (buoyancy) of the heated smoke, which causes it to move Weather conditions — wind direction and velocity as well as temperature conditions Mechanical air-handling systems These factors create pressure differences across barriers (e.g., walls, doors, floors) that result in the spread of smoke.
APPENDIX C3: Design of Seaplanes - Elsevier.com
booksite.elsevier.comThe Archimedes Principle The principle is named after Archimedes of Syracuse (287-212 BCE), who first discovered this law. The law states that any object, entirely or partially immersed in a fluid, experiences a force of buoyancy equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. The law ignores surface tension (capillarity) acting on the body.
Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER MECHANICAL PROPERTIES …
ncerthelp.comthe body and this point is called the centre buoyancy. Archimedes’ Principle When a body is partially or fully immersed in a liquid, it loses some of its weight. and it is ... Density of a substance is defined as the ratio of its mass to its volume. Density of a liquid = Mass / Volume
Real-life applications - Density and Volume
tonkadensity.weebly.comintriguing is the concept of buoyancy expressed in Archimedes's principle. More than twenty-two centuries ago, the Greek mathematician, physicist, and inventor Archimedes (c. 287-212 B.C. ) received orders from the king of his hometown—Syracuse, a Greek colony in Sicily—to weigh the gold in the royal crown. According to legend, it was while ...
bseodisha.ac.in
bseodisha.ac.inHydrostatics, Buoyancy, Archimedes Principle, laws of flotation. Unit — 4 Sound 02 Marks Waves, progressive and stationary waves, mechanical waves, equation of a progressive wave, transverse vibration of a string, speed of sound waves, Newton's formula, Superposition of sound waves, Beats, Echo,
CHAPTER 12 SHIP STABILITY AND BUOYANCY
www.globalsecurity.organ object without being in direct contact with it. The ... on the ship causes a change in the location of the ship’s center of gravity, and thereby affects the stability of the ship.
PHYS 1001: Thermal Physics
www.physics.usyd.edu.au• Galilean thermometer – change in buoyancy • EM radiation – artery thermometer . Is human skin a thermometer? • Can you tell the temperature of an object by touching it? Thermometers Any property X that changes with temperature can be used to construct a thermometer, and hence construct a temperature scale: ...
Fish Dissection Lesson Plan
www.dec.ny.gov– found only in “ray-finned” fish; a double sac used to assist in buoyancy. • Urinary System – the kidneys remove nitrogen (ammonia) from the blood and regulate water balance in the blood and tissues. • Vertebrate – an organism with a backbone or spine. Vocabulary words will show up once in . bold. Background
Chapter 2 Review of Forces and Moments - Brown University
www.brown.edulaw; buoyancy forces are governed by laws describing hydrostatic forces in fluids. Some of these universal force laws are listed in Section 2.6. Some forces have to be measured. For example, to determine friction forces acting in a machine, you may need to measure the coefficient of friction for the contacting surfaces. Similarly, to determine
ME 101: Engineering Mechanics - IIT Guwahati
www.iitg.ac.inArchimedes (287-212 BC): Principles of Lever and Buoyancy! Mechanics is a branch of the physical sciences that is concerned with the state of rest or motion of bodies subjected to the action of forces. Rigid-body Mechanics ME101 Statics Dynamics Deformable-Body Mechanics, and Fluid Mechanics
Fluid dynamics - Equation of continuity and Bernoulli’s ...
ce.engineeringdesignresources.comprinciple. Fluid statics •What is a fluid? Density ! Pressure! •Fluid pressure and depth Pascal’s principle •Buoyancy Archimedes’ principle Fluid dynamics! •Reynolds number •Equation of continuity! •Bernoulli’s principle •Viscosity and turbulent flow •Poiseuille’s equation .
EXPERIMENT (2) BUOYANCY & FLOTATION …
site.iugaza.edu.psArchimedes’Principle states that the buoyant force has a magnitude equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body and is directed vertically upward. •Buoyant force is a force that results from a floating or submerged body in a fluid. • The force results from different pressures on the top and bottom of the object. 2
Lighter Than Air: Why Do Balloons Float?
kicp-workshops.uchicago.eduHelium balloons also work by the law of buoyancy. In this case, the helium balloon that you have is floating in a "pool" of air (in a swimming pool you are standing in a "pool of water" perhaps 10 feet deep - in an open field you are at the bottom of …
Archimedes’ Principle - content.grantham.edu
content.grantham.eduTo connect the words of Archimedes’ Principle to the actual behavior of submerged objects. To examine the cause of buoyancy, that is the variation of pressure with depth in a fluid. To use Archimedes’ Principle to determine the density of an unknown material.
Buoyancy: Archimedes Principle - MIT Haystack Observatory
www.haystack.mit.eduBuoyancy Worksheet Page 1 Buoyancy: Archimedes Principle There are two types of flying machines that allow for lift to overcome gravity. The first type, called the aerodynamic machines such as helicopters and airplanes, rely on thrust and forward speed to produce lift. The second type,
Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle
ef.engr.utk.edu1 Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle Assume block is in equilibrium. Then upward forces must equal downward forces. Upward force: pressure from fluid Downward force: atmospheric pressure plus weight Therefore Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle In this case, the object is less dense than the fluid, and it floats Here, the object has the same
Buoyancy Problem Set
www.mcvts.netBuoyancy Problem Set 1) A stone weighs 105 lb in air. When submerged in water, it weighs 67.0 lb. Find the volume and specific gravity of the stone. (Specific gravity of an object: ratio object density to water density) 2) A standard basketball (mass = 624 grams; 24.3 cm in diameter) is held fully under water. Calculate the buoyant force and ...
Buoyancy Archimedes Principle Fluid flow Viscosity
www.tcd.ieBuoyancy and Archimedes Principle • If an object floats then the buoyant force must equal its weight. Buoyant force F b F b = P 2 A 2 - P 1 A 1 F b = weight of fluid
Similar queries
Barge Stability Guidelines, Buoyancy, Buoyancy. Archimedes, Metacentric height, Archimedes Principle, Archimedes, FE Review Course Fluid Mechanics, Stability, Principle, Test, Density, Archimedes Principle and Buoyancy, STABILITY OF, Floating body, The law of buoyancy, Density and Buoyancy Practice Test, Problems, Mechanical Engineering Principles, Thermal expansion, Principle of buoyancy, What You Need To Know, Solving, Solving problems, Archimedes’ Principle, Physics, NFPA, Real-life, CHAPTER 12 SHIP STABILITY AND BUOYANCY, Direct, Ship, Brown University, Buoyancy Archimedes, EXPERIMENT (2) BUOYANCY & FLOTATION, Balloon, Buoyancy: Archimedes Principle, Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle, Buoyancy Archimedes Principle, Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle