Transcription of The Importance of National Qualifications Framework in the ...
1 6/6/2015 1 1997 ASEAN Summit in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia - ASEAN vision 2020 - Decision made to transform ASEAN into a highly competitive Region with equitable economic development and reduced poverty and socio-economic disparities 2003 ASEAN Summit in Bali, Indonesia - Declared that the goal of the regional economic integration is the ASEAN Economic Integration (Bali Concord II) by 2020. 2006 ASEAN Summit in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia - Agreement to develop a blueprint for AEC and advancing it to 2015 2007 ASEAN Summit in Cebu, Philippines - Affirmed the establishment of the ASEAN Economic community 2015 OBJECTIVES To transform ASEAN into a stable, prosperous, and highly competitive region with equitable economic development, and reduced poverty and socio-economic disparities To have a single market and production base characterized by.
2 Free flow of goods Free flow of capital Free flow of investment Free flow of skilled labor Free flow of professional services 6/6/2015 2 Free Flow of Professional Services Recognition of Professional Qualifications Movement of Professionals PROMOTES COMPETITIVENESS AQRF MRA RECOGNITION HARMONIZATION NQF DEVELOPMENT OF Qualifications COMPETITIVENESS MOBILITY OF PROFESSIONALS AQRF MRA Conceptual Framework Complete MRAs for major professional services, including Priority Integration Services (PIS) sectors of e-commerce, healthcare, air travel, tourism and logistics by 2008 Develop core competencies (concordance of skills and Qualifications ) for job/occupational skills required in PIS by 2009 Develop core competencies (concordance of skills and Qualifications ) for job/occupational skills in all service sectors by 2015 6/6/2015 3 OBJECTIVES Facilitate mobility Exchange information and enhance cooperation Promote adoption of best practices on standards and Qualifications Provide opportunities for capacity building and training SUBJECT TO DOMESTIC LAWS RECOGNITION Education Examination Experience COLLABORATION WITH LOCAL PROFESSIONALS Ethics Continuing Professional Development 6/6/2015 4 6.
3 Has declared that there is no investigation or legal proceeding pending against him/her in Country of Origin or another country 7. In compliance with any other assessment or requirement as may be imposed on any such applicant for registration as deemed fit by the Professional Regulatory Authority or other relevant authorities of the Host Country (Patterned after the Medical Practitioners, Noche, 2015) The ten ASEAN Member States have already agreed on conferring temporary licensing or temporary registration on the following five (5) areas: Practice Visits and Training Missions (Noche, 2015) PROCESS OF RECOGNITION ASEAN JOINT COORDINATING COMMITTEE ON LIBRARIANS (to be constituted)
4 PROFESSIONAL REGULATORY AUTHORITY FOR LIBRARIANS the implementation of ASEAN MRA ASEAN Member States to standardize and adopt mechanisms and procedures exchange of information on laws, practices and developments in the practice of librarianship within the region the Qualifications , training and experiences recognition and register eligible Librarians to practice in the Host Country and assess the compliance of the Librarians practice and conduct necessary actions in case any Librarian failed to practice in accordance with code of conduct and standards of the Host Country 6/6/2015 5 Diversity in LIS curricula among the ASEAN countries offering Library and Information Science/Studies/Management courses Some ASEAN countries do not yet offer LIS courses (Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar) Information about LIS education is not available for some countries The present graduates of Library Science in the Philippines lack two years of basic education (Grades 11 and 12) Philippine Qualifications Framework vs.
5 The National Qualifications Framework of other ASEAN Countries Harmonization of Qualifications towards Mutual Recognition Arrangement (MRA) Only the Philippines has a regulatory body that requires passing of Librarians Licensure Examination (LLE) prior to practice Others have metrics assessed by Councils of Deans or other bodies such as Library Associations Continuing Professional Development (Career Progression) Credit Accumulation and Transfer (CATS) 6/6/2015 6 FINAL AQRF DOCUMENT COMPONENT STRUCTURE REFERENCING Scope Purpose Principles Quality Assurance Learning Outcomes Level Descriptors Credit or Amount of Learning Linking National Qualifications Framework Criteria Procedure Scope Addresses education and training sectors (incorporates formal, non-formal and informal learning) and the wider objective of promoting lifelong learning Principles Does not require Member States to make changes to their National qualification systems Respects specific structures and processes Purpose Supports recognition of Qualifications Promotes and encourages education and mobility students, skilled workers and professionals Quality Assurance Promotes QA of education and training across the region Underpinned by a set of agreed QA principles and broad standards related to the functions of the registering and accrediting agencies, systems for the assessment of learning and the issuing of Qualifications , and regulation of the issuance of certificates Learning Outcomes Emphasizes the results of learning rather than focusing on inputs.
