Transcription of The Fourier Transform (What you need to know)
1 FOURIERBOOKLET-1 SchoolofPhysicsTHEUNIVERSITYOFEDINBURGHT heFourierTransform(Whatyouneedtoknow)Mat hematicalBackgroundfor:SeniorHonoursMode rn OpticsSeniorHonoursDigitalImageAnalysisS eniorHonoursOpticalLaboratoryProjectsMSc TheoryofImageProcessingSession:2007-2008 .. DimensionalFourierTransform.. niteComb..125 ConvolutionofTwo .. DimensionalConvolution..146 CorrelationofTwo .. ()function..28 SchoolofPhysicsFourierTransformRevised:1 0 September2007-2 FOURIERBOOKLET1 IntroductionFourierTransformtheoryis essentialtomany areasofphysicsincludingacousticsandsigna lprocessing,opticsandimageprocessing,sol idstatephysics,scatteringtheory, andthemoregenerally, inthesolutionofdifferentialequationsinap plicationsasdiverseasweathermodel-ingto quantum (sineandcosine),ora shiftofspacefromrealspacetore-ciprocalsp ace.
2 Actuallythesetwo conceptsaremathematicallyidenticalalthou ghthey tocovertheFourierTheoryrequiredprimarily forthe JuniorHonourscourseOPTICS. SeniorHonourscourseMODERNOPTICS1andDIGIT ALIMAGEANALYSIS rangeofexamplesandmathematicalproofs,som eofwhicharefairlydif cult,particularlythepartsinitalic. Themathematicalproofsarenotinthemselvesa nexaminalpartofthelecturecourses, IntroductiontotheFourierTransformanditsA pplications byBracewelland MathematicalMethodsforPhysicsandEngineer ing byRiley, Hobson& many mathematical eldofscience,FourierTransformtheorydoesn othave a wellde :x;y!RealSpaceco-ordinatesu;v!Frequency Spaceco-ordinatesandlowercasefunctions(e g f(x)), beinga realspacefunctionanduppercasefunctions(e gF(u)), beingthecorrespondingFouriertransform,th us:F(u) =Fff(x)gf(x) =F 1fF(u)gwhereFfgis willbeusedtodenotep 1,it shouldbenotedthatthischaracterdiffersfro mtheconventionali(orj).
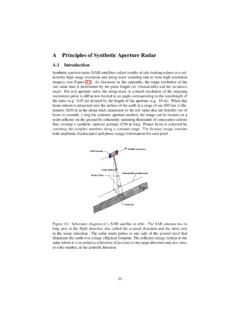
3 Thisslightlyoddconventionandistoavoidcon fusionwhenthedigitalversionoftheFourierT ransformis 0 1-10-5 0 5 10sinc(x)Figure1:Thesinc() specialfunctionswillalsobeemployed,these beingsinc()de ned2as,sinc(x) =sin(x)x(1)givingsinc(0) =13andsinc(x0) =0 atx0= p; 2p; : : :, asshownin gure1. ThetophatfunctionP(x), is givenby,P(x) =1forjxj 1=2=0else(2)beinga functionofunitheightandwidthcenteredabou tx=0, andis shownin gure2 0 1 0 1 2 Figure2:TheP(x)function2 TheFourierTransformThede nitionofa onedimensionalcontinuousfunction,denoted byf(x), theFouriertransformis de nedby:F(u) =Z f(x)exp( 2pu x)dx(3)2 Thesinc()functionis sometimesde nedwitha stray 2p, :10 September2007-4 FOURIERBOOKLET withtheinverseFouriertransformde nedby;f(x) =Z F(u)exp( 2pu x)du(4)whereit (x).
