Search results with tag "Thrombocytosis"
Deconstructing the Complete Blood Count (CBC)
www.childrensmercy.orgThrombocytosis in Children Relatively common in young children Usually transient, benign finding secondary to infection/inflammation – Repeat in 1-2 months and will likely resolve Platelets are acute phase reactants Reactive thrombocytosis – Iron deficiency – Major trauma – Surgery – Postsplenectomy 40
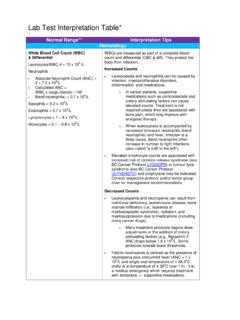
Lab Test Interpretation Table - BC Cancer
www.bccancer.bc.caPlatelets are measured as part of a complete blood count (CBC). They are involved in blood clotting. Increased Counts Thrombocytosis can be caused by bone marrow , various cancers, inflammatory disease, or surgical removal of the spleen. o In patients with myeloproliferative disorders, thrombocytosis is generally caused by the malignancy.
of the Patient
www.mpnresearchfoundation.orgDec 15, 2021 · The predominant feature of ET is thrombocytosis (increased platelet count). A Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) enzyme mutation, JAK2 3V617F, is present in approximately 50 -60% of patients living with ET.,4 Additionally, calreticulin (CALR) mutation is present in approximately 20 -25% of ET patients.4 Common
Complete Blood Count
www.meddean.luc.eduheart disease, high altitude)-Elevated erythropoietin due to malignancy Low ... • Platelets/thrombocytes principal function is to prevent bleeding ... • Numbers of platelets – Increased (Thrombocytosis)
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE)
evs.nci.nih.govJun 14, 2010 · thrombocytosis and leukocytosis Prophylactic antibiotics indicated - Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Death Definition: A disorder of the spleen. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Evidence of RBC destruction (schistocytosis) without clinical consequences - Laboratory findings with clinical consequences (e.g., renal
ADULT HAEMATOLOGY GP Pathway Guides
mft.nhs.ukThrombocytosis 10. Thrombocytopenia 11. Paraprotein 12. Microcytic anaemia 13. Normocytic or Macrocytic Anaemia ... • high haemoglobin or increased platelet count • Evidence of haemolysis • High WBC ... Platelets >450x109/L Platelets >450 x …
Medicare Limited Coverage Policies Table of Contents ...
www.sonoraquest.comdisorders such as anemia, leukemia, polycythemia, thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia. Many other conditions secondarily affethe ct blood or bone marrow, including reaction to inflammation and infections, coagulopathies, neoplasms and exposure to toxic substances.
Medicare National Coverage Determination Policy
www.questdiagnostics.comLast Updated: Medicare National Coverage Determination Policy as anemia, leukemia, polycythemia, thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia. Many other conditions secondarily affect the blood or
LCA Haemato-Oncology Clinical Guidelines
www.londoncanceralliance.nhs.ukLCA HAEMATO-ONCOLOGY CLINICAL GUIDELINES 6 2. Clinical Features 2.1. Essential thrombocythaemia (ET) ET is characterised by a persistent thrombocytosis.
Thrombocytosis (High Platelets)
www.northdevonhealth.nhs.ukThe clinical features can relate to an increased incidence of arterial and venous thrombosis and bleeding. Most can remain well for decades. ... If haematocrit is normal and no splenomegaly, repeat CBC, ferritin, and CRP in 2 to 3 weeks. If ferritin is low, consider iron deficiency.