Chapter 5 2 Benzene
Found 10 free book(s)Reactions of Benzene & Its Derivatives
colapret.cm.utexas.eduBenzene & Its Derivatives Chapter 22 Organic Lecture Series 2 Reactions of Benzene The most characteristic reaction of aromatic compounds is substitution at a ring carbon: + + Chlorobenzene Halogenation: H Cl2 Cl FeCl3 HCl + + Nitrobenzene Nitration: HNOHNO3 2 H2 SO4 H2 O
Homework #2 Chapter 16 - UC Santa Barbara
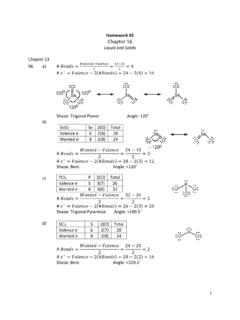
people.chem.ucsb.eduHomework #2 Chapter 16 Liquid and Solids 7. Vapor Pressure: The pressure exerted by the vapor of a liquid when the vapor and the ... Look at the table in problem 20 – benzene (which only has London dispersion forces) has a higher boiling point than acetone (which has dipole-dipole and London dispersion forces). Therefore, the London
ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS OF …
www.saplinglearning.com750 CHAPTER 16 • THE CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE AND ITS DERIVATIVES This hybridization allows one of its electron pairs to occupy a 2p orbital, which has the same size, shape, and orientation as the carbon 2p orbitals of the ring. In other words, an oxygen 2p orbital overlaps more effectively with the carbon 2p orbitals of the ring than an oxygen sp3 or- bital would.
Chapter 5.12 Styrene - World Health Organization
www.euro.who.intChapter 5.12 Styrene General description Styrene (vinylbenzene, styrole) is a colourless, viscous liquid with a pungent odour and tendency to polymerize. Its chemical structure is C6H5.CH=CH2 and its molecular mass 104.15. Styrene is slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and very soluble in benzene and petroleum ether. Sources
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
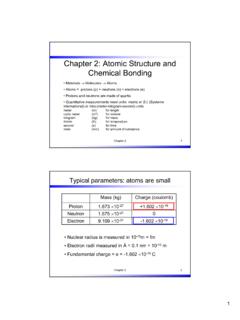
physics.uwo.caChapter 2 31 Benzene (C 6H 6) important for some polymeric materials Chapter 2 32 2.7 Metallic Bonding • Consider Na metal: what holds it together? • In solid state metal atoms are packed in a systematic pattern or crystal structure • The valence electrons are weakly bonded to the positive-ion cores and can readily move as “free ...
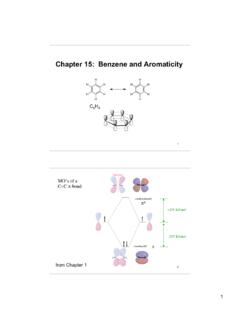
Chapter 15: Benzene and Aromaticity
as.vanderbilt.edu(chapter 2.5 and 2.6) 1. No one resonance forms accurately depicts the structure of the molecule. The real structure is a composite or hybrid of all resonance forms 2. Resonance forms differ only by the placement of π- or non-bonding electrons. Neither the position or hybridization of the atoms changes. 3. Resonance forms are not necessarily ...
Chapter 8 - Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic Compounds
wou.eduChapter 8 - Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic Compounds . This text is published under creative commons licensing, for referencing and adaptation, please click . here. Opening Essay. 2 . 8.1 Alkene and Alkyne Overview. 4. 8.2 Properties of Alkenes. 5 Looking Closer: Environmental Note 6 . 8.3 Alkynes. 10 . 8.4 Aromatic Compounds: Benzene. 12 ...
Structure Determination of Organic Compounds
bionmr.unl.eduadded a new chapter with reference data for 19F and 31P NMR spectroscopy and, in the chapter on infrared spectroscopy, we newly refer to important Raman bands. ... 5 2.1 General Tables .....5 2.1.1 Calculation of the Number of Double Bond Equivalents from the Molecular Formula .....5 2.1.2 Properties of Selected Nuclei ...
Solutions - NCERT
ncert.nic.in(CCl4) if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride. 2.2 Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride. 2.3 Calculate the molarity of each of the following solutions: (a) 30 g of Co(NO3)2. 6H2O in 4.3 L of solution (b) 30 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4 diluted to 500 mL.
Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and ...
www.chem.tamu.eduChapter 5 Energy and Chemical Reactions 80 25. To accomplish the process, one must: 1) heat the ethanol from 20.0 ˚C to 78.29 ˚C (ΔT = 58.29 K) 2) boil the ethanol (convert from liquid to gas) at 78.29 ˚C Using the specific heat for ethanol, the energy for the first step is: (2.44 J g • K )(1000 g)(58.29 K) = 142,227.6 J ( 142,000 J to 3 sf)