Transcription of Physics Reference Tables - Mr. Bigler
1 Physics Reference Tables * * Data from various sources, including: The University of the State of New York, The State Education Department. Albany, NY, Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ Physics , 2006 , SparkNotes: SAT Physics website. , The engineering toolbox : , and The College Board: Equations and Constants for AP Physics 1 and AP Physics 2. Contents: Table A. Metric Prefixes .. 1 Table B. Physical Constants .. 2 Table C. Quantities, Variables and Units .. 3 Table D. Mechanics Formulas and Equations .. 4 Table E. Approximate Co fficients of Friction .. 4 Table F. Angular/Rotational Mechanics Formulas and Equations .. 5 Table G. Moments of Inertia .. 5 Table H. Heat and Thermal Physics Formulas and Equations .. 6 Table I. Thermal Properties of Selected Materials.
2 6 Table J. Electricity Formulas & Equations .. 7 Table K. Electricity & Magnetism Formulas & Equations .. 8 Table L. Resistor Color Code .. 8 Table M. Symbols Used in Electrical Circuit Diagrams .. 8 Table N. Resistivities at 20 C .. 8 Table O. Waves & Optics Formulas & Equations .. 9 Figure P. The Electcromagnetic Spectrum .. 9 Table Q. Properties of Water and Air .. 10 Table R. Absolute Indices of Refraction .. 10 Table S. Fluid Mechanics Formulas and Equations .. 11 Table T. Planetary Data .. 11 Table U. Sun & Moon Data .. 11 Table V. Atomic & Particle Physics (Modern Physics ) .. 12 Figure W. Quantum Energy Levels .. 12 Figure X. Particle Sizes .. 13 Figure Y. Classification of 13 Table Z. The Standard Model of Elementary Particles .. 13 Figure AA.
3 Periodic Table of the Elements .. 14 Table BB. Symbols Used in Nuclear Physics .. 15 Table CC. Selected 15 Table DD. Constants Used in Nuclear Physics .. 15 Figure EE. Neutron/Proton Stability Band .. 15 Table FF. Geometry & Trigonometry Formulas .. 16 Table GG. Values of Trigonometric Functions .. 17 Table HH. Some Exact and Approximate 18 Table II. Greek Alphabet .. 18 Table A. Metric Prefixes Move Decimal Point to the Left Move Decimal Point to the Right Factor Prefix Symbol 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 1024 yotta Y 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 1021 zeta Z 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 1018 exa E 1 000 000 000 000 000 1015 peta P 1 000 000 000 000 1012 tera T 1 000 000 000 109 giga G 1 000 000 106 mega M 1 000 103 kilo k 100 102 hecto h 10 101 deca da 1 100 10 1 deci d 10 2 centi c 10 3 milli m 001 10 6 micro 000 001 10 9 nano n 000 000 001 10 12 pico p 000 000 000 001 10 15 femto f 000 000 000 000 001 10 18 atto a 000 000 000 000 000 001 10 21 zepto z 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 10 24 yocto y
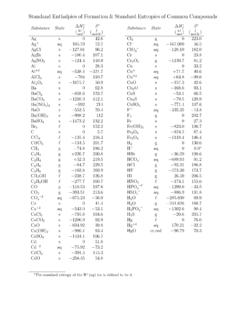
4 Physics Reference Tables Page 2 Table B. Physical Constants Description Symbol Precise Value Common Approximation acceleration due to gravity / strength of gravity field on Earth s surface g to average value at sea level is 65 or 2mNkgs1010 universal gravitational constant G 84(80) 10 10 speed of light in a vacuum c ms299 792 458* 10 elementary charge (proton or electron) e 19* 176 634 10C 10C 1 coulomb (C) 509 074 10 elementary charges 10 elementary charges (electric) permittivity of a vacuum o 243-12 Askg 187 82 10 24312 Askg 10 (magnetic) permeability of a vacuum o 637 06 10 = 10 electrostatic constant k 551 787 368 176 