Search results with tag "Respiratory distress"
Approach to Respiratory Distress in Dogs & Cats
todaysveterinarypractice.comof respiratory distress in small breed dogs with chronic valvular disease (eg, mitral endocardiosis), such as Cavalier King Charles spaniels. • Lower airway obstruction associated with asthma is a common cause of respiratory distress in cats, with certain breeds, such as the Siamese, overrepresented. Approach to Respiratory Distress in Dogs ...
Airway, Respiration, & …
content.nremt.orgV. Respiratory distress vs. failure a. Respiratory conditions are dynamic i. Range from minor respiratory distress to respiratory arrest ii. Can be acute, chronic, or chronic with acute exacerbation iii. Signs/symptoms are dynamic and may change over time depending on the state of patient’s disease process b.
Guideline: Newborn baby assessment (routine)
www.health.qld.gov.ausepsis, other respiratory/ vascular problems • If respiratory distress or cardiac signs o SpO 2 and cardio-respiratory monitoring • Consider CXR, 4 limb BP, echocardiography • Delay discharge • If baby is well, repeat screen in 3–4 hours • Contact RSQ as required Respiratory distress: • Tachypnoea > 60/min • Grunting • Chest ...
Acute Lung Injury and Acute Respiratory Distress …
examdev.theaba.orgThe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a devas-tating injury to the lungs, characterized by diffuse pulmonary inflammation, hypoxemia, and respiratory distress (1). In 1994, the American–European Consensus Committee (AECC) on ARDS defined diagnostic criteria to include acute onset;
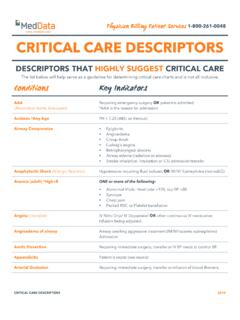
Critical Care Descriptors-1 - MedData
www.meddata.comThe list below will help serve as a guideline for determining critical care charts and is not all inclusive. ... • >3 respiratory treatments (i.e. DuoNeb, Albuterol, Ventalin, Proventil) and still in distress. ... Respiratory Distress/Failure/Arrest BiPAP, CPAP or Intubation! Physician Billing Patient Services 1-800-261-0048
Pediatric Respiratory Distress
medicine.umich.edu• Acute viral infection • Characterized by : Bark like cough Hoarseness. Inspiratory stridor • Symptoms worse at night - typically last 4-7 days • Spectrum of respiratory distress • Mild to resp failure requiring intubation • Disease most often self limited • Rarely can lead to severe obstruction and death ( < 2%)
ARRDDSSnneett A OXYGENATION GOAL: PaO 55-80 mmHg …
www.ardsnet.org1. Place on T-piece, trach collar, or CPAP ≤ 5 cm H 2O with PS < 5 2. Assess for tolerance as below for up to two hours. a. SpO 2 ≥ 90: and/or PaO 2 ≥ 60 mmHg b. Spontaneous V T ≥ 4 ml/kg PBW c. RR ≤ 35/min d. pH ≥ 7.3 e. No respiratory distress (distress= 2 or more) ¾HR > 120% of baseline ¾Marked accessory muscle use ¾Abdominal ...
PEDIATRIC VENTILATION GUIDELINES
www.health.gov.fjObjectives of Mechanical Ventilation in the pediatric patient include: • Improved pulmonary gas exchange • Relief of respiratory distress (by relieving upper and lower airway obstruction, reducing oxygen consumption, and relieving respiratory fatigue) • Management of pulmonary mechanisms (by normalizing and maintaining the
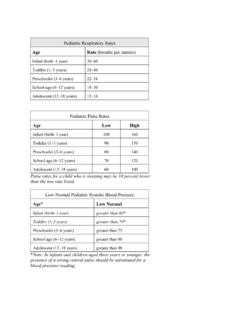
Pediatric Respiratory Rates
www.health.ny.govrespiratory distress, active bleeding, shock; near-drowning; unresponsiveness Potentially unstable Normal airway, breathing, circulation, and mental status BUT ... Newborn (birth to 1 month) Likes to be held and kept warm May be soothed by having something to suck on Avoid loud noises, bright lights
Thermoregulation Self Learning Module FINAL 2013 06
www.cmnrp.ca• Respiratory distress, apnea, hypoxemia, metabolic acidosis • Decreased activity, lethargy, hypotonia • Feeble cry, poor feeding • Decreased weight gain (ACoRN, 2012; Aylott, 2006; Blackburn, 2007) NOTE: All these signs are non-specific and may indicate other significant conditions such as bacterial infection in the newborn.
