Transcription of Pressure Temperature Chart
1 Conversions and FormulasPressure Temperature making your life easier COIL Temperature Chart INSTRUCTIONSS elect design Temperature for your evaporator and condenser-Match to approx. operational - 120 condensing / 40 evaporator approx. 234 psig head / 60 psig suctionHot Shot - 100 condensing / 28 evaporatorapprox. 126 psig head / 26 psig suctionNU-22 - 100 condensing / -30 evaporatorapprox. 176 psig head / 3 psig evaporatorHot Shot - 100 condensing / -20 evaporatorapprox. 126 psig head / 0 psig suctionCUBIC of WATER COLUMN2547= + 32=FAHRENHEITS ingle PhaseLoadsW = WattsI = AmperesE = VoltageR = OhmsTo obtain any value in the center circle, perform the operationin the adjacent segment of the outer Load Current = Watts (1 )VoltageFull Load Current = Watts (3 ) x VoltageVolts = Amps x ResistanceWatts = Volts x AmpsWATER SIDE - Chillers,CondensersBTUH = 500 x GPM x T BTUH 500 x GPMGALLON of WATER = lbs/GAL x 60 = 500 lbs/hrDENSITY = lbs/cubic ft GPM x Ft.
2 Water Pump Eff. x 3960 Approx. Weights of Refrigerant in CU lines - lbs/100 Lineal FeetLine Size Refrigerant Suction LiquidLine Size Refrigerant Suction 1 3 5 1 (Does not apply to residential appliances)Air Cooled condensing unitINDOOR - NO FAN CYCLING - per HP Hot Shot - Two (2) pounds NU-22 - Three (3) pounds Plus the liquid line weightOUTDOOR - FLOODED CONDENSER - per HP Hot Shot - Four (4) pounds NU-22 - Five (5) pounds Plus the liquid line weightOUTDOOR FAN CYCLING - per HP Hot Shot - Three (3) pounds NU-22 - Four (4) pounds Plus the liquid line weightWATER COOLED CONDENSING UNIT - per HP Hot Shot - One (1) pound NU-22 - Two (2) pounds Plus the liquid line weight* NU-22 RESIDENTIAL A/C APPLICATIONSUSE A 1 / 1 CHARGING RATIOAIR COILS - In BTUHQ sensible = x CFM x TQlatent = x CFM x SH Qtotal = x CFM x HQ = Heat Flow in BTUHSH = Specific Humidity(grains of moisture)H = EnthalpyAlways unload the cylinder in liquid phase.
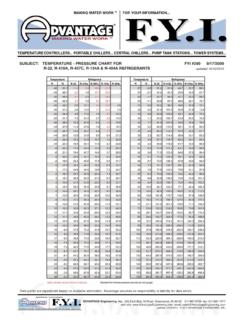
3 Don t clear the sightglass. As temperatureapproaches design, verify superheat, adjust charge if necessary to optimize IR EE2RE2 WWI212 x REx 11x RWx R E RWEWIEIW RICOR International Coil Temperature ChartHOT SHOT and NU-22 Evaporator CondensingDesign Temp. F -40 -38 -36 -34 -32 -30 -28 -26 -24 -22 -20 -18 -16 -14 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 46NU-22 PSIG 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 14 15 16 18 19 20 22 24 25 Hot Shot PSIG 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Hot Shot PSIG 131415161718192224 252628303234363840424446485052 Design Temp.
4 F 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54NU-22 PSIG 27 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 51 53 55 58 61 63 66 69 72 75 78 81NU-22 PSIG 151 156 161 166 171 176 182 187 193 198 204 210 216 Hot ShotPSIG 106 110 112 116 121 126 131 136 141 145 149 154 159 DesignTemp. F116 118 120 122 124 126 128 130 132 134 136 138 140NU-22 PSIG 222 228 234 241248254261 267 275 282 289 317 305 Hot ShotPSIG 164 169 174 180 184 190 196 200 204 210 216 222 227 Design Temp. F 90 92 94 96 98 100 102 104 106 108 110 112 114 KILOWATT T =CHARGING TIPS-REFRIGERATION APPLICATIONSPump HP = Pressure Temp Chart -'01 10/31/01 2:54 PM Page 1 EVAPORATORSUCTIONCOMPRESSORCHECK SUCTIONPRESSUREDISCHARGELIQUIDCONDENSERC HECK LIQUIDPRESSURE(always use bubblepoint for conversion)CHECK LIQUIDTEMPERATURE(always use dew point for conversion)Check at evap.
5 Ifpossible, add for suctionline Pressure drop iftaken at SUCTIONTEMPERATURESUCTION Temperature -- EVAPORATOR Temperature = SUPERHEATCONDENSING Temperature -- LIQUID Temperature = SUBCOOLINGSUPERHEATSUBCOOLINGT emperature F -40 -38 -36 -34 -32 -30 -28 -26 -24 -22 -20 -18 -16 -14 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -20 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 100 102 104 106 108 110 112 114 116 118 120 122 124 126 128 130 132 134 136 138 140R-417A BUBBLE POINT
6 DEW POINT 220 253 260 329 BUBBLE POINT 142 165 185 224 230 255R-414B DEW POINT 95 199 87 90 171 37 60 90 97 112 120
7 156 166 193 174 179 Chart - PSIG vs TemperatureTemperature - F Refrigerant - PSIGBold Italics = IN. HgFor 5000 ft. elevation PSIG + Temp Chart -'01 10/31/01 2:54 PM Page 2