Transcription of 急性間質性肺炎が疑われたARDS症例 - SQUARE
1 30 1 Web 2013 3 27 2012 7 18 2012 11 28 acute respiratory distress syn drome ARDS ARDS acute interstitial pneumonia AIP 1 AIP ARDS airway pressure release ventilation APRV 77 152cm 70kg 5 8 3 1 g/ 100mg/ SpO2 ICU 135/57 mmHg 82/min 38/min C CT LDH CRP Table 1 KL 6 D 352U/mL P/F 89mmHg 65 ARDS ARDS 77 acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS P/F 73mmHg 27cmH2O 1 g/ 3 P/F 63 206mmHg P/F 10 ARDS CT 30 1 Web 2013 3 27 24 P/F 73mmHg bronchoalveolar lavage BAL BAL
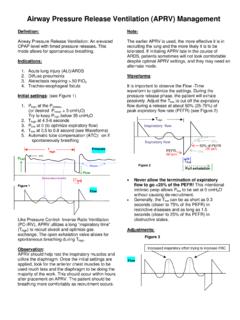
2 ARDS CT AIP 1g/ 3 APRV APRV Pressure high P High 27cmH2O Pressure low P Low 0 cmH2O Time of P High T High Time of P Low T Low FIO2 P/F 15 153mmHg 63 206mmHg D DNA RNP Fig. 1 Chest computed tomography on admission to the ICUThe arrows indicated bilateral ground glass opacity in the lower lung cell countBlood biochemistryBlood gas analysisWBCRBCHbHtPlat9,500296 104/mm3/mm3g/dL /mm3 TPALTASTT testPTAPTTFibATD secmg/dL g/mLTable 1 Laboratory data on admission to the ICUPlat platelet PT prothrombin time APTT activated partial thromboplastin time Fib fibrinogen AT anthithrombin TP total protein T bil total bilirubin BUN blood urea nitrogen Cre 2 Chest X ray on the second ICU dayBilateral pulmonary infiltrations were prominent.
3 30 1 Web 2013 3 27 Sm SS A SS B 5 IgE 5 40mg/ 8 P/F 300mmHg APRV 15 ICU ICU A B RS 4 ARDS ARDS CT AIP 3 ARDS AIP 2 AIP ARDS 1 AIP diffuse alveolar damage DAD 3 DAD ARDS 4 5 AIP CT 1 APRV APRV 6 8 16 7 APRV 15 P/F 73mmHg 153mmHg APRV AIP 5 8, 9 AIP ARDS APRV COI 1 Acute interstitial pneumonia AIP 2004 42 23 Avnon LS, Pikovsky O, Sion Vardy N.
4 Et al Acute interstitial pneumonia Hamman Rich syndrome clinical characteristics and diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Anesth Analg. 2009 108 232 Bonaccorsi A, Cancellieri A, Chilosi M, et al Acute interstitial pneumonia report of a series. Eur Respir J. 2003 21 187 Tomashefski JF Jr Pulmonary pathology of acute respi ratory distress syndrome. Clin Chest Med. 2000 21 435 Vourlekis JS Acute interstitial pneumonia. Clin Chest Med. 2004 25 739 Frawley PM, Habashi NM Airway pressure release ven tilation theory and practice. AACN Clin Issues. 2001 12 234 Sydow M, Burchardi H, Ephraim E, et al Long term of two different ventilator modes on oxygenation in acute lung injury. Comparison of airway pressure release ventilation and volume controlled inverse ratio ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 149 1550 Suh GY, Kang EH, Chung MP, et al Early intervention can 30 1 Web 2013 3 27 improve clinical outcome of acute interstitial pneumonia.
5 Chest. 2006 129 753 Tamama K, Yamato T, Yoshida M, et al A case of probable interstitial pneumonia with a dramatic response to pulse corticosteroid administration. J Med. 2000 31 77 case of acute respiratory distress syndrome suspected of acute interstitial pneumoniaYoshinori NISHIYAMAI ntensive Care Unit, Ehime Rosai HospitalCorresponding author Yoshinori NISHIYAMAI ntensive Care Unit, Ehime Rosai Hospital13 27, Minamikomatsubara cho, Niihama, Ehime, 792 8550, JapanKey words acute respiratory distress syndrome airway pressure release ventilation pulse steroid therapy acute interstitial pneumoniaAbstract A 77 year old woman developed acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS Since the P/F ratio had decreased to 73mmHg, airway pressure release ventilation with a CPAP phase of 27cmH2O and pulse steroid administration 1g/day methylprednisolone for 3 days were commenced.
6 The P/F ratio increased to 206mmHg 63 hours later. Afterwards, the pulmonary oxygenation and bilateral infiltrations on the chest radiogram smoothly improved and the patient was weaned from mechanical ventilation on the tenth disease day. According to the clinical history and the results of detailed examinations, lung diseases, such as community acquired pneumonia, atypical pneumonia, pulmonary involvements in collagen disease, drug induced pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia, hypersensitivity pneumonitis and sarcoidosis were ruled out. Although the etiology of ARDS could not be determined in this case, the chest CT finding suggested a possibility of the patient suffering from acute interstitial pneumonia.