Pediatric Coding - AAPC
static.aapc.comthe ED at three weeks old with respiratory distress. • The ED physician provides an hour of critical care and Lucky is admitted to the PICU on the same day by the pediatrician. – ED physician = 99291 Critical Care first 30-74 min. – Pediatrician = 99 6899468 Initial Inpatient neonatal critical care, per day for neonate 28 days or less 17
The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults
www.diabetologists-abcd.org.ukrespiratory distress syndrome, and co-morbid states such as pneumonia, acute myocardial infarction and sepsis (Hamblin 1989). Introduction Ketonaemia 3 mmol/L and over or significant ketonuria (more than 2+ on standard urine sticks) Blood glucose over 11 mmol/L or known diabetes mellitus Bicarbonate (HCO3 - ) below 15 mmol/L and/or venous pH ...
Triage First Fast Track Guidelines
www.triagefirst.comNear drowning Persistent N/V/D Petechiae Respiratory distress Seizure Stopped breathing—required M to M Tachypnea/retractions Trauma of any type except as above
Maternal Newborn Case Study
epugh3.yolasite.comComplications Complications during pregnancy include advance maternal age, a history of two LEEP’s, two spontaneous abortions, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Complications during labor and delivery include meconium staining, and late decelerations of the FHR. Complications of the newborn include mild respiratory distress.
NATIONAL GUIDELINES FOR LASSA FEVER CASE …
ncdc.gov.ngARDS Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome AST Aspartate Aminotransferase AVPU Alert-Voice-Pain-Unresponsive BCS Blantyre Coma Scale Ca Calcium CNS Central Nervous System CPAP MRIContinuous Positive Airway Pressure CPR Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation C/S Caesarean Section CrCL Creatinine Clearance
CARE OF NORMAL NEWBORN
newbornwhocc.orgNo postnatal illness such as respiratory distress, sepsis, dyselectrolemia, hypoglycemia or polycythemia Care at birth Personnel and Equipment to be present at delivery 1, 2: One health provider (physician or nurse) trained in neonatal resuscitation must be physically available at time of birth of all infant irrespective of
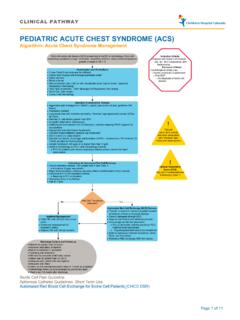
Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS) - Children's Hospital Colorado
www.childrenscolorado.orgAcute chest syndrome (ACS) is the second most common reason for hospitalization in children with sickle cell disease and a leading cause of mortality. ACS is defined as a new pulmonary infiltrate on chest radiograph in the presence of ... percent despite supplemental oxygen, increasing respiratory distress, progressive pulmonary infiltrates,
Chest Tube Management 2013 PV - RN.com
lms.rn.comrespiratory distress. If multiple adhesions, giant blebs, or coagulopathi es are present and the patient is relatively stable, the benefit of chest tube therapy can be carefully weighed against the higher risks of complications for these patients (Doelken, 2010).
Treatment of Malaria: Guidelines for Clinicians (United ...
www.cdc.govGeneral Approach to Treatment It is preferable that treatment for malaria not be initiated until the diagnosis has been established by ... injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, circulatory collapse/shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, spontaneous bleeding, acidosis, jaundice [along with at least one other sign of severe ...
RESPIRATORY FAILURE DIAGNOSIS CODING
www.hiacode.comCoding of ARDs is assigned to code J80, Acute respiratory distress syndrome when the ARDS is not further specified and affects an adult or child. For ARDS in a newborn (perinatal) assign code P22.0. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to surgery is assigned based on the type of surgery that the ARDS is associated with.
Similar queries
Approach to Respiratory Distress, Respiratory distress, RESPIRATORY, Acute, Newborn, Acute Respiratory Distress, Acute respiratory distress syndrome, Critical Care Descriptors-1, Guideline, Distress, CPAP, Pediatric, Thermoregulation Self Learning Module, Triage First Fast Track Guidelines, LASSA FEVER, Acute chest syndrome ACS, Children's Hospital Colorado, Chest tube, Of Malaria: Guidelines for Clinicians United, Approach