Magnitudes Y
Found 10 free book(s)Problemas de Física y Química 2º ESO
chopo.pntic.mec.esCapítulo 2 Magnitudes y su medida. Sistema Internacional de Unidades 2º ESO – pag 4 2. Las magnitudes y su medida. El Sistema Internacional de Unidades. La medida. Magnitudes y unidades 1. ¿Qué diferencia hay entre la información cualitativa y la información cuantitativa relativa a un fenómeno?
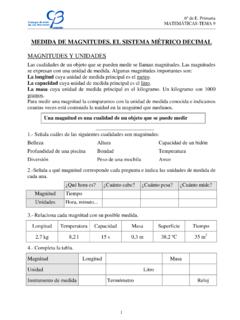
MEDIDA DE MAGNITUDES. EL SISTEMA MÉTRICO DECIMAL
clarionweb.esMAGNITUDES Y UNIDADES Las cualidades de un objeto que se pueden medir se llaman magnitudes. Las magnitudes se expresan con una unidad de medida. Algunas magnitudes importantes son: La longitud cuya unidad de medida principal es el metro.
NORMA OFICIAL MEXICANA NOM-008-SCFI-2002, SISTEMA …
www.economia-noms.gob.mxcandela y mol. Las magnitudes, unidades, símbolos y definiciones se describen en la Tabla 1. 4.2 Unidades SI derivadas Estas unidades se obtienen a partir de las unidades de base, se expresan utilizando los símbolos
A Contribution to the Empirics of Economic Growth
eml.berkeley.eduthe magnitudes of the coefficients on saving and population growth, we can gauge whether there are important biases in the estimates obtained with OLS. As described above, data on factor shares imply that, if the model is correct, the elasticities of Y/L with respect to s and n + g + ...
Lecture 14: Polarization - Harvard University
scholar.harvard.eduIn particular, it implies that their magnitudes are related by E~ 0 =c B~ 0 (3) and that k~·E~ 0 =0, k~ ·B~0 =0, E~0 ·B~0 =0 (4) In other words, the polarization vector of the electric field, the polarization vector of the mag-netic field, and the direction ~k that the plane wave is propagating are all orthogonal.
MAGNITUDES FÍSICAS y UNIDADES de MEDICIÓN 1.- …
univirtual.utp.edu.coMAGNITUDES FÍSICAS y UNIDADES de MEDICIÓN 1.- Definición de magnitud física Desde el punto de vista físico, una magnitud es toda aquella propiedad o entidad abstracta que puede ser medida en una escala y con un instrumento adecuados. En definitiva, magnitud es toda aquella propiedad que se puede medir.
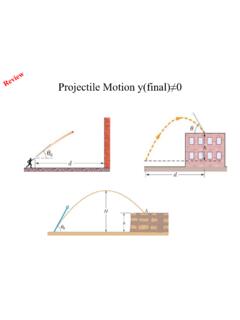
Projectile Motion y(final)Projectile Motion y(final) 0
www.phys.lsu.eduy y =v t g t2 (a) we solve for y = h: which yields h = 51.8 m for y 0 = 0, v 0 = 42.0 m/s, q 0 = 60.0° and t = 5.50 s. − 0 0y − 2 (b) The horizontal motion is steady, so v x = v 0x = v 0 cos θ 0, but the vertical component of velocity varies according the equations before. Thus, the speedi id at impact is v = ()v 0 cosθ 0 2 + v 0 sinθ 0 ...
Edge detection - University of Nevada, Reno
www.cse.unr.eduGx(x, y)isthe derivate of G(x, y)with respect to x: Gx(x, y) = −x 2 G(x, y) Gy(x, y)isthe derivate of G(x, y)with respect to y: Gy(x, y) = −y 2 G(x, y) 2. Compute the gradient magnitude magn(i, j) =√ f x2 +f y 2 3. Apply non-maxima suppression. 4. Apply hysteresis thresholding/edge linking.
Lecture 16 - Correlation and Regression
www2.stat.duke.eduCov(X;Y) = 1 n Xn i=1 (x i X)(y i Y) Covariance is not a measure of uncertainly but rather a measure of the degree to which X and Y tend to be large (or small) at the same time or the degree to which one tends to be large while the other is small. Statistics 102 (Colin Rundel) Lec 16 April 1, …
Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
www.phys.utk.eduPhysics 231 Lecture 1-9 Fall 2008 Example 1 Q2 Q1 g d12 Q2 d23 Q3 A charged ball Q1 is fixed to a horizontal surface as shown. When another massive charged ball Q2 is brought near, it achieves an equilibrium position at a distance d12 directly above Q1. When Q1 is replaced by a different charged ball Q3, Q2 achieves an equilibrium position at a distance d23 (< d12) directly …