Search results with tag "Of light"
CHAPTER10 Light – Reflection and Refraction
ncert.nic.inWe shall try to understand in this Chapter the r eflection of light by spherical mirrors and refraction of light and their application in real life situations. 10.1 REFLECTION OF LIGHT A highly polished surface, such as a mirror, reflects most of the light falling on it. Y ou ar e already familiar with the laws of r eflection of light.
ICSE Class 10 Sample Paper Physics Semester 1 for 2022 Exam
cdn1.byjus.com4. Speed of light does not change when it enters from one optical medium to another of different optical density. [1] (b) When a light ray enters from a denser medium to a rarer medium 1. The light ray bends towards the normal. 2. Angle of incidence is less than angle of refraction. 3. Speed of light decreases. 4. Speed of light remains ...
Properties of Light - University of Maryland College of ...
science.umd.eduMeasuring light intensity • Irradiance is total amount of light incident on a surface – Includes scattered light – Measured with a 180° lens (photographic light meter) • Radiance is light emitted from specific area – Measured with tube over area of …
Polarization of Light - San Jose State University
www.sjsu.edudispersion of a waveplate is the sensitivity of the retardation to wavelength ... 2≈π but the total thickness d≈2mm 24! ! = 2" #! nd d! ! d" = ! 2# "2! nd. 16. Summary Polarization of light can be described as linear, circular, elliptical or unpolarized unpolarized light is really just polarized light that has the polarization changing ...
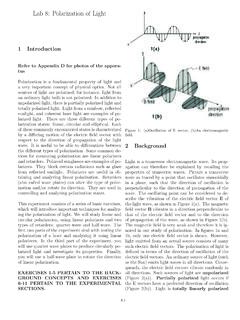
Lab 8: Polarization of Light - York University
www.yorku.caFigure 2: Polarization of light, z is the direction of propagation. (or plane polarized) if all the electric fleld vectors oscillate in the same plane, parallel to a flxed direction referred to as the polarization direction. The special case of vertically polarized light is represented by a vertical arrow (Figure 2(c)), while the special case of
Experimental Determination of the Speed of Light by the ...
www.phys.ksu.edureturning beam of light will be reflected off at a separate angle. The difference in the angle between the light source to the rotating mirror and the rotating mirror the second reflected beam is related to the time that was required by the light to travel the distance between the fixed and rotating mirrors. Using the
CHAPTER 17 Reflection and Mirrors
nguyenmapleleaf.weebly.comA ray of light strikes one mirror at an angle of 30° to the normal. It then reflects toward the second mirror. What is the angle of reflection of the light ray off the second mirror?! r1!! i1! 30°! i2! 90° "! r1! 90° " 30° ! 60° Section Review 17.1 Reflection from Plane Mirrors pages 457–463 page 463 6. Reflection A light ray strikes a ...
Electromagnetic Radiation: Interactions in the Atmosphere
www.geo.oregonstate.eduof refraction of the material Index of refraction (n) is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum relative to the speed of light through the material n = c/cn Snell’s Law describes refraction angles: n1 sinq1 = n2 sinq2
Chapter 2: Radio Wave Propagation Fundamentals
www.ihe.kit.edu-“the rays of light (EM-waves) traverse the path of stationary optical length” This results in* Snell’s laws:-“ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equivalent to the opposite ratio of the indices of refraction”-“the incidence and reflection angles are equal and they are in the same plane” n x H r,xT i PT ...
TOPIC 2.2: PARTICLE AND WAVE MODELS OF LIGHT
www.edu.gov.mb.caS3P-2-06 Outline several historical models used to explain the nature of light. Include: tactile, emission, particle, wave models S3P-2-07 Summarize the early evidence for Newton’s particle model of light. Include: propagation, reflection, refraction, dispersion S3P-2-08 Experiment to show the particle model of light predicts that the velocity
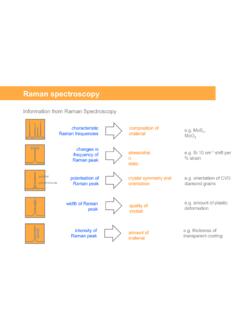
Raman spectroscopy - University of California, Irvine
www.chem.uci.educollected Raman light. The Rayleigh criteria requires that the distance between two points sources of light of equal intensity be greater than the distance from the peak to the first airy disk minimum. Complete discrimination of two adjacent materials occurs at twice the Rayleigh criteria Laser focused spot size Delivering the light Airy disk ...
The Free High School Science Texts: A Textbook for High ...
www.nongnu.orgenergy of the light emitted is the same as the gap in the energy between the two energy levels! In teresti ing Fact: In teresti ing Fact: Light has the properties of both a particle and a wave! Einstein dis-covered that light comes in energy packets which are called photons. When an electron in an atom changes energy levels, a photon of light ...
