Transcription of Alcohol A (CH3 2CHCH(OH)CH3 undergoes reactions ... - …
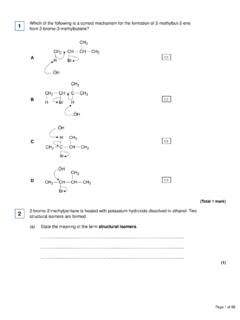
1 Alcohol A (CH3)2 CHCH(OH)CH3 undergoes reactions separately with acidified potassiumdichromate(VI) and with concentrated sulfuric acid.(a) Deduce the IUPAC name for Alcohol (1)1(b) Draw the structure of the organic product, B, formed when A is oxidised in the reaction withacidified potassium dichromate(VI). (1)(c) Two isomeric alkenes, C and D, are formed when A is dehydrated in the reaction withconcentrated sulfuric the mechanism for this dehydration (1)(d) Draw the structure of each C Isomer D (2)(e) Name the type of structural isomerism shown by C and (1)(f) List Alcohol A, product B and isomer C in order of increasing boiling (1)Page 1 of 105(g) Draw the structure of the isomer of A that is not oxidised by acidified potassiumdichromate(VI). (1)(h) Draw the structure of the isomer of A that cannot be dehydrated to form an alkene byreaction with concentrated sulfuric acid.
2 (1)(Total 9 marks)Ethanol can be oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) to ethanoic acid in a ethanal ethanoic acid(a) In order to ensure that the oxidation to ethanoic acid is complete, the reaction is carried outunder what happens when a reaction mixture is refluxed and why it is necessary, in thiscase, for complete oxidation to ethanoic (3)2 Page 2 of 105(b) Write a half-equation for the overall oxidation of ethanol into ethanoic (1)(c) The boiling points of the organic compounds in a reaction mixture are shown in thefollowing table. Compoundethanolethanalethanoic acid Boiling point / C7821118 Use these data to describe how you would obtain a sample of ethanal from a mixture ofthese three compounds. Include in your answer a description of the apparatus you woulduse and how you would minimise the loss of ethanal. Your description of the apparatus canbe either a description in words or a labelled (5)(d) Use your knowledge of structure and bonding to explain why it is possible to separateethanal in this (2)Page 3 of 105(e) A student obtained a sample of a liquid using the apparatus in part (c).
3 Describe how the student could use chemical tests to confirm that the liquid containedethanal and did not contain ethanoic (5)(Total 16 marks)The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by simple test tube each pair of compounds, give a reagent (or combination of reagents) that, when addedseparately to each compound, could be used to distinguish between what is observed in each case.(a) Butan 2 ol and 2 methylpropan 2 olReagent ..Observation with butan 2 with 2 methylpropan 2 (3)3 Page 4 of 105(b) Propane and propeneReagent ..Observation with with (3)(c) Aqueous silver nitrate and aqueous sodium nitrateReagent ..Observation with aqueous silver with aqueous sodium (3)(d) Aqueous magnesium chloride and aqueous barium chlorideReagent ..Observation with aqueous magnesium with aqueous barium (3)(Total 12 marks)Page 5 of 105(a) Propanone can be formed when glucose comes into contact with bacteria in the absence ofair.
4 (i) Balance the following equation for this reaction of glucose to form propanone, carbondioxide and ..CH3 COCH3 + ..CO2 + ..H2O(1)(ii) Deduce the role of the bacteria in this (1)4(b) Propanone is also formed by the oxidation of propan 2 ol.(i) Write an equation for this reaction using [O] to represent the oxidising (1)(ii) State the class of alcohols to which propan 2 ol (1)(c) A student determined a value for the enthalpy change when a sample of propanone wasburned. The heat produced was used to warm some water in a copper student found that the temperature of 150 g of water increased by C when 10 3 mol of pure propanone was burned in the student s results to calculate a value, in kJ mol 1, for the enthalpy change whenone mole of propanone is burned.(The specific heat capacity of water is J K 1 g 1)..(3)Page 6 of 105(d) Define the term standard enthalpy of (3)(e) Use the mean bond enthalpy data in the table and the equation given below the table tocalculate a value for the standard enthalpy change when gaseous propanone is burned.
5 C HC CC OO HC=OO=O Mean bond enthalpy /kJ mol 1412348360463805496CH3 COCH3(g) + 4O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)..(3)Page 7 of 105(f) Suggest two reasons why the value obtained by the student in part (c) is different from thevalue calculated in part (e).Reason 1 ..Reason 2 ..(2)(Total 15 marks)This question concerns the oxidation of a primary experiment was carried out using the distillation apparatus shown in the oxidation product was distilled off as soon as it was (a) Suggest the identity of reagent (1)(b) State the chemical change that causes the solution in the flask to appear green at the endof the (1)Page 8 of 105(c) Give one reason why using a water bath is better than direct heating with a Bunsen (1)(d) Suggest a reagent that could be used to confirm the presence of an aldehyde in the observation you would expect to make if an aldehyde were ..Observation ..(2)(Total 5 marks)A sample of 2-methylpropan-2-ol was contaminated with butan-2-ol.
