Of Charged Particles In Electric And Magnetic
Found 10 free book(s)Chapter 27 – Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces
physics.ucf.edu5. Applications of Motion of Charged Particles Velocity selector Source of charged particles - Particles of a specific speed can be selected from the beam using an arrangement of E and B fields. - Fm (magnetic) for + charge towards right (q v B). - FE (electric) for + charge to left (q E). - Fnet = 0 if Fm = F E-qE + q v B = 0 v = E/B
Chapter 8 Introduction to Magnetic Fields
web.mit.eduSince electric current consists of a collection of charged particles in motion, when placed in a magnetic field, a current-carrying wire will also experience a magnetic force. FB G Consider a long straight wire suspended in the region between the two magnetic poles. The magnetic field points out the page and is represented with dots (•).
Lecture 5 Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field
www.tcm.phy.cam.ac.ukWhat is effect of a static electromagnetic field on a charged particle? Classically, in electric and magnetic field, particles experience a Lorentz force: F = q (E + v × B) q denotes charge (notation: q = −e for electron). Velocity-dependent force qv × B very different from that derived from scalar potential, and programme for ...
Chapter 2 Motion of Charged Particles in Fields
ocw.mit.eduMotion of Charged Particles in Fields Plasmas are complicated because motions of electrons and ions are determined by the electric and magnetic fields but also change the fields by the currents they carry. For now we shall ignore the second part of the problem and assume that Fields are Prescribed.
Problem - University of California, San Diego
courses.physics.ucsd.edu12.A velocity selector uses a 60-mT magnetic field and a 24 kN/C electric field. At what speed will charged particles pass through the selector undeflected? Solution The condition for zero deflection is v= E=B = (24 kN/C)=(0.06 T) = 400 km/s. Problem 13.A region contains an electric field E = 7.4î + 2.8ˆ j kN/C and a magnetic field B = 15ˆ j ...
Class IX Chemistry Chapter 4: Structure of the Atom
jsuniltutorial.weebly.comIn the absence of external magnetic or electric field these rays travel in straight line. Cathode rays are called cathode rays because they are emitted by the negative electrode, or cathode, in a vacuum tube. In 1897, an English physicist Sir J.J. Thomson showed that the rays were made up of a stream of negatively charged particles.
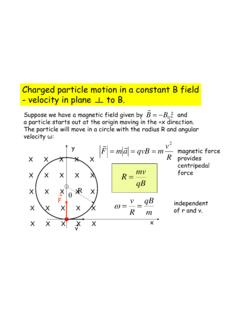
Charged particle motion in a constant B field - velocity ...
www.phys.hawaii.eduElectric/Magnetic Velocity Selector A charged particle enters a region with perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. The electric and magnetic forces will cancel if the velocity is just right. Particles with this velocity will go through undeflected. Others will be deflected. E m F qE F qv B r r r r r = =− =− × sin qE qv B qv B 1 r rr ...
Chapter 3 Basic Plasma Physics - NASA
descanso.jpl.nasa.govElectric propulsion achieves high specific impulse by the acceleration of charged particles to high velocity. The charged particles are produced by ionization of a propellant gas, which creates both ions and electrons and forms what is called a plasma. Plasma is then a collection of the various