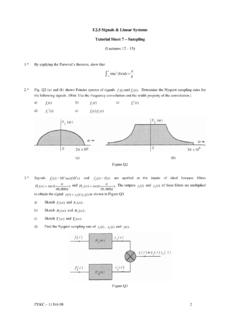
Transcription of 3: Nodal Analysis
1 3: Nodal Analysis3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 1 / 12 Aim of Nodal Analysis3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 2 / 12 The aim of Nodal Analysis is to determine the voltage at each node relativeto the reference node (or ground).
2 Once you have done this youcan easilywork out anything else you of Nodal Analysis3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 2 / 12 The aim of Nodal Analysis is to determine the voltage at each node relativeto the reference node (or ground). Once you have done this youcan easilywork out anything else you are two ways to do this:(1) Nodal Analysis - systematic; always works(2)Circuit Manipulation- ad hoc; but can be less work and clearerAim of Nodal Analysis3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 2 / 12 The aim of Nodal Analysis is to determine the voltage at each node relativeto the reference node (or ground).
3 Once you have done this youcan easilywork out anything else you are two ways to do this:(1) Nodal Analysis - systematic; always works(2)Circuit Manipulation- ad hoc; but can be less work and clearerReminders:A node is all the points in a circuitthat are directly assume the interconnectionshave zero resistance so all pointswithin a node have the samevoltage. Five nodes:A, , of Nodal Analysis3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 2 / 12 The aim of Nodal Analysis is to determine the voltage at each node relativeto the reference node (or ground).
4 Once you have done this youcan easilywork out anything else you are two ways to do this:(1) Nodal Analysis - systematic; always works(2)Circuit Manipulation- ad hoc; but can be less work and clearerReminders:A node is all the points in a circuitthat are directly assume the interconnectionshave zero resistance so all pointswithin a node have the samevoltage. Five nodes:A, , s Law:VBD=IR5 Aim of Nodal Analysis3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 2 / 12 The aim of Nodal Analysis is to determine the voltage at each node relativeto the reference node (or ground).
5 Once you have done this youcan easilywork out anything else you are two ways to do this:(1) Nodal Analysis - systematic; always works(2)Circuit Manipulation- ad hoc; but can be less work and clearerReminders:A node is all the points in a circuitthat are directly assume the interconnectionshave zero resistance so all pointswithin a node have the samevoltage. Five nodes:A, , s Law:VBD=IR5 KVL:VBD=VB VDAim of Nodal Analysis3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 2 / 12 The aim of Nodal Analysis is to determine the voltage at each node relativeto the reference node (or ground).
6 Once you have done this youcan easilywork out anything else you are two ways to do this:(1) Nodal Analysis - systematic; always works(2)Circuit Manipulation- ad hoc; but can be less work and clearerReminders:A node is all the points in a circuitthat are directly assume the interconnectionshave zero resistance so all pointswithin a node have the samevoltage. Five nodes:A, , s Law:VBD=IR5 KVL:VBD=VB VDKCL:Total current exiting any closed region is Analysis Stage 1: Label Nodes3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 3 / 12To find the voltage at each node, the firststep is to label each node with its voltageas follows(1) Pick any node as the voltage reference.
7 Label its voltageas0 V.(2) If any fixed voltage sources are connected to a labelled node, label theirother ends by adding the value of the source onto the voltage of thelabelled end.(3) Pick an unlabelled node and label it withX, Y, .., then go back tostep (2) until all nodes are Analysis Stage 1: Label Nodes3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 3 / 12To find the voltage at each node, the firststep is to label each node with its voltageas follows(1) Pick any node as the voltage reference.
8 Label its voltageas0 V.(2) If any fixed voltage sources are connected to a labelled node, label theirother ends by adding the value of the source onto the voltage of thelabelled end.(3) Pick an unlabelled node and label it withX, Y, .., then go back tostep (2) until all nodes are Analysis Stage 1: Label Nodes3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 3 / 12To find the voltage at each node, the firststep is to label each node with its voltageas follows(1) Pick any node as the voltage reference.
9 Label its voltageas0 V.(2) If any fixed voltage sources are connected to a labelled node, label theirother ends by adding the value of the source onto the voltage of thelabelled end.(3) Pick an unlabelled node and label it withX, Y, .., then go back tostep (2) until all nodes are Analysis Stage 1: Label Nodes3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 3 / 12To find the voltage at each node, the firststep is to label each node with its voltageas follows(1) Pick any node as the voltage reference.
10 Label its voltageas0 V.(2) If any fixed voltage sources are connected to a labelled node, label theirother ends by adding the value of the source onto the voltage of thelabelled end.(3) Pick an unlabelled node and label it withX, Y, .., then go back tostep (2) until all nodes are Analysis Stage 1: Label Nodes3: Nodal Analysis Aim of Nodal Analysis Nodal Analysis Stage 1:Label Nodes Nodal Analysis Stage 2:KCL Equations Current Sources Floating Voltage Sources Weighted Average Circuit Digital-to-AnalogConverter Dependent Sources Dependent VoltageSources Universal Nodal AnalysisAlgorithm Analysis of Circuits (2017-10216) Nodal Analysis : 3 3 / 12To find the voltage at each node, the firststep is to label each node with its voltageas follows(1) Pick any node as the voltage reference.