Transcription of POTENTIALLY INAPPROPRIATE DRUGS FOR ELDERLY …
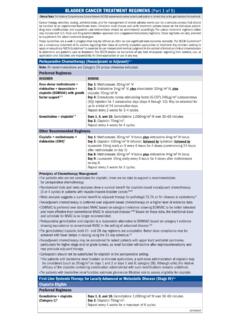
1 POTENTIALLY INAPPROPRIATE DRUGS FOR ELDERLY ( beers list )* (PART 1 OF 3). Alprazolam (increased sensitivity to benzodiazepines. Clidinium-chlordiazepoxide (highly anticholinergic, uncer- Increased risk of cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, frac- tain effectiveness). tures, and motor vehicle accidents in older adults) Clomipramine (highly anticholinergic, sedating, and cause Amiodarone (data suggest that rate control yields better orthostatic hypotension). balance of benefits and harms than rhythm control for most Clonazepam (increased sensitivity to benzodiazepines.))
2 Older adults) Increased risk of cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, frac- Amitriptyline (highly anticholinergic, sedating, and cause tures, and motor vehicle accidents in older adults). orthostatic hypotension) Clonidine (high risk of adverse CNS effects; may cause bra- Amobarbital (high rate of physical dependence; tolerance to dycardia and orthostatic hypotension; not recommended as sleep benefits; risk of overdose at low dosages) routine treatment for hypertension). Aripiprazole (increased risk of cerebrovascular accident Clozapine (increased risk of cerebrovascular accident [stroke] and mortality in persons with dementia) [stroke] and mortality in persons with dementia).
3 Asenapine (increased risk of cerebrovascular accident Cyclobenzaprine (most muscle relaxants are poorly toler- [stroke] and mortality in persons with dementia) ated by older adults because of anticholinergic adverse Aspirin (>325mg/d) (increases risk of GI bleeding and effects, sedation, risk of fracture). peptic ulcer disease in high-risk groups, including those aged Cyproheptadine (highly anticholinergic; clearance reduced >75 or taking corticosteroids or anticoagulants) with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hypnotic; risk Belladonna alkaloids (highly anticholinergic, uncertain of confusion, dry mouth, constipation).)
4 Effectiveness) Dessicated thyroid (concerns about cardiac effects; safer Benztropine (oral) (not recommended for prevention of alternatives available). extrapyramidal symptoms with antipsychotics; more-effective Dexbrompheniramine (highly anticholinergic; clearance agents available for treatment of Parkinson disease) reduced with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hyp- Brompheniramine (highly anticholinergic; clearance notic; risk of confusion, dry mouth, constipation). reduced with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hyp- Dexchlorpheniramine (highly anticholinergic; clearance notic; risk of confusion, dry mouth, constipation) reduced with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hyp- notic; risk of confusion, dry mouth, constipation).
5 Butabarbital (high rate of physical dependence; tolerance to sleep benefits; risk of overdose at low dosages) Diazepam (increased sensitivity to benzodiazepines. Increased risk of cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, frac- Butalbital (high rate of physical dependence; tolerance to tures, and motor vehicle accidents in older adults). sleep benefits; risk of overdose at low dosages). Diclofenac (increases risk of GI bleeding and peptic ulcer Carbinoxamine (highly anticholinergic; clearance reduced disease in high-risk groups, including those aged >75 or tak- with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hypnotic; risk ing corticosteroids or anticoagulants).)
6 Of confusion, dry mouth, constipation). Dicyclomine (highly anticholinergic, uncertain effectiveness). Carisoprodol (most muscle relaxants are poorly tolerated by older adults because of anticholinergic adverse effects, seda- Diflunisal (increases risk of GI bleeding and peptic ulcer dis- tion, risk of fracture) ease in high-risk groups, including those aged >75 or taking corticosteroids or anticoagulants). Chloral hydrate (tolerance occurs within 10 days, and risks outweigh benefits in light of overdose with doses only 3 times Digoxin (> ) (in heart failure, higher dosages the recommended dose) associated with no additional benefit and may increase risk of toxicity; slow renal clearance may lead to risk of toxic effects).
7 Chlorazepate (increased sensitivity to benzodiazepines. Increased risk of cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, frac- Diphenhydramine (oral) (highly anticholinergic; clearance tures, and motor vehicle accidents in older adults) reduced with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hyp- notic; risk of confusion, dry mouth, constipation). Chlordiazepoxide (increased sensitivity to benzodiazepines. Increased risk of cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, frac- Dipyridamole (oral short acting [does not apply to tures, and motor vehicle accidents in older adults) extended-release combination with aspirin]) (may cause orthostatic hypotension; more effective alternatives Chlordiazepoxide-amitryptyline (highly anticholinergic, available; intravenous form acceptable for use in cardiac sedating, and cause orthostatic hypotension) stress testing).
8 Chlorpheniramine (highly anticholinergic; clearance Disopyramide (a potent negative inotrope and therefore reduced with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hyp- may induce heart failure in older adults; strongly anticholiner- notic; risk of confusion, dry mouth, constipation) gic; other antiarrhythmic DRUGS preferred). Chlorpromazine (increased risk of cerebrovascular accident Dofetilide (data suggest that rate control yields better bal- [stroke] and mortality in persons with dementia) ance of benefits and harms than rhythm control for most Chlorpropamide (prolonged half-life in older adults; can older adults).)
9 Cause prolonged hypoglycemia; causes syndrome of inappro- Doxazosin (high risk of orthostatic hypotension; not recom- priate antidiuretic hormone secretion) mended as routine treatment for hypertension; alternative Chlorzoxazone (most muscle relaxants are poorly tolerated agents have superior risk/benefit profile). by older adults because of anticholinergic adverse effects, Doxepin (>6mg/d) (highly anticholinergic, sedating, and sedation, risk of fracture) cause orthostatic hypotension). Clemastine (highly anticholinergic; clearance reduced with Doxylamine (highly anticholinergic; clearance reduced with advanced age, and tolerance when used as hypnotic; risk of advanced age, and tolerance when used as hypnotic; risk of confusion, dry mouth, constipation) confusion, dry mouth, constipation) (continued).
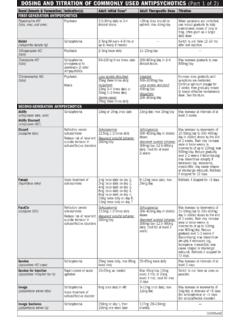
10 Adapted from: American Geriatrics Society Updated beers criteria for POTENTIALLY INAPPROPRIATE Medication Use in Older Adults. (Table 2). The American Geriatrics Society 2012 beers criteria Update Expert Panel. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60:616-631. (Rev. 6/2012). POTENTIALLY INAPPROPRIATE DRUGS FOR ELDERLY ( beers list )* (PART 2 OF 3). Dronedarone (worse outcomes have been reported in Isoxsuprine (lack of efficacy). patients taking dronedarone who have permanent atrial fibrilla- Ketoprofen (increases risk of GI bleeding and peptic ulcer tion or heart failure) disease in high-risk groups, including those aged >75 or tak- Ergot mesylates (lack of efficacy) ing corticosteroids or anticoagulants).