2 Ultraviolet Visible Absorption Spectroscopy
Found 6 free book(s)ULTRAVIOLET AND VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY
www.uobabylon.edu.iqUltraviolet and Visible Spectroscopy This absorption spectroscopy uses electromagnetic radiations between 190 nm to 800 nm and is divided into the ultraviolet (UV, 190-400 nm) and visible (VIS, 400-800 nm) regions. Since the absorption of ultraviolet or visible radiation by a molecule leads transition among electronic
Fundamentals of UV-Visible Spectroscopy (5965-5123E)
web.uni-plovdiv.bgUV-visible spectroscopy. These provide valuable insight into the uses and limitations of this technique for chemical analysis. The primary applications of UV-visible spectroscopy are also briefly reviewed. Basic principles The electromagnetic spectrum Ultraviolet (UV) and visible …
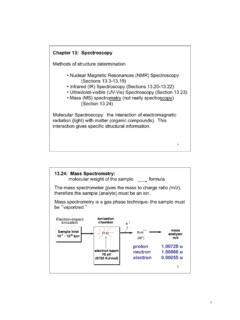
13.24: Mass Spectrometry
as.vanderbilt.edu• Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy (Section 13.23) • Mass (MS) spectrometry (not really spectroscopy) (Section 13.24) Molecular Spectroscopy: the interaction of electromagnetic radiation (light) with matter (organic compounds). This interaction gives specific structural information. 2 13.24: Mass Spectrometry:
Applications of IR Spectroscopy - Chemistry
www2.chemistry.msu.eduRaman Spectroscopy . A spectroscopic technique used to observe vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency [modes in a system. 1] It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range.
The Basics of UV-Vis Spectroscopy
www.agilent.comwavelength has higher energy, and, for UV-Vis spectroscopy, the low (short) Figure 2. Electronic transitions in formaldehyde. UV light at 187 nm causes excitation of an electron in the C-O bond and light at 285 nm wavelength causes excitation and transfer of an electron from the oxygen atom to the C-O bond. Ultraviolet Visible Infrared LOWER ENERGY
RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY - G.C.G.-11
cms.gcg11.ac.in• (1). Raman Spectroscopy can be used not only for gases but also for liquids & solids for which the infrared spectra are so diffuse as to be of little quantitative value. • (2). Raman Effect is exhibited not only by polar molecules but also by non-polar molecules such as O2, N2, Cl2 etc. • …