Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase G
Found 12 free book(s)Table of Genetic Disorders - Loyola University Chicago
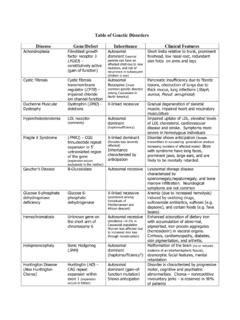
www.meddean.luc.eduGlucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase X-linked recessive (prominent among individuals of Mediterranean and African descent) Anemia (due to increased hemolysis) induced by oxidizing drugs, sulfonamide antibiotics, sulfones (e.g. dapsone), and certain foods (e.g. fava beans) Hemochromatosis Unknown gene on ...
Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen Metabolism, and the Pentose ...
academic.mu.edu3. the release of glucose-6-phosphate and glucose from glycogen for entry into metabolism need to be explored. ... NADH is required in the cytoplasm for the Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase step. In the cytoplasm the ratio of [NADH] / [NAD] is normally very low, about 8 × 10–4. These different
Glycolysis The Glycolytic Pathway The Reactions of ...
biochem.siu.eduPhosphoglucose isomerase (glucose-6-phosphate isomerase) isomerization (aldose to ketose) reaction pH dependent, pK = 6.7 (Glu) and pK = 9.3 (Lys) absolute stereospecificity. Reactions of Glycolysis Phosphofructokinase ... phosphate dehydrogenase Excess fructose depletes liver Pi ...
Selected Normal Pediatric Laboratory Values
wps.prenhall.comGlucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (RBC)2 150–215 units/dL Glucose Tolerance Test Results in Serum a2 GLUCOSE INSULIN TIME mg/dL mmol/L U/mL pmol/L Fasting 59–96 3.11–5.33 5–40 36–287 30 min 91–185 5.05–10.27 36–110 258–789 60 min 66–164 3.66–9.10 22–124 158–890
Drugs to Avoid in G6PD Deficiency Background: Glucose 6 ...
kucpn.netGlucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is a genetic blood disorder where an acute attack of a haemolytic anaemia occurs. It is highly common in certain ethnic groups such as: Asians, Africans and Mediterranean and more prevalent in males more than females (1,2).
Laboratory Procedure Manual
www.cdc.govadenine dinucleotide (NAD), G-6-P is oxidized by the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) to 6-phosphogluconate and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). The increase in NADH concentration is directly proportional to the glucose concentration and can be measured spectrophotometrically at 340 nm. (1–3).
The Structure Adenine and Hydrolysis of ATP
www.nslc.wustl.eduGlucose (C 6H 12O 6) Fructose (C 6H 12O 6) Figure 8.13 Course of reaction without enzyme E A without enzyme E A with enzyme is lower Course of ... phosphate dehydrogenase Phospho- glycerokinase 6 7 . Figure 9.9d Glycolysis: Energy Payoff Phase 2 ATP 2 ADP 2 2 2 2 2 H 2O Phosphoenol- Pyruvate
Updating the WHO G6PD classification of variants and the ...
www.who.intGlucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is an X-linked recessive disorder. It is the most common genetic abnormality affecting an estimated 400 million people worldwide. Although mostly asymptomatic, G6PD deficiency can lead to three clinical manifestations: (i) neonatal jaundice; (ii)
Electron Transport Chain (overview)
www.csun.eduGlycerol-3-Phosphate Shuttle • Functions in the skeletal muscle and brain. • NADH on the cytoplasmic side is oxidized to NAD+ with coupled reduction of DHAP to glycerol-3-phosphate. Enzyme: cytoplasmic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. • The oxidation of glycerol 3-phosphate back to DHAP is
Glycolysis
www.csun.edu• Regulated only by excess glucose-6-phosphate. If G6P accumulates in the cell, there is feedback inhibition of hexokinase till the G6P is consumed. • Glucose-6-phosphate is required for other pathways including the pentose phosphate shunt and glycogen synthesis. So hexokinase step is not inhibited unless G-6-P accumulates.
Sugar Metabolism in Yeasts: an Overview of Aerobic and ...
repositorium.sdum.uminho.ptmetabolites, and further phosphorilates fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. These steps are the first part of glycolysis that requires energy in the form of ATP. The subsequently acting enzymes are aldolase, triosephosphate isomerase, glyc-eraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerate kinase, phosphoglycerate mutase ...
REGULATION OF GLYCOLYSIS
aqu2018.weebly.compermits initiation of glycolysis even when blood glucose levels are relatively low. However, its Vmax is relatively low. • Hexokinase is inhibited by the product of its reaction, glucose-6-phosphate. This is a very important regulatory step, since it prevents the consumption of too much cellular ATP to form G6P when glucose is not limiting.