4 InthiscasetheFouriertransformcanbesepara tedtogive,F(u) =Fr(u) + F (u)(5)wherewehave,Fr(u) =Z f(x)cos(2pu x)dxF (u) = Z f(x)sin(2pu x)dxSotherealpartoftheFouriertransformis thedecompositionoff(x)intermsofcosinefun c-tions,andtheimaginaryparta frequency, forexampleiff(x)isa soundsignalwithxmeasuredinsecondsthenF(u )is itsfrequency spectrumwithumeasuredinHertz(s 1).NOTE: Clearly(u x)mustbedimensionless,soifxhasdimensions oftimethenu musthavedimensionsoftime oneofthemostcommonapplicationsforFourier Transformswheref(x)is a detectedsignal(forexamplea soundmadebya musicalinstrument),andtheFourierTransfor mis usedtogive rangeofusefulproperties,someofwhichareli stedbelow. Inmostcasestheproofofthesepropertiesis simpleandcanbeformulatedbyuseofequation3 Theproofsofmany :TheFouriertransformis a linearoperationsothattheFouriertransform ofthesumoftwo functionsis ,Ffa f(x) +b g(x)g=a F(u) +b G(u)(6)whereF(u)andG(u)aretheFouriertran sformsoff(x)andandg(x) :TheFouriertransformoftheComplex Conjugateofa functionis givenbyFff (x)g=F ( u)(7)4 Therearevariousde a frequency or angularfrequency.
5 Thedifferencebetweenthede nitionsareclearlyjusta scalingfactor. TheopticsanddigitalFourierapplicationsth e2pis usuallyde nedtobeinsidethekernelbutinsolidstatephy sicsanddifferentialequationsolutionthe2p constantis :10 September2007 FourierTransformSchoolofPhysicsFOURIERBO OKLET-5whereF(u)is theFouriertransformoff(x).ForwardandInve rse:We have thatFfF(u)g=f( x)(8)sothatif weapplytheFouriertransformtwicetoa function,wegeta that,F 1ff(x)g=F( u)(9)sothattheFourierandinverseFouriertr ansformsdifferonlybya :TheFouriertransformofthederivative ofa functionsis givenbyF df(x)dx = 2pu F(u)(10)andthesecondderivative is givenbyF d2f(x)dx2 = (2pu)2F(u)(11)Thispropertywillbeusedinth eDIGITALIMAGEANALYSISandTHEORYOFIMAGEPRO -CESSING coursetoformthederivative :ThePowerSpectrumofa signalis de nedbythemodulussquareoftheFouriertransfo rm,beingjF(u)j2.
6 Thiscanbeinterpretedasthepowerofthefrequ ency functionanditsFouriertransformobey theconditionthatZ jf(x)j2dx=Z jF(u)j2du(12)whichisfrequentlyknownasPar seval's Theorem5. Iff(x)isinterpretedata voltage,thenthistheoremstatesthatthepowe risthesamewhethermeasuredinreal(time),or Fourier (frequency) DimensionalFourierTransformSincethethree coursescoveredbythisbookletusetwo-dimens ionalscalarpotentialsorimageswewillbedea lingwithtwo willde nethetwo dimensionalFouriertransformofa continuousfunctionf(x;y)by,F(u;v) =Z Zf(x;y)exp( 2p(ux+vy))dxdy(13)withtheinverseFouriert ransformde nedby;f(x;y) =Z ZF(u;v)exp( 2p(ux+vy))dudv(14)wherethelimitsofintegr ationaretakenfrom ! 65 StrictlyspeakingParseval's TheoremappliestothecaseofFourierseries,a ndtheequivalenttheoremforFouriertransfor msis correctly, butlesscommonly, knownasRayleigh's theorem6 Unlessotherwisespeci edallintegrallimitswillbeassumedtobefrom !
7 SchoolofPhysicsFourierTransformRevised:1 0 September2007-6 FOURIERBOOKLETA gainfora realtwo dimensionalfunctionf(x;y), theFouriertransformcanbeconsideredasthed ecompositionofa (x;y)is consideredto beanimagewiththe brightness oftheimageat point(x0;y0)givenbyf(x0;y0), thenvariablesx;yhave ;vhave thereforethedimensionsofinverselength,wh ichis : Typicallyxandyaremeasuredinmmsothatuandv have areinunitsofmm di-mensionalsinusoidalspatialfrequency f(x;y) x = 2pu F(u;v)(15)andwithF f(x;y) y = 2pv F(u;v)(16)yieldingtheimportantresultthat ,F 2f(x;y) = (2pw)2F(u;v)(17)wherewehave thatw2=u2+v2. SothattakingtheLaplacianofa functioninrealspaceisequivalenttomultipl yingitsFouriertransformbya circularlysymmetricquadraticof dimensionalFourierTransformF(u;v), ofa functionf(x;y)is a separableoperation,andcanbewrittenas,F(u ;v) =ZP(u;y)exp( 2pvy)dy(18)whereP(u;y) =Zf(x;y)exp( 2pux)dx(19)whereP(u;y)istheFourierTransf ormoff(x;y)withrespecttoxonly.