4 104o = * 10 1 electron volt (eV) 176 565(35) 10J 10J Planck s constant h 34* 070 15 10J s 10J s 1 universal (atomic) mass unit (u) 061(21) MeV/ c 538 921(73) 10kg 2931 MeV/c 10kg Avogadro s constant NA 140 76 10 mol * 10 mol Boltzmann constant kB 649 10 * 10 universal gas constant R Jmol 4621(75) Jmol Rydberg constant HR 41m2310 973 8eomehc = 10 m Stefan-Boltzmann constant 5482432Jm s 374 419 1015 Rch = 824Jm s 10 standard atmospheric pressure at sea level 101 325 Pa bar* 100 000 Pa bar rest mass of an electron me 382 15(45) 10kg 10kg mass of a proton mp 621 777(74) 10kg 10kg mass of a neutron mn 927 351(74) 10kg 10kg *denotes an exact value (by definition)
5 Physics Reference Tables Page 3 Table C. Quantities, Variables and Units Quantity Variable MKS Unit Name MKS Unit Symbol Base Unit position x meter* m m distance/displacement, (length, height) , , ( , )dL hd meter* m m angle radian, degree , area A square meter m2 m2 volume V cubic meter, liter m3 m3 time t second* s s velocity v meter/second sm sm speed of light c angular velocity radians/second 21s, 1s 21s, 1s acceleration a meter/second2 2sm 2sm acceleration due to gravity g angular acceleration radians/second2 21s, 2s 21s, 2s mass m kilogram* kg kg force F newton N 2smkg gravitational field g newton/kilogram Nkg 2sm pressure P pascal Pa 2smkg energy (generic) E joule J 22smkg potential energy U kinetic energy K ,kE heat Q work W joule , newton-meter J , N m 22smkg torque newton-meter N m 22smkg power P watt W 32smkg momentum p newton-second N s smkg impulse J moment of inertia I kilogram-meter2 kg m2 kg m2 angular momentum L newton-meter-second N m s smkg2 frequency f hertz Hz s 1 wavelength meter m m period T second s s index of refraction n electric current I ampere* A A electric charge q coulomb C A s electric potential potential difference (voltage) electromotive force (emf)
6 V V volt V 32sAmkg electrical resistance R ohm 322sAmkg capacitance C farad F kgmsA242 electric field E netwon/coulomb volt/meter mV,CN 3sAmkg magnetic field B tesla T 2sAkg temperature T kelvin* K K amount of substance n mole* mol mol luminous intensity Iv candela* cd cd Variables representing vector quantities are typeset in bold italics with arrows. * = base unit Physics Reference Tables Page 4 Table D. Mechanics Formulas and Equations Kinematics (Distance, Velocity & Acceleration) o= = dxxx .2oveoatt += ==xxdvvv ot = =vv va 212oott = = +xxdva 222)2(oo = = vvada xx =name of quantity (unit)var. ()()()() in something ( means change in )sumdistance (m)displacement (m)position (m)time (s)velocity average velocity acceleration frequency Hzforce ( , xxdtf = ===========dxvvaF2m sNkg)force due to friction (N)force due to gravity (N)normal force (N)mass (kg)acceleration due to gravity10on Earthstrength of gravity field10 on Earth grnet force (N)NnetfgFmG==========FFFgg22 Nmkg11avitational 10radius (m)r = = _____ *characteristic property of a substance (to be looked up)
