Transcription of TECHNICAL Baldor Basics: Motors - Power Transmission
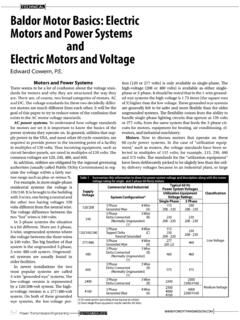
1 IntroductionIndustrial electric Motors have been available for nearly a century. In that time there have been a great many changes. One of the most obvious has been the ability to pack more horsepower in a smaller physical size. Another important achievement has been the standardization of Motors by the National Electric Manufacturers Association (NEMA).A key part of motor interchangeability has been the stan-dardization of frame sizes. This means that the same horse- Power , speed, and enclosure will normally have the same frame size from different motor manufacturers. Thus, a motor from one manufacturer can be replaced with a similar motor from another company provided they are both in standard frame GenerationsThe standardization effort over the last forty-plus years has resulted in one original grouping of frame sizes called origi-nal. In 1952, new frame assignments were made. These were called U frames.
2 The current T frames were introduced in 1964. T frames are the current standard and most likely will continue to be for some time in the though T frames were adopted in 1964, there are still a great many U frame Motors in service that will have to be replaced in the future. Similarly there are also many of the original frame size Motors (pre-1952) that will reach the end of their useful life and will have to be replaced. For this reason it is desirable to have reference material available on frame sizes and some knowledge of changes that took place as a part of the so-called re-rate Size Reference TablesTables 1 and 2 show the standard frame size assignments for the three different eras of Motors . As you will note, these tables are broken down for open drip proof (Table 1) and totally enclosed (Table 2). You will also find that for each horsepower rating and speed, there are three different frame sizes first is the original frame size; the middle one is the U frame size; and the third one is the T frame.
3 These are handy reference tables since they give general information for all three vintages of three-phase Motors in integral horse- Power frame important item to remember is that the base mount-ing hole spacing ( E and F dimensions) and shaft height ( D dimension) for all frames having the same three dig-its regardless of vintage will be the and TemperaturesThe ability to re-rate motor frames to get more horsepower in a frame has been brought about mainly by improvements made in insulating materials. As a result of this improved insulation, Motors can now be run much hotter. This allows more horsepower in a compact frame. For example, the origi-nal NEMA frame sizes ran at very low temperatures. The U frame Motors were designed for use with Class A insulation, which has a rating of 105 C. The motor designs were such that the capability would be used at the hottest spot within the motor.
4 T frame motor designs are based on utilizing Class B insulation with a temperature rating of 130 C. This increase in temperature capability made it possible to pack more horsepower into the same size frame. To accommo-date the larger mechanical horsepower capability, shaft and bearing sizes had to be increased. Thus, you will find that the original 254 frame (5 HP at 1,800 RPM) has a 11 8" shaft. The 254U frame (7 HP at 1,800 RPM) has a 13 8" shaft, and the current 254T frame (15 HP at 1800 RPM) has a 15 8" shaft. Bearing diameters were also increased to accommodate the larger shaft sizes and heavier loads associated with the higher Size BasisOn page 14 you will find a Baldor frame size chart that is a great reference on T frame, U frame and original frame Motors . Most of the dimensions are standard dimensions that are common to all motor manufacturers. One exception to this is the C dimension (overall motor length) which will change from one manufacturer to horsepower MotorsThe term fractional horsepower is used to cover those frame sizes having two-digit designations as opposed to the three-digit designations that are found in Tables 1 and 2.
5 The frame sizes that are normally associated with industrial fractional horsepower Motors are 42, 48, and 56. In this case, each frame size designates a particular shaft height, shaft diameter, and face or base mounting hole pattern. In these Motors specific frame assignments have not been made by horsepower and speed, so it is possible that a particular horsepower and speed combination might be found in three different frame sizes. In this case, for replacement it is essen-tial that the frame size be known as well as the horsepower , speed and enclosure. The derivation of the two-digit frame number is based on the shaft height in sixteenths of an inch. Baldor Basics: MotorsEdward Cowern, continuing series of articles, courtesy of the Baldor Electric Co., dedicated primarily to motor basics; how to specify them; how to operate them; how and when to repair or replace them, and considerably more.
