Transcription of B ನಮೂೆ 2 ಿಷ +ಗಳು ಿಜ್ಞಾನ ಿದ್ಯುನ್ಮಾನ ಶಾಸ್ರ …
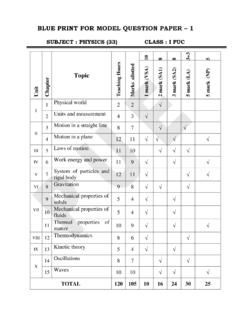
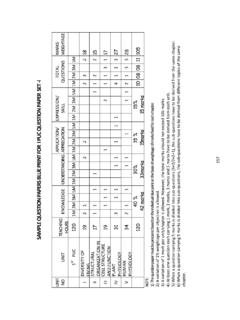
1 B 2 ( ) ( , , , , , ) 70+30 : : 33 : .. 1 15-07-2021 15-09-2021 1. Electric Charges and Fields Introduction Electric Charge Conductors and Insulators Charging by Induction Basic Properties of Electric Charge Coulomb s Law Forces between Multiple Charges Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Flux Electric Dipole Dipole in a Uniform External Field Continuous Charge Distribution Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law Field due to infinitely long straight uniformly charged wire. Field due to uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. 2.
2 Electric Potential and Capacitance Introduction Electrostatic Potential Potential due to a Point Charge Potential due to an Electric Dipole Potential due to a System of Charges Equipotential Surfaces Potential Energy of a System of Charges Potential Energy in an External Field Electrostatics of Conductors Dielectrics and Polarisation Capacitors and Capacitance The Parallel Plate Capacitor Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance 1. Resistance per unit length of a wire 2. Resistivity of a wire using a meter bridge 3. Comparison of EMF s of two cells 4. Internal resistance of a cell 35 Combination of Capacitors Energy Stored in a Capacitor 3. Current Electricity Introduction Electric Current Electric Currents in Conductors Ohm s law Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity Limitations of Ohm s Law Temperature Dependence of Resistivity Electrical Energy, Power Cells, emf, Internal Resistance Cells in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules Wheatstone Bridge Meter Bridge Potentiometer 4.
3 Moving Charges and Magnetism Introduction Magnetic Force Motion in a Magnetic Field Motion in Combined Electric and Magnetic Fields Velocity Selector Magnetic Field due to a Current Element, Biot-Savart Law Magnetic Field on the Axis of a Circular Current Loop 2 1 13-09-2021 15-09-2021 ( ) 3 - 1 4 16-09-2021 30-11-2021 4. Moving Charges and Magnetism Ampere s Circuital Law The Solenoid and the Toroid Force between Two Parallel Currents, the Ampere Torque on Current Loop, Magnetic Dipole The Moving Coil Galvanometer 5. Magnetism and Matter Introduction The Bar Magnet The magnetic field lines Magnetism and Gauss s Law 5.
4 Figure of merit of a galvanometer 6. Conversion of a galvanometer into: (A) an ammeter (B) a voltmeter 7. Frequency of AC 8. Focal length of a convex lens 9. Focal length of a concave lens 32 The Earth s Magnetism Magnetisation and magnetic intensity 5. Electromagnetic Induction Introduction The Experiments of Faraday and Henry Magnetic Flux Faraday s Law of Induction Lenz s Law and Conservation of Energy Motional Electromotive Force Energy Consideration: A Quantitative Study Eddy Currents Inductance AC Generator 6. Alternating Current Introduction AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor Representation of AC Current and Voltage by Rotating Vectors Phasors AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor AC Voltage Applied to a Capacitor AC Voltage Applied to a Series LCR Circuit LC Oscillations Transformers 7.
5 Electromagnetic Waves Introduction Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Spectrum 8. Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Introduction refraction Total Internal Reflection refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by lenses refraction through a Prism Some Natural Phenomena due to Sunlight Rainbow Optical Instruments 5 20-11-2021 30-11-2021 1 2 6 - 2 ( ) 7 01-12-2021 30-01-2021 10. Wave Optics Introduction Huygens Principle refraction and Reflection of Plane Waves using Huygens Principle Coherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves Interference of Light Waves and Young s Experiment Diffraction The single slit Seeing the single slit diffraction pattern the validity of ray optics 11.
6 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Introduction Electron Emission Photoelectric Effect Experimental Study of Photoelectric Effect Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light Einstein s Photoelectric Equation: Energy Quantum of Radiation Particle Nature of Light: The Photon Wave Nature of Matter 12. Atoms Introduction Alpha-particle Scattering and Rutherford s Nuclear Model of Atom Atomic Spectra Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom The Line Spectra of the Hydrogen Atom de Broglie s Explanation of Bohr s Second Postulate of Quantisation 13. Nuclei Introduction Atomic Masses and Composition of Nucleus Size of the Nucleus Mass-Energy and Nuclear Binding Energy ((except binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number) Nuclear Force Nuclear Energy 10.)
7 Angle of minimum deviation of a prism 11. Refractive index of a glass slab 12. Refractive index of a liquid (water) 13. Semiconductor diode characteristics 32 14. Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits Introduction Classification of Metals, Conductors and Semiconductors Intrinsic Semiconductor Extrinsic Semiconductor p-n Junction Semiconductor Diode Application of Junction Diode as a Rectifier Special Purpose p-n Junction Diodes OPTOELECTRONIC JUNCTION DEVICES Digital Electronics and Logic Gates 8 2 28-01-2022 31-01-2022 9 01-02-2022 31-03-2022 1. Electric Charges and Fields Uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside). 3. Current Electricity Carbon resistors, colour code for carbon resistors; Combination of Resistors Series and Parallel 4.
8 Moving Charges and Magnetism Cyclotron 5. Magnetism and Matter Magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis. Torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field Para-, dia- and ferro - magnetic substances, with examples. Electromagnets and factors affecting their strengths, permanent magnets. 7. Alternating Current Power factor, wattless current 8. Electromagnetic Waves Basic idea of displacement current 9. Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, (recapitulation) mirror formula Scattering of light - blue colour of sky and reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset 14. Verification of laws of combination of resistances using a meter-bridge 15. Focal length of a concave mirror 16.
9 Focal length of a convex mirror 17. Zener diode characteristics 32 10. Wave Optics Resolving power of microscope and astronomical telescope Polarisation, plane polarised light, Brewster's law, uses of plane polarised light and Polaroids. 11. Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Davisson-Germer experiment 13. Nuclei Radioactivity, alpha, beta and gamma particles/rays and their properties; radioactive decay law, half-life and mean life. Binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number 14. Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits Zener diode and their characteristics, Zener diode as a voltage regulator 10 24-03-2022 30-03-2022 11 : 14 ( observation calculation column ).
10