Hydrolysis Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Found 9 free book(s)Caboxylic acid Derivatives - Rutgers University
crab.rutgers.eduCh21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape).docx Page 1 Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are esters, amides and nitriles, although acid halides and anhydrides are also derivatives (really …
Organometallic Chemistry - uni-regensburg.de
www-oc.chemie.uni-regensburg.dereaction amounts to an alkylation of a carboxylic acid. • In the presence of a catalytic amount of CuI, Grignard ... Hydrolysis of the silyl enol ether regenerates the carbonyl group. ... allowing the preparation of functionalized derivatives.
Chapter 19: Lipids - latech.edu
www.chem.latech.eduglycerides: esterification, hydrolysis, saponification, and hydrogenation. 4. Understand the functions of prostaglandins in physiological processes. ... derivatives functions as chemical messengers in the body. ... because of carboxylic acid …
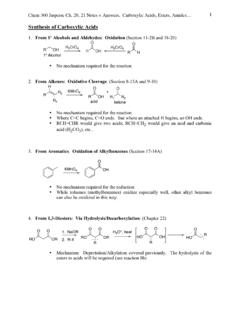
Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids
web.mnstate.eduChem 360 Jasperse Ch. 20, 21 Notes + Answers. Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Amides… 3 8. From Acid Chlorides, Anhydrides, Esters, or Amides: Hydrolysis (Section 20-8C) a) “Downhill” hydrolysis: From acids or anhydrides with NEUTRAL WATER alone
AMIDES AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
webhome.auburn.eduderivatives of carboxylic acids in which the -OH of the acid has been replaced by -NR2 where R= H, alkyl, aryl, etc.): Like amines, amides can be classified as "primary", "secondary" or "tertiary" depending on the degree of carbon substitution on nitrogen: Amides may also be sub-classified as aliphatic, aromatic (i.e. anilides or benzamides) or ...
Carboxylic Acids
crab.rutgers.eduCarboxylic acid derivatives differ in the nature of the group bound to the acyl group. -OH is an acid-Cl is the acid chloride-OCOR' is the anhydride-OR' is the ester-NR 2 is the amide Nucleophilic acyl substitution can interconvert all of these different acid derivatives.
Thermo Scientific Crosslinking Technical Handbook
tools.thermofisher.comCarboxylic acid-reactive chemical groups Carboxylic acids (–COOH) exist at the C-terminus of each polypeptide chain and in the side chains of aspartic acid (Asp, D) and glutamic acid (Glu, E). Like primary amines, carboxyls are usually on the surface of protein structure. Carboxylic acids are reactive towards carboiimides.
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis - California State University ...
www.csun.edua complex called as fatty acid synthase (FAS). • The product of FAS action is palmitic acid. (16:0). • Modifications of this primary FA leads to other longer (and shorter) FA and unsaturated FA. • The fatty acid molecule is synthesized 2 carbons at a time • FA synthesis begins from the methyl end and proceeds toward the carboxylic acid end.
12.112.112.1 Nomenclature and Structure of Carbonyl Group
ncert.nic.inderived from the common names of the corresponding carboxylic acids [Section 12.6.1] by replacing the ending – ic of acid with aldehyde. At the same time, the names reflect the Latin or Greek term for the original source of the acid or aldehyde. The location of the substituent in the carbon chain is indicated by Greek letters α, β, γ, δ ...