7 Forces & Dynamics netm== FFa fs NFF fk NFF = 221gGm mmr==Fg Circular/ Centripetal Motion & Force 2cvar= ccFma= Simple Harmonic Motion 1Tf= 2smTk = 2pLTg = sk= Fx 212sUkx= Momentum m=pv iiffmm + = vJv nett= = JpF Energy, Work & Power 12gGm mUmghr== 22122pKmvm== ()WEK U= = + llcosWF dFd = = =Fd (..)totalEU KQ= + + + cosWPFvt = = =Fv Table E. Approximate Co fficients of Friction Substance Static ( s) Kinetic ( k) Substance Static ( s) Kinetic ( k) rubber on concrete (dry) wood on wood (dry) rubber on concrete (wet) wood on wood (wet) rubber on asphalt (dry) wood on metal rubber on asphalt (wet) wood on brick rubber on ice wood on concrete steel on ice Teflon on Teflon waxed ski on snow Teflon on steel aluminum on aluminum graphite on steel cast iron on cast iron leather on wood steel on steel leather on metal (dry) copper on steel leather on metal (wet) diamond on diamond glass on glass diamond on metal metal on glass ()Nmco fficient of friction*()angle ( , rad)
8 Spring constant displacement of spring (m)length of pendulum (m)energy (J)kinetic energy (J)potential energy (J)h eight (m)kdimensionlesskLEKEUhQ == ========x heat (J)power (W)work (J, N m)(time) period (Hz)momentum (N s)impulse (N s)pi (mathematical constant) 26535 === == = ==pJPhysics Reference Tables Page 5 Table F. Angular/Rotational Mechanics Formulas and Equations Angular Kinematics (Distance, Velocity & Acceleration) o = .2oaovett += == ot = = 212ott = + 222 ()o = name of quantity (unit) ()2mschange in something ( = change in )sumsarc length (m)time (s)centripetal acceleration centripetal force (N)mass (kg)radius (m)radius (vector)angle ( , rad) , xxtaFmr = ========= =r ()2radsrads velocity angular velocity torque (N m)position (m)frequency (Hz)amplitude (m)phase offsetn ( , rad)energytranslational kinetic e ergy c) (J)kineti energy (J)(JtrkxfAEKEKK = = = ====== == power (W)work (J, N m)momentum (N s)angular momentum (N m s)rotational kinetic energy (J)
9 PW== = = pL Circular/ Centripetal Motion TTs rvrar = == 22cva rr== Rotational Dynamics iicmimxxm= 220__mmrr dm== I 2ccFmamr == = r F sinrFr F == net== I Simple Harmonic Motion 12Tf == cos(2)xAft =+ Angular Momentum = =Lr p I sinL rp ==I t = L Angular/ Rotational Energy, Work & Power 212rK =I 221122trmvKKK ++==I rW = WPt == Table G. Moments of Inertia Point Mass: 2mr=I Hollow Cylinder: 2mr=I Solid Cylinder: 212mr=I Hoop About Diameter: 212mr=I Hollow Sphere: 223mr=I Solid Sphere: 225mr=I Rod About the Middle: 2112mL=I Rod About the End: 213mL=I Physics Reference Tables Page 6 Table H. Heat and Thermal Physics Formulas and Equations Temperature () 32TT =+ =+ var. = name of quantity (unit) *characteristic property of a substance (to be looked up) Heat Q mC T= meltfusQm H= boilvapQm H= pvCCR = iLL T = iVV T = 1iQTPkAA TtLR = == 4QP ATt== Thermodynamics 121212P VP VTT= PVnRT= P VnR T = BPVNk T= BP VNk T = U Q W = + 32 UnRT= 32 UnR T = ()WPVP V= = Table I.
10 Thermal Properties of Selected Materials Substance Melting Point ( C) Boiling Point ( C) Heat of Fusion (),fus HkJJkgg Heat of Vaporiz-ation (),vap HkJJkgg Specific Heat Capacity (),pC kJJkg Cg Cat 25 C Thermal Conductivity () kJm s C at 25 C Emissivity black body = 1 Coefficients of Expansion at 20 C Linear )C( -1 Volumetric )C( -1 air (gas) aluminum (solid) 659 2467 395 10460 250 * ammonia (gas) 75 339 1369 argon (gas) 189 186 161 carbon dioxide (gas) 78 574 copper (solid) 1086 1187 134 5063 401 * brass (solid) 120 * diamond (solid) 3550 4827 10 000 30 000 2200 6101 6103 ethanol (liquid) 117 78 104 858 glass (solid) gold (solid) 1063 2660 1577 310 * granite (solid) 1240 helium (gas) 269 21 hydrogen (gas) 259 253 452 iron (solid) 1535 2750 289 6360 80 lead (solid) 327 1750 870 35 mercury (liquid) 39 357 293 8 paraffin wax (solid) 46 68 ~300 ~210 silver (solid) 962 2212 111 2360 429 * steam (gas) @ 100 C 2260 water (liq.)