6 Stay tuned!THIS ISSUE:The Mystery of Motor Frame SizePrimer on Two-Speed Motors38 Power Transmission Engineering] 2017 TECHNICALT able 1 Open Drip-ProofTHREE PHASE FRAME SIZES - GENERAL PURPOSERPM NEMA Program Rerate1964 Rerate1964 Rerate1964 Rerate1964 444T100445S405US365TS504S444US404T 444T 445T125504S444US404TS505S445US405T 445T 150505S445US405TS 444T 200444TS 445T 250445TS Table 2 Totally Enclosed, Fan-CooledTHREE PHASE FRAME SIZES - GENERAL PURPOSERPM NEMA Program Rerate1964 Rerate1964 Rerate1964 Rerate1964 444T100505S445US405TS505S445US405T 444T 445T125444TS 444T 445T 150445TS 445T39 Power Transmission EngineeringFEBRUARY 2017 Drawings represent standard TEFC general purpose Motors . *Dimensions are for reference only. NEMA Keyseat NEMA Keyseat Shaft Dimensions Shaft Dimensions (U) (R) (S) (U) (R) (S) 3/8 21/64 FLAT 1-7/81-19/321/2 1/2 29/64 FLAT 2-1/81-27/321/2 5/8 33/64 3/16 2-3/82-1/645/8 7/8 49/64 3/16 2-1/22-3/165/81-1/863/64 1/4 2-7/82-29/643/41-3/81-13/645/16 3-3/82-7/87/81-5/81-13/323/8 3-7/83-5/161*Contact your local Baldor Sales Office for C Dimensions.
7 Dimensions - N, O, P, AB and XO are specific to above chart provides typical Baldor Reliance motor dimensions. For more exact dimensional data, please check the specifi c drawing for each catalog number. NEMA states only a minimum value for AA dimension. AA dimensions shown in chart are Baldor typical values meeting or exceeding NEMA. Please check motor drawing for actual L449T is not included in this chart. Please refer to the Large AC motor chart, or to the specifi c motor drawings for L449T ELECTRIC BOX 2400 FORT SMITH, ARKANSAS72902-2400 C-FaceBA Dimensions143-5TC2-3/4182-4TC3-1/2213-5T C4-1/4254-6TC4-3/4 FrameNEMA FRAMES PRIOR TO 1953 DEFNUVBA664-1/82-15/162-1/22-1/43/42-1/4 3-1/8203542-3/42-7/163/423-1/82043-1/422 45-1/24-1/23-3/83-1/4133-1/22253-3/42546 -1/454-1/83-7/161-1/83-3/84-1/428475-1/2 4-3/44-1/41-1/43-3/44-3/432486-1/45-1/45 -3/81-5/84-7/85-1/43266364975-5/85-5/81- 7/85-3/85-7/83656-1/84041086-1/86-3/82-1 /86-1/86-5/84056-7/84441197-1/47-1/82-3/ 86-7/87-1/24458-1/450412-1/21088-5/82-7/ 88-3/88-1/25059 NEMA QUICK REFERENCE CHARTNEMAFRAMEDE2 FHNOPUVAAABAHAJAKBABBBDXOTAP422-5/81-3/4 1-11/169/32 SLOT1-1/254-11/163/81-1/83/84-1/321-5/16 3-3/432-1/161/84-5/81-9/161/4-204832-1/8 2-3/411/32 SLOT1-7/85-7/85-11/161/21-1/21/24-3/81-1 1/163-3/432-1/21/85-5/82-1/41/4-205656H3 -1/22-7/163511/32
8 SLOT2-7/162-1/86-7/86-5/85/81-7/81/252-1 /165-7/84-1/22-3/41/86-1/22-1/43/8-16143 T145T3-1/22-3/44511/322-1/26-7/86-5/87/8 2-1/43/45-1/42-1/85-7/84-1/22-1/41/86-1/ 22-1/43/8-16182184182T184T4-1/23-3/44-1/ 25-1/24-1/25-1/213/322-11/162-11/163-9/1 63-9/168-11/167-7/87/87/81-1/81-1/82-1/4 2-1/42-3/42-3/43/45-7/82-1/82-1/82-5/82- 5/85-7/85-7/87-1/47-1/44-1/24-1/28-1/28- 1/22-3/41/81/81/41/46-1/26-1/2992-3/83/8 -163/8-161/2-131/2-13213215213T215T5-1/4 4-1/45-1/275-1/2713/323-1/23-1/23-7/83-7 /810-1/49-9/161-1/81-1/81-3/81-3/8333-3/ 83-3/817-3/82-3/42-3/43-1/83-1/87-1/48-1 /23-1/21/492-3/41/2-13254U256U254T256T6- 1/458-1/4108-1/41017/324-1/164-1/164-5/1 64-5/1612-7/812-15/161-3/81-3/81-5/81-5/ 83-3/43-3/44419-5/83-1/23-1/23-3/43-3/47 -1/48-1/24-1/41/410 1/2-13284U286U284T286T284TS286TS75-1/29- 1/2119-1/2119-1/21117/325-1/85-1/84-7/84 -7/83-3/83-3/814-5/814-5/81-5/81-5/81-7/ 81-7/81-5/81-5/84-7/84-7/84-5/84-5/83-1/ 43-1/41-1/213-1/84-5/84-5/84-3/84-3/8339 10-1/24-3/41/411-1/4 1/2-13324U326U324T326T324TS326TS86-1/410 -1/21210-1/21210-1/21221/325-7/85-7/85-1 /25-1/23-15/163-15/1616-1/216-1/21-7/81- 7/82-1/82-1/81-7/81-7/85-5/85-5/85-1/45- 1/43-3/43-3/4214-1/85-3/85-3/8553-1/23-1 /21112-1/25-1/41/413-3/8 5/8-11364U365U364T365T364TS365TS9711-1/4 12-1/411-1/412-1/411-1/412-1/421/326-3/4 6-3/46-1/46-1/44418-1/219-1/22-1/82-1/82 -3/82-3/81-7/81-7/86-3/86-3/85-7/85-7/83 -3/43-3/43181818-1/1618-1/1618-1/1618-1/ 166-1/86-1/85-5/85-5/83-1/23-1/21112-1/2 5-7/81/413-3/8 5/8-11404U405U404T405T404TS405TS10812-1/ 413-3/412-1/413-3/412-1/413-3/413/167-3/ 167-3/167-5/167-5/164-1/24-1/221-5/1622- 1/22-3/82-3/82-7/82-7/82-1/82-1/87-1/87- 1/87-1/47-1/44-1/44-1/4319-1/419-1/419-5 /1619-5/1619-5/1619-5/166-7/86-7/8774411 12-1/26-5/81/413-7/8 5/8-11444U445U444T445T447T449T444TS445TS 447TS449TS11914-1/216-1/214-1/216-1/2202 514-1/216-1/2202513/168-5/88-5/88-9/168- 9/168-9/168-9/164-13/164-13/164-13/164-1 3 5/8-11 Leading Provider of Energy EfficientIndustrial Electric Motors and
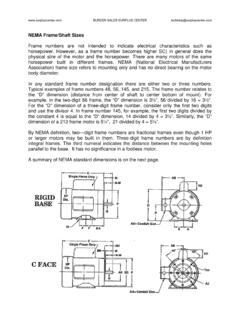
9 DrivesLeading Provider of Energy EfficientIndustrial Electric Motors and Drives40 Power Transmission Engineering] 2017 TECHNICALYou can figure that a 48-frame motor will have a shaft height of 48 divided by 16 or 3 inches. Similarly, a 56-frame motor would have a shaft height of 3 inches. The largest of the cur-rent fractional horsepower frame sizes is a 56-frame that is available in horsepower greater than those normally associ-ated with fractionals. For example, 56-frame Motors are built in horsepower up to 3 HP and, in some cases, 5 HP. For this reason calling Motors with 2-digit frame sizes fractionals is somewhat horsepower MotorsThe term integral- horsepower motor generally refers to those Motors having three-digit frame sizes such as 143T or larger. When dealing with these frame sizes one rule of thumb applies: the centerline shaft height ( D dimension) above the bottom of the base is the first two digits of the frame size divided by four.
10 For example, a 254T frame would have a shaft height of 25 4 = inches. Although the last digit does not directly relate to an inch dimension, larger numbers do in-dicate that the rear bolt holes are moved further away from the shaft end bolt holes (the F dimension becomes larger).VariationsIn addition to the standard numbering system for frames, there are some variations that will appear; these are itemized below along with an explanation of what the various letters Designates a C face (flange) mounted motor. This is the most popular type of face-mounted motor and has a spe-cific bolt pattern on the shaft end to allow mounting. The critical items on C face Motors are the bolt circle (AJ dimension), register (also called rabbet), diameter (AK di-mension) and shaft size (U dimension). C flange Motors always have threaded mounting holes in the face of the The D flange has a special type of mounting flange in-stalled on the shaft end; the flange diameter is larg-er than the body of the motor and it has clearance holes suitable for mounting bolts to pass through from the back of the motor into threaded holes in the mating part.