Home Lab 5 Refraction of Light
mrsrochephysics.weebly.comrefraction we will learn that the angle of the ray when transmitted through the material changes and depends on the speed of light in the two materials. Many phenomena encountered in our daily lives can be simply explained on the basis of refraction and reflection. Some of these are: why do fish look larger in the water,
Microscopy I Light and Electron Microscopy
www.auburn.eduPosition of light source and objectives is “inverted”--light source is above specimen and objective lenses are located beneath the stage. Light Objectives The basic design of bright field microscopes has been modified for special uses. Inverted microscopes (right) allow viewing of cells in flasks, welled-plates, or other deep containers
Chapter 2 The Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
radiojove.gsfc.nasa.govsecond). That is, it travels at the speed of light. Indeed light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation. Some other forms of electromagnetic radiation are X-rays, microwaves, infrared radiation, AM and FM radio waves, and ultraviolet radiation. The properties of electromagnetic radiation depend strongly on its frequency.
Electron Energy and Light Key
www.gardencity.k12.ny.us(white light) Prism 520±565 reens 3824th Blues 1. Trace the arrows in Model I and shade in the table with colored pencils where appropriate. 2. What happens to white light when it passes through a prism? -TÎIL 4. Do I col s of light travel at the same speed? 5. Do all colors of light have the same energy?
Charged Particle Accel - MIT
web.mit.eduor less than the speed of light. The waves are therefore useful for continuous acceleration of synchronized charged particles. A variety of models are used to illustrate the physics of the iris-loaded waveguide, a structure incorporated in many traveling wave accelerators. The interpretation of dispersion relationships is discussed in Section ...
International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme Subject …
www.ibo.orgA. Light is both a wave and a particle B. Both wave and particle models can explain all the properties of light C. Different properties of light can be more clearly explained by using one of the wave or particle models D. Scientists feel more confident when using more than one model to explain a phenomenon (Paper 1)
Topic 3 Waves - Physics Resources
faisalj.webs.comTotal Internal Reflection: Consider a ray of light passing from glass to air. If the ray is along the normal then it will not refract. When the angle of incidence is small; we get a weak internally reflected ray (light grey) and strong refracted ray (dark grey). As we increase the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases.
NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light ...
cdn1.byjus.comNCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light-Reflection and Refraction 6. Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the Figure10.3. Which of the following could be inside the box? (a) A rectangular glass slab (b) A convex lens (c) A concave lens
Carbon Dioxide Absorption in the Near Infrared
jvarekamp.web.wesleyan.eduunsuccessful. We began by aligning the three mirrors of the cell so that the beam of light can travel into the chamber of the device, bounce through the cell 16 times and then exit out the other side. The path length was set to 16 passes and the total path length was calculated using the dimensions of the chamber. Next, a light source, chopper, and
CHAPTER10 Light – Reflection and Refraction
www.ncert.nic.in4. Figure 10.1 shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is (a) 3/ 2 (b) 2/ 3 (c) 1/ 2 (d) 2 Light – Reflection and Refraction CHAPTER10 Fig. 10.1
CHAPTER10 Light – Reflection and Refraction
www.ncert.nic.in4. Figure 10.1 shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is (a) 3/ 2 (b) 2/ 3 (c) 1/ 2 (d) 2 Light – Reflection and Refraction CHAPTER10 Fig. 10.1
Wave Optics Chapter Ten WAVE OPTICS - Prashanth Ellina
ncertbooks.prashanthellina.com351 Wave Optics Chapter Ten WAVE OPTICS 10.1 INTRODUCTION In 1637 Descartes gave the corpuscular model of light and derived Snell’s law. It explained the laws of reflection and refraction of light at an interface.
Reflection and Refraction - UTSA
www.utsa.edureflection. Refraction The most common example of refraction is the bending of light on passing from air to a liquid, which causes submerged objects to appear displaced from their actual positions. Refraction is also the reason that prisms separate white light into its constituent colors. Refraction is commonly explained in terms
Exercises in Physics - Pearson Education
assets.pearsonschool.com13 Reflection and Refraction 171 13-1 The Speed of Light 171 13-2 Reflection 173 13-3 Refraction 177 14 Lenses, Diffraction, and Interference 183 14-1 Lenses, Telescopes, and Magnifying Glasses 183 14-2 Eyeglasses 189 14-3 Diffraction and Interference 192 15 Electrostatics 197 15-1 Electrostatic Force 197 15-2 Electric Field 200 15-3 Electrical ...
CONTENTS
ncertbooks.prashanthellina.comCONTENTS FOREWORD v PREFACE vii CHAPTER NINE RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS 9.19.1 Introduction 309 9.29.2 Reflection of Light by Spherical Mirrors 310 9.39.3 Refraction 316 9.49.4 Total Internal Reflection 319
P Points, Lines, Angles, and Parallel Lines P
www.pcrest3.comSect on . — Po nts, L nes, Angles, and Parallel L nes A ray is sometimes described as a half line—it has a beginning point but no ending point. Ray USES: A ray is like a beam of light shone into space—it has a source or beginning—but goes
Similar queries
Light, Reflection, The r eflection of light, Mirrors, Of light, REFLECTION OF LIGHT, R eflection of light, Class 10, Refraction, Properties of Light, San Jose State University, Sensitivity, Arrow, Mirror, PARTICLE AND WAVE MODELS OF LIGHT, Models, Particle, Wave models, Wave, Refraction of Light, Lenses, Properties, Shade, International Baccalaureate, Subject, Particle models, Reflection and Refraction, Wave Optics Chapter Ten WAVE OPTICS, Reflection and refraction of light, Physics, CONTENTS, Points, Lines, Angles, and Parallel Lines