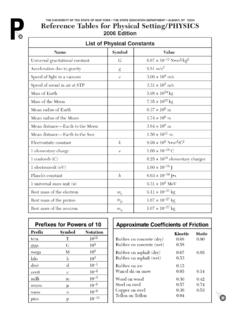
Transcription of Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Earth Science
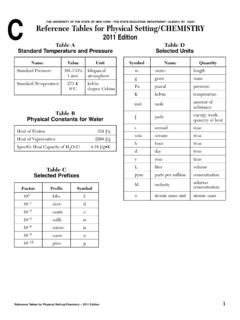
1 The University of the State of New York THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT Albany, New York 12234 Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Earth Science . Radioactive Decay Data Specific Heats of Common Materials RADIOACTIVE DISINTEGRATION HALF-LIFE MATERIAL SPECIFIC HEAT. ISOTOPE (years) (Joules/gram C). 14 14 3 Liquid water Carbon-14 C N 10. Solid water (ice) 40. 40 Ar 9 Water vapor Potassium-40 K 40 10. Ca Dry air 238 206 9. Uranium-238 U Pb 10 Basalt 10. Granite 87 87. Rubidium-87 Rb Sr 10. Iron Copper Equations Lead distance between foci Eccentricity = Properties of Water length of major axis change in field value Heat energy gained during melting.
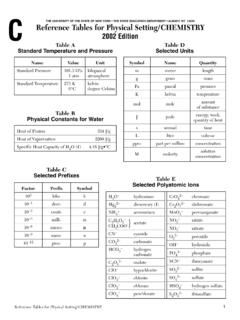
2 334 J/g Gradient =. distance Heat energy released during freezing .. 334 J/g change in value Heat energy gained during vaporization .. 2260 J/g Rate of change =. time Heat energy released during condensation .. 2260 J/g mass Density = Density at C .. g/mL. volume Average Chemical Composition of earth 's Crust, Hydrosphere, and Troposphere ELEMENT CRUST HYDROSPHERE TROPOSPHERE. (symbol) Percent by mass Percent by volume Percent by volume Percent by volume Oxygen (O) Silicon (Si) Aluminum (Al) Iron (Fe) Calcium (Ca) Sodium (Na) Magnesium (Mg) Potassium (K) Nitrogen (N) Hydrogen (H) Other 2011 EDITION Eurypterus remipes This edition of the earth Science Reference Tables should be used in the classroom beginning in the 2011 12 school year.
3 The first examination for which these Tables will be used is the January 2012 Regents Examination in New York State Fossil Physical Setting/Earth Science . Generalized Landscape Regions of New York State ds Interior an wl Grenville Province Lowlands e Lo (Highlands) e nc awr S t. L. Interior Lowlands Adirondack Mountains Champlain Lowlands Lake Ontario Tug Hill Plateau ce Physical Setting/Earth Science Reference Tables 2011 Edition vin Erie-Ontario Lowlands P. (Plains). s). a nd ro ins l Lake Erie i gh nd wlands En ounta (H gla Allegheny Plateau M. ew k Lo i c N. w n o h a The Catskills M. Taco o n- ) nds nds H ighla o n Huds pla H uds U rong ( h a t tan P.
4 U Man ea at Key Pl n Major geographic province boundary lain ia a l P. h st ds Landscape region boundary c Coa l an rk State boundary n tic ala w N. la p At Lo ewa International boundary Ap Miles N. 0 10 20 30 40 50. W E. 0 20 40 60 80. Kilometers S. 2. 73 . 75 74 45 . 45 . Generalized Bedrock Geology of New York State er MASSENA. iv R. e modified from nc re PLATTSBURGH. w GEOLOGICAL SURVEY. La t. NEW YORK STATE MUSEUM. S. 76 . 1989. AIN. MPL. A. MT. MARCY. VERMONT. CH. 44 . 44 . WATERTOWN. R iv e r LAKE. elevation 75 m OLD FORGE. on ds LAKE ONTARIO. Hu 79 78 77 . OSWEGO. ROCHESTER UTICA. NIAGARA FALLS.
5 Physical Setting/Earth Science Reference Tables 2011 Edition SYRACUSE. 43 . ar a River 43 . ag Moha wk Ni R iv e r BUFFALO. r ve elevation 175 m ALBANY. Ri LAKE FINGER LAKES. see ERIE. ne Ge ITHACA. Rive r er MASSACHUSETTS. iv JAMESTOWN ELMIRA BINGHAMTON. R. SLIDE MT. Susquehanna 42 . 42 KINGSTON. 79 78 77 76 . De Hu ds on law P E N N S Y L V A N I A. are Rive r GEOLOGIC PERIODS AND ERAS IN NEW YORK. CONNECTICUT. 75 . CRETACEOUS and PLEISTOCENE (Epoch) weakly consolidated to unconsolidated gravels, sands, and clays NE. LATE TRIASSIC and EARLY JURASSIC conglomerates, red sandstones, red shales, basalt, and diabase (Palisades sill) W UND.