8 Thispropertyofseparabilitywillbeconsider edingreaterdepthwithregardstodigitalimag esandwillleadtoanimplementationoftwo dimensionaldiscreteFourierTransformsin a functionf(~r)where~r= (x;y;z), thenthethree-dimensionalFourierTransform F(~s) =Z Z Zf(~r)exp( 2p~r:~s)d~rwhere~s= (u;v;w)beingthethreereciprocalvariablese achwithunitslength givenbyf(~r) =Z Z ZF(~s)exp( 2p~r:~s)d~sRevised:10 September2007 FourierTransformSchoolofPhysicsFOURIERBO OKLET-7 Thisis usedextensivelyinsolidstatephysicswheret hethree-dimensionalFourierTransformofa crystalstructuresis independentofthedimensionalityandmulti-d imensionalFourierTrans-formcanbeformulat edasa , whichissomewhatabstractlyde nedas:d(x) =0forx6=0Z d(x)dx=1(20)Thiscanbethoughtofasa very tall-and-thin spike withunitarealocatedattheorigin,asshownin gure3.
9 3 20 1123xd( )Figure3 : Thed-functionsshouldnotbeconsideredtobea nin nitelyhighspike ofzerowidthsinceit scalesas:Z ad(x)dx=awhereais a nota truefunctionintheanalysissenseandif oftencalledanimproperfunction. Therearea rangeofde nitionsoftheDeltaFunctionintermsofproper function,someofwhichare:De(x) =1eppexp x2e2 De(x) =1eP x 12ee!De(x) =1esinc xe 7 Thisis alsoreferredtoas~k-spacewhere~k=2p~sScho olofPhysicsFourierTransformRevised:10 September2007-8 FOURIERBOOKLET beingtheGaussian,Top-HatandSincapproxima tionsrespectively. Alloftheseexpressionshave thepropertythat,Z De(x)dx=18e(21)andwemayformtheapproximat ionthat,d(x) =lime!0De(x)(22)whichcanbeinterpretedasm akingany oftheabove approximationsDe(x)a very tall-andthin spike eldofopticsandimaging,wearedealingwithtw o dimensionaldistributions,soit isespeciallyusefultode netheTwo DimensionalDiracDeltaFunction, as,d(x;y) =0forx6=0 &y6=0Z Zd(x;y)dxdy=1(23)whichis thetwo dimensionalversionofthed(x)functionde nedabove, andinparticular:d(x.)
10 Y) =d(x)d(y):(24)Thisisthetwo ,thisfunctioncanbeconsideredasa singlebrightspotinthecentreofthe eldofview, forexamplea singlebrightstarviewedbya usedextensively, andhassomeuseful,andslightlyperculiarpro perties,it is functionf(x), beingintegrable,thenwehave thatZ d(x)f(x)dx=f(0)(25)whichis oftentakenasanalternative de functionmultipliedbyad-functionlocatedab outzerois justthevalueofthefunctionat theShiftingProperty, againfora functionf(x),giving,Z d(x a)f(x)dx=f(a)(26)whered(x a)is justad-functionlocatedatx=aasshownin dimensions,fora functionf(x;y), wehave that,Z Zd(x a;y b)f(x;y)dxdy=f(a;b)(27)whered(x a;y b)isad-functionlocatedatpositiona;b. Thispropertyiscentraltotheideaofconvolut ion,whichis usedextensivelyinimageformationtheory, Deltafunctionis canbeformedbydirectintegrationofthede nitionoftheFouriertransform,andtheshiftp ropertyinequation25above.