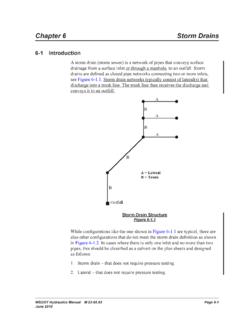
Transcription of Chapter 1260 Sight Distance
1 WSDOT Design Manual M Page 1260-1 July 2016 Chapter 1260 Sight Distance General References Stopping Sight Distance (Eye height ft, Object height ft) Passing Sight Distance (Eye height ft, Object height ft) Decision Sight Distance (Eye height ft, Object height ft) Documentation General Sight Distance allows the driver to assess developing situations and take actions appropriate for the conditions. Sight Distance relies on drivers being aware of and paying attention to their surroundings and driving appropriately for conditions presented.
2 For the purposes of design, Sight Distance is considered in terms of stopping Sight Distance , passing Sight Distance , and decision Sight Distance . For additional information, see the following chapters: Chapter Subject 1250 Sight Distance at railroad crossings 1310 Sight Distance at intersections at grade 1320 Sight Distance at roundabouts 1340 Sight Distance at driveways 1515 Sight Distance for shared-use paths References (1) Design Guidance Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Streets and Highways, USDOT, FHWA.
3 As adopted and modified by Chapter 468-95 WAC Manual on uniform traffic control devices for streets and highways (MUTCD) (2) Supporting Information A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets (Green Book), AASHTO Passing Sight Distance Criteria, NCHRP 605 Stopping Sight Distance (Eye height ft, Object height ft) (1) Design Criteria Stopping Sight Distance is provided when the Sight Distance available to a driver equals or exceeds the stopping Distance for a passenger car traveling at the design speed.
4 Stopping Distance for design is very conservatively calculated, with lower deceleration and slower perception reaction time than normally expected from the driver. Provide design stopping Sight Distance at all points on all highways and on all intersecting roadways, unless a design analysis is deemed Distance Chapter 1260 Page 1260-2 WSDOT Design Manual M July 2013 (1)(a) Stopping Sight Distance Stopping Sight Distance is the sum of two distances: the Distance traveled during perception and reaction time and the Distance to stop the vehicle.
5 The perception and reaction Distance used in design is the Distance traveled in seconds at the design speed. The design stopping Sight Distance is calculated using the design speed and a constant deceleration rate of feet/second2. For stopping Sight distances on grades less than 3%, see Exhibit 1260-1; for grades 3% or greater, see Exhibit 1260-2. (1)(b) Design Stopping Sight Distance Exhibit 1260-1 gives the design stopping Sight distances for grades less than 3%, the minimum curve length for a 1% grade change to provide the stopping Sight Distance for a crest (Kc) and sag (Ks) vertical curve, and the minimum length of vertical curve for the design speed (VCLm).
6 For stopping Sight distances when the grade is 3% or greater, see Exhibit 1260-2. Design Speed (mph) Design Stopping Sight Distance (ft) Kc Ks VCLm (ft) 25 155 12 26 75 30 200 19 37 90 35 250 29 49 105 40 305 44 64 120 45 360 61 79 135 50 425 84 96 150 55 495 114 115 165 60 570 151 136 180 65 645 193 157 195 70 730 247 181 210 75 820 312 206 225 80 910 384 231 240 Design Stopping Sight Distance Exhibit 1260-1 Chapter 1260 Sight Distance WSDOT Design Manual M Page 1260-3 July 2013 (2) Effects of Grade The grade of the highway has an effect on the stopping Sight Distance .
7 The stopping Distance is increased on downgrades and decreased on upgrades. Exhibit 1260-2 gives the stopping Sight distances for grades of 3% and steeper. When evaluating Sight Distance with a changing grade, use the grade for which the longest Sight Distance is needed. Design Speed (mph) Stopping Sight Distance (ft) Downgrade Upgrade -3%-6%-9%3% 6% 9% 25 158 165 173 147 143 140 30 205 215 227 200 184 179 35 257 271 287 237 229 222 40 315 333 354 289 278 269 45 378 400 427 344 331 320 50 446 474 507 405 388 375 55 520 553 593 469 450 433 60 598 638 686 538 515 495 65 682 728 785 612 584 561 70 771 825 891 690 658 631 75 866 927 1,003 772 736 704 80 965 1,035 1,121 859 817 782 Design Stopping Sight Distance on Grades Exhibit 1260-2 For stopping Sight distances on grades between those listed.
8 Interpolate between the values given or use the equation in Exhibit 1260-3. += ) ( : S = Stopping Sight Distance on grade (ft) V = Design speed (mph) G = Grade (%) Stopping Sight Distance on Grades Exhibit 1260-3 (3) Crest Vertical Curves When evaluating an existing roadway, refer to (7). Use Exhibit 1260-4 or the equations in Exhibit 1260-5 to find the minimum crest vertical curve length to provide stopping Sight Distance when given the algebraic difference in grades. Exhibit 1260-4 does not show the Sight Distance greater than the length of curve equation.
9 Sight Distance Chapter 1260 Page 1260-4 WSDOT Design Manual M July 2013 When the Sight Distance is greater than the length of curve and the length of curve is critical, the S>L equation given in Exhibit 1260-5 shall be used to find the minimum curve length. When a new crest vertical curve is built or an existing one is rebuilt with grades less than 3%, provide design stopping Sight Distance from Exhibit 1260-1. For grades 3% or greater, provide stopping Sight Distance from (2). Eye height h1= 'SObject height h2= 'The minimum length can also be determined by multiplying the algebraic difference in grades by the KC value from Exhibit 1260-1 (L=KC*A).
10 Both the exhibit and the equation give approximately the same length of curve. Neither use the S>L equation. Length of Vertical Curve, L (ft)Algebraic Difference in Grade, A (%)0050010001500200024681012141625 mph, S=155 mph, S=200 mph, S=250 mph, S=305 mph, S=360 mph, S=425 mph, S=495 mph, S=570 mph, S=645 mph, S=730 mph, S=820 mph, S=910 Sight Distance : Crest Vertical Curves Exhibit 1260-4 Chapter 1260 Sight Distance WSDOT Design Manual M Page 1260-5 July 2013 When S>L ASL21582 =22158 +=ALSWhen S<L 21582 ASL=ALS2158=Where.