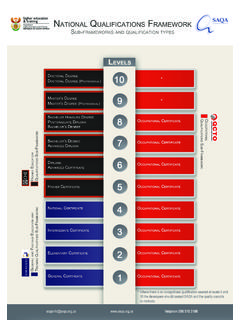
6 Such as length of study Supports the transfer of Qualifications , including credit accumulation and transfer Level Descriptors Has 8 levels of complexity of learning outcomes Includes 2 domains : Knowledge and skills Application and responsibility Knowledge and Skills Application and Responsibility LEVEL 6 is specialized technical and theoretical within a specific field involve critical and analytical thinking are complex and changing require initiative and adaptability as well as strategies to improve activities and to solve complex and abstract issues LEVEL 7 is at the forefront of a field and show mastery of a body of knowledge involve critical and independent thinking as the basis for research to extend or redefine knowledge or practice are complex and unpredictable and involve the development and testing of innovative solutions to resolve issues require expert judgement and significant responsibility for professional
7 Knowledge, practice and management LEVEL 8 is at the most advanced and specialised level and at the frontier of a field involve independent and original thinking and research, resulting in the creation of new knowledge or practice are highly specialized and complex involving the development and testing of new theories and new solutions to resolve complex, abstract issues require authoritative and expert judgement in management of research or an organization and significant responsibility for extending professional knowledge and practice and creation of new ideas and/or processes Referencing Confirmation that the accrediting and registering agencies meet agreed quality principles and broad standards; applies concept of Best Fit (Principle of benchmarking and comparability) Referencing procedure Aims to : 1.
8 Describe a common structure for linking National Qualifications Frameworks to the AQRF; 2. ensure that the linking process undertaken is robust and transparent; and 3. provide a common reporting structure for the referencing report Referencing Criteria to optimize consistency and to make the process of referencing transparent as agreed upon by the ASEAN Member States (critically important for the integrity of the AQRF) 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Country (A) Country (B) AQRF 8 35 Referencing Process requires the following: of National Qualifications Framework 2. Documentation of processes, Quality Assurance mechanisms 3. Each country forms referencing panel 4. Panel includes international expert and one observer from another ASEAN country ASEAN Qualifications REFERENCE Framework (AQRF)
9 Target date of referencing process is in 2018 The structure of the education and training system is described The responsibilities and legal basis of all relevant National bodies involved in the referencing process are clearly determined and published by the main public authority responsible for the referencing process The procedures for inclusion of Qualifications in the National Qualifications Framework or for describing the place of Qualifications in the National qualification system are transparent 1 2 3 There is a clear and demonstrable link between the Qualifications levels in the National Qualifications Framework or system and the level descriptors of the AQRF The basis in agreed standards of the National Framework or Qualifications system and its Qualifications is described The National quality assurance system(s) for education and training refer(s) to the National Qualifications Framework or system are described.
10 All of the bodies responsible for quality assurance state their unequivocal support for the referencing outcome 6 5 4 6/6/2015 7 The process of referencing has been devised by the main public authority and has been endorsed by the main stakeholders in the qualification system People from other countries who are experienced in the field of Qualifications are involved in the referencing process and its reporting One comprehensive report, setting out the referencing and the evidence supporting it, shall be published by the competent National bodies and shall address separately and in order each of the referencing criteria 7 8 9 The outcome of referencing is published by the ASEAN Secretariat and by the main National public body Following the referencing process, all certification and awarding bodies are encouraged to indicate a clear reference to the appropriate AQRF level on new qualification certificates, diplomas issued 11 10 COUNTRY LEVELS Brunei Darussalam 8 Cambodia 8 Indonesia 9 Laos 4 (TVET) Malaysia 8 COUNTRY LEVELS Myanmar 4 Philippines 8 Singapore 6 Thailand 9 Vietnam 5 6/6/2015 8 S2 S1 S3 General High School 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 6 Professional Specialist D I D IV D III D II Subspecialist Vocational Senior High School Elementary/Junior High School 2 2 MYANMAR (Ministry of Labour Employment and Social Security) qualification Certificate System qualification Job level Skill, Knowledge and Ability Certificate 1 1.