6 JE ND SO. PENNSYLVANIAN and MISSISSIPPIAN conglomerates, sandstones, and shales Dominantly RS ISLA. EY N G 73 41 . DEVONIAN sedimentary LO 41 . limestones, shales, sandstones, and conglomerates 41 RIVERHEAD 72 . SILURIAN } SILURIAN also contains salt, gypsum, and hematite. origin NEW YORK D. ORDOVICIAN CITY ISLAN. limestones, shales, sandstones, and dolostones LONG. CAMBRIAN }. CAMBRIAN and EARLY ORDOVICIAN sandstones and dolostones moderately to intensely metamorphosed east of the Hudson River } Dominantly 40 30'. 73 . ATLANTIC OCEAN. CAMBRIAN and ORDOVICIAN (undifferentiated) quartzites, dolostones, marbles, and schists 74 73 30'.
7 Metamorphosed intensely metamorphosed; includes portions of the Taconic Sequence and Cortlandt Complex rocks Miles TACONIC SEQUENCE sandstones, shales, and slates Miles N. slightly to intensely metamorphosed rocks of CAMBRIAN through MIDDLE ORDOVICIAN ages 20 30 40 50. MIDDLE PROTEROZOIC gneisses, quartzites, and marbles Lines are generalized structure trends. } Intensely metamorphosed rocks 0 100 2010 30. 0. 40 50. 20 40 60. W. 80. E. MIDDLE PROTEROZOIC anorthositic rocks } (regional metamorphism about 1,000 ) 0 20 40 60 80. Kilometers Kilometers S. 3. Surface Ocean Currents Physical Setting/Earth Science Reference Tables 2011 Edition 4.
8 Tectonic Plates Iceland Hot Spot North American Eurasian Eurasian Plate Plate h e Plate Aleutian Trenc Yellowstone idg Juan de Hot Spot Fuca Plate ti cR. n la At Canary d- Islands P. ab Mi San Andreas Hot Spot Fault Ar late ian Philippine an African Plate Hawaii ibbe e n ch Plate a Mi t d Hot Spot Cocos Car late P. Physical Setting/Earth Science Reference Tables 2011 Edition Tr ria n a M Plate -In Fiji Plate Pacific Galapagos South frican Rif Plate Hot Spot Pe American st A. r dian Ridge Plate Ea Tr e n c h To n g a u-C. Easter Island St. Helena Indian-Australian Hot Spot Nazca Hot Spot n Plate Plate hile Tren idge ia ch S.
9 Ind ou Tasman Mid-Atlantic Ridge cR. e st e the Hot Spot cifi g as t t Scotia Pa hw Rid u Ind ia n Plate So st Ridg e Ea Bouvet Hot Spot Antarctic Antarctic Plate Plate Sandwich Plate overriding Key plate Transform plate boundary subducting Complex or uncertain Mantle Relative motion at plate plate boundary (transform fault) plate boundary hot spot Divergent plate boundary (usually broken by transform Convergent plate boundary faults along mid-ocean ridges) (subduction zone). NOTE: Not all mantle hot spots, plates, and 5. boundaries are shown. Rock Cycle in earth 's Crust Relationship of Transported r Depo Particle Size to Water Velocity nd/o s and B ition na ctio ation uria Boulders pa ent l om em C C Cobbles SEDIMENTS PARTICLE DIAMETER (cm).
10 SEDIMENTARY. n E r o s i on Pebbles Weathering & Erosio ROCK. We (U. athe plift). H. ring e & Ero a M e lt i n g sio t n a M e ta m or p h nd/or Pre m ( U p l if t ). r Pressure t and/o Sand Hea tamorphism M e n lift) rosio ss ur is (U p IGNEOUS. &E Silt e e r in g ROCK th Wea lting METAMORPHIC Me Clay n ROCK. io atic di f 1. 100. 1000. li 10. 500. 5. 50. Me l ti n MAGMA So g STREAM VELOCITY (cm/s). This generalized graph shows the water velocity needed to maintain, but not start, movement. Variations occur due to differences in particle density and shape. Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification CRYSTAL.