Linear Combination Of Atomic Orbitals
Found 8 free book(s)Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules
www.cpp.eduLCAO = linear combination of atomic orbitals node = zero electron density because of opposite phases ∆E = bond energy There is a big energy advantage for a hydrogen molecule over two hydrogen atoms. Sigma (σ) bonding molecular orbital - Shared electron density is directly between the bonding atoms, along the bonding axis.
Problems forSolid State Physics (3rdYearCourse6) Hilary ...
www-thphys.physics.ox.ac.ukThis technique is know as the molecularorbital approach, or the LCAO (linear combination of atomic orbitals) approach. It is used heavily in numerical simulation of molecules. However, more generally, one cannot assume that the basis set of orbitals is orthonormal. In problem A.2.1. we properly consider a non-orthonormal basis.
Band Structures and the Meaning of the Wave Vector k
www.mrl.ucsb.eduNow seeing how karises in a crystal due to a periodic potential, we can use a linear combination of atomic orbitals approach to calculate the energy of the chain with varying kto see how a band develops. The wave function of the chain can be written as (x) = X n c n˜ n(x) (16) where c n= eiknaand ˜ n(x) is the wavefunction of the atomic ...
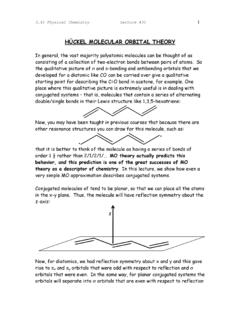
HÜCKEL MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY
ocw.mit.edu1) Define a basis of atomic orbitals. Here, since we are only interested in the πz orbitals, we will be able to write out MOs as linear combinations of the pz orbitals. If we assume there are N carbon atoms, each contributes a pz orbital and we can write the µ th MOs as: N πµ = ∑c i µ p z i i=1 2) Compute the relevant matrix representations.
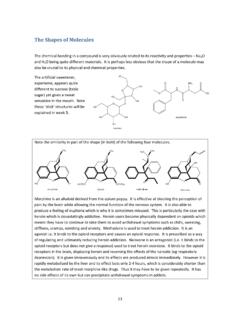
Shapes of Molecules - The University of Sydney - One of ...
www.sydney.edu.auLinear 2 0 Linear BeCl2, CO 2, N 3 ... A multiple bond is made up of a combination of sigma and pi bonds (π-bonds). The electron density ... • Determine the number and type of atomic orbitals used by the atom; include all the electrons in the valence shell. For example, boron, with three valence electrons, uses one s ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM CHEMISTRY
www.msg.chem.iastate.eduexpressed as a linear combination of Slater determinants • Optimization of the orbitals (minimization of the energy with respect to all orbitals), based on the Variational Principle) leads to: 14 ... wavefunction for the given atomic basis • Complete CI generally impossible for any but
Organometallic Chemistry - Ferrocene
alpha.chem.umb.edu1 orbitals are both fully occupied in the electronic configuration of the Cp‐anion whereas the e 2 orbitalsare netanti‐bondingandare unfilled. • For a bis‐cyclopentadienylmetal complex ( 5‐Cp) 2 M , suchas ferrocene, the ‐orbitals of the two Cp ligands are combined pairwise to form the symmetry‐adapted linear combination of
Miessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM Ch 05 CM
www.chem.uci.eduorbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the infinite-fold rotation axis of the orbitals on the basis of the change in wave function sign upon crossing the nodes on the bond axis. 5.10 a. OF– has 14 valence electrons, four in the π 2p* orbitals (see the diagram in the answer to Problem 5.9). b.