6 The student separated thetwo alcohols using a reagent or combination of reagents that the student could use to distinguish betweenthese alcohols. State what would be observed for each (s) ..Observation with 2-methylpropan-2-ol ..Observation with butan-2-ol ..(Total 3 marks)6In each of the following questions, you should draw the structure of the compound in the spaceprovided.(a) Draw the structure of the alkene that would form 1,2-dibromo-3-methylbutane whenreacted with bromine. (1)7 Page 9 of 105(b) Draw the structure of the Alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O that is resistant tooxidation by acidified potassium dichromate(VI). (1)(c) Draw the structure of the alkene that has a peak, due to its molecular ion, at m/z = 42 in itsmass spectrum. (1)(d) Draw the structure of the organic product with Mr = 73, made from the reaction between2-bromobutane and ammonia. (1)(Total 4 marks)Glucose is an organic molecule.
7 Glucose can exist in different forms in aqueous solution.(a) In aqueous solution, some glucose molecules have the following structure.(i) Deduce the empirical formula of (1)8 Page 10 of 105(ii) Consider the infrared spectrum of solid / cm 1 State why it is possible to suggest that in the solid state very few molecules have thestructure may find it helpful to refer to Table 1 on the Data (1)(b) In the absence of oxygen, an aqueous solution of glucose can be fermented to produceethanol for use in alcoholic an equation for this fermentation two other essential conditions for the production of ethanol in this ..Condition 1 ..Condition 2 ..(3)Page 11 of 105(c) Any ethanol present in the breath of a drinker can be detected by using a ethanol is converted into ethanoic acid. The breathalyser has negative and positiveelectrodes. A current is measured and displayed in terms of Alcohol overall redox equation is as followsCH3CH2OH(I) + O2(g) CH3 COOH(I) + H2O(I)(i) Draw the displayed formula for ethanoic acid.
8 (1)(ii) Deduce a half-equation for the reduction of atmospheric oxygen to water in acidicsolution at one electrode of the breathalyser..(1)(iii) Deduce a half-equation for the oxidation of ethanol in water to ethanoic acid at theother electrode of the breathalyser..(1)(iv) The earliest breathalysers used laboratory chemicals to oxidise the ethanol toethanoic acid. Detection was by a colour a reagent or combination of reagents that you would use in the laboratory tooxidise ethanol to ethanoic the colour change that you would expect to or combination of reagents ..Colour change ..(2)Page 12 of 105(d) The fermentation of glucose from crops is the main method for the production of product is called bioethanol . The European Union has declared that bioethanol iscarbon-neutral.(i) State the meaning of the term (Extra space) ..(1)(ii) Other than carbon-neutrality, state the main advantage of the use of glucose fromcrops as the raw material for the production of (1)(iii) Give one disadvantage of the use of crops for the production of (1)(Total 13 marks)The reaction of butane-1,4-diol with butanedioic acid produces the polymer PBS used inbiodegradable packaging and disposable acid is produced by two different 1 Aqueous sodium hydroxide reacts with 1,4-dibromobutane to make butane-1,4-diol.
9 Butane-1,4-diol is oxidised to butanedioic 2 Glucose reacts with carbon dioxide in the presence of microorganisms to producebutanedioic acid directly. The carbon dioxide used in this process is obtained from a local factory that 13 of 105(a) Deduce one safety reason and one environmental reason why Process 2 is preferred toProcess (Extra space) ..(2)(b) (i) Name and outline a mechanism for the following reaction that occurs in Process 1. BrCH2CH2CH2CH2Br+NaOHBrCH2CH2CH2CH2OH+Na Br .. (3)Page 14 of 105(ii) The infrared spectra shown are those of three A 1,4-dibromobutaneCompound B butane-1,4-diolCompound C butanedioic acidIdentify the compound responsible for each spectrum by writing the correct letter, A,B or C, in the box next to each may find it helpful to refer to Table 1 on the Data Sheet.(3)Page 15 of 105(c) In the production of bioethanol , glucose (C6H12O6) is converted into a dilute aqueoussolution of ethanol and carbon the name of this process and state three essential conditions necessary to produce agood yield of (Extra space).
10 (4)Page 16 of 105(d) State the class of alcohols to which the diol butane-1,4-diol a suitable reagent or combination of reagents for the conversion of butane-1,4-diolinto butanedioic acid (HOOCCH2CH2 COOH).Write an equation for this oxidation reaction using [O] to represent the oxidising (Extra space) ..(3)(Total 15 marks) Page 17 of 105 Some alcohols can be oxidised by an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(Vl).Aldehydes can be oxidised by Tollens reagent or by Fehling s unknown pure liquid A contains only a single a simple procedure to allow you to determine whether A is a primary, a secondary or atertiary (Total 3 marks)10 Page 18 of 105 The table below shows the structures of three isomers with the molecular formula C5H10O Isomer 1(E)-pent-3-en-2-olIsomer 2pentanalIsomer 3 (a) Complete the table by naming Isomer 3.(1)11(b) State the type of structural isomerism shown by these three (1)(c) The compound (Z)-pent-3-en-2-ol is a stereoisomer of (E)-pent-3-en-2-ol.