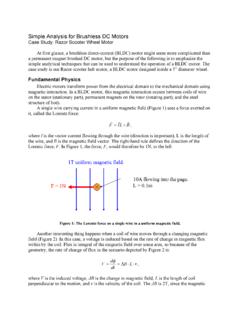
Transcription of The Basics of Permanent Magnet Motor Operations
1 COURSE# - 1 The Basics of Permanent Magnet Motor OperationsBy George HollingCOURSE# - 2 Introduction Introduction The physics of Permanent magnets Basic PM Motor operating principles Basic Motor parameters Motor constructionCOURSE# - 3 The Physics of Permament MagnetsCOURSE# - 4 The Physics of Permament Magnets a typical magnetization curve for a PM Magnet is shown hereCOURSE# - 5 The Physics of Permament Magnets the outmost outline of the magnetization curve is for a single cycle of a fully magnetized Magnet as the operating point of the magnetic circuit s permeance PPline intersects with the demagnetization curve the Magnet weakens the magnetization is not a single curve, but a family of curves COURSE# - 6 The Physics of Permament Magnets the permeance PPof the magnetic circuit determines the operating point of the Permanent Magnet inches influx of direction theparallel thicknessgapair - typically-factor reluctance magnetic : inches influx of direction theparallel cknessmagnet thi :leakageflux magnetic.
2 GmFgmFP =COURSE# - 7 The Physics of Permament Magnets plotting the permeance into the magnetization curve yields the operating point of the magnetic circuit idealistic assumption no saturated steel r>>1 ignores the effects of demagnatization internal field from windings demagnetization curve Magnet temperature ignores the effect of the Magnet s temperatureCOURSE# - 8 The Physics of Permament Magnets the Magnet s flux changes with temperature reversible irreversibleCOURSE# - 9 The Physics of Permament Magnets the Magnet s linear, reversible flux change as a function of temperature is:C)( peraturemagnet tem :ationdemagnetiz oft coefficienlinear : tureat temperadensity flux gapair :)( tureat temperadensity flux gapair :)()](1)[()(0000 =TTTBTTBTTTBTB COURSE# - 10 The Physics of Permament Magnets irreversible changes can occur in the Magnet well below its Curie temperatureCOURSE# - 11 The Physics of Permament Magnets the Motor s conductors can cause irreversible damage to its Magnet the flux generated by an inductor in the Magnet is: inches influx of direction theparallel thicknessgapair :inches influx of direction theparallel cknessmagnet thi :circuit magnetic theof permeance the:Pcurrent winding the:iconductors ofnumber total.
3 (3gmZgmPiZH+ =COURSE# - 12 The Physics of Permament Magnets each PM Motor therefore has a thermal current rating due to wire constraints an absolute peak current rating due to Magnet constraints COURSE# - 13 The Physics of Permament Magnets most PM motors use one of the following PM Magnet materials Alnico: Aluminum Nickel Cobalt Fe3O4: Ceramic/Ferrite SmCo: Samarium Cobalt NeFeBo: Neodymium Iron Boron none is generally better or worse COURSE# - 14 The Physics of Permament Magnets a comparison of different Magnet materialsCOURSE# - 15 Basic PM Motor operating principlesCOURSE# - 16 Basic PM Motor operating principles PM motors operate on the principle that a force is generated when current flows in an inductor that is placed in a magnetic fieldCOURSE# - 17 Basic PM Motor operating principles force generated in a conductor in a magnetic fieldrflux vecto magnetic :flux) magnetic ular to(perpendicconductor theof length :conductor thein flowingcurrent : vectorforce mechanical.)
4 LiF liFmm =COURSE# - 18 Basic PM Motor operating principles this force generates torque in a rotary Motor conductor thein flowingcurrent :conductors ofnumber :length)(stack lengthconductor effective :radius windingaverage :flux magnetic :uerotor torq :iZlrBTiZlrBT =COURSE# - 19 Basic PM Motor operating principles a conductor that moves in a magnetic field generates a voltagerflux vecto magnetic :field magnetic thelar toperpendicuinductor ofy velocit: voltageinduced : 0xylxyBvVvlBdzBvV = = COURSE# - 20 Basic PM Motor operating principles a rotary Motor produces the back-EMF (Lenz s Law)locityangular ve :condutors ofnumber :length)(stack lengthconductor effective :radius :rflux vecto magnetic : voltageinduced.
5 ZlrBVZlrBV =COURSE# - 21 Basic PM Motor operating principles inductor loop in a magnetic fieldCOURSE# - 22 Basic PM Motor operating principles adding a mechanical commutator yields a brush PMDC Motor adding two or more mechanically offset windings yields a PM DLDC or PM BLAC motorCOURSE# - 23 Basic Motor parametersCOURSE# - 24 Basic Motor parameters the torque constant KtA) / m(N m)(N = =ZlrBKKTtt COURSE# - 25 Basic Motor parameters the back-EMF (voltage) constant Kesec)(volt/rad/ (volt) ZlrBKKVEE = = COURSE# - 26 Basic Motor parameters armature resistance Ra (Ohm) armature inductance La (Henry) electrical time constant e(sec) rotor inertia Jr(Kg m2) damping constant Dm (N m / rad / sec) mechanical time constant m (sec) thermal resistance R ( C / Watt) thermal capacitance C (Joules / C) thermal time constant therm(sec)COURSE# - 27 Basic Motor parameters example of a typical speed/torque curve of a PM motorCOURSE# - 28 Basic Motor parameters the Safe Continuous Operating Area SCOA the Motor can safely be operated continuously anywhere in this region the Safe Intermittent Operating Area SIOA the Motor may be operated in this region for short periods of time (typically < 1 min)COURSE# - 29 Basic Motor parameters the electrical equation for the PM DC machine is: + + =EaaKIRdtdILVCOURSE# - 30 Basic Motor parameters the electrical equation for a single phase of the PM BLDC/BLAC machine with sinusoidal phase current is.
6 ()dtdKIRLVEaa + + =)3602sin(3602)3602sin()3602cos(3602 COURSE# - 31 Basic Motor parameters the power balance for the PM DC machine is: ++ ++ + + = + + =)()()2()2()2(222222 LmLMETTDDJdtdIRILdtdPIKIRILdtdPCOURSE# - 32 Basic Motor parameters the power analysis reveals that:losses friction : )(losses damping : )(energy mechanical : )2(heat - windings thein lossescopper electrical : energy ionmagnetizat : )2(2222 + + > LmLMTTDDJdtdIRILdtdCOURSE# - 33 Basic Motor parameters the power supplied to the load is: - 2 =mMEmechTDIKPCOURSE# - 34 Basic Motor parameters the maximum continuous torque allowed is:(A) )( 25maxcont =RTRTTI riseCrise the maximum continuous current allowed is:m)(N )( )( 25maxcont = RTRTTTKT riseCriserisetCOURSE# - 35 Motor constructionCOURSE# - 36 Motor construction the field in the stator poles changes continuously, thus we must use laminated steel to reduce eddy current losses the backiron to support the PM flux is relatively constant and solid steel can be usedCOURSE# - 37 Motor constructionCOURSE# - 38 Motor construction the eddy current losses are:)m / (ohmy resistivit electrical me volu: volumelamination :(T)density flux ACpeak :(m) slamonation theof kness thic:(Hz) Motor theoffrequency electrical.
7 632222eddy V fV fPPP=COURSE# - 39 Motor construction Motor steel choicesCOURSE# - 40 Motor construction Motor windings are generally copper wire with insulation ( Magnet wire) Magnet wire comes in different grades temperature B, F, H, C insulation double, triple voltage ratingCOURSE# - 41 Motor construction the resistance of the Magnet wire changes with (the wire s) is value theecopper wirfor t coefficien thermal :C)( re temperatu winding :(ohm) C25 typicallyre, temperatureferenceat resistance : ]1[000 + = T)R(T)(T - T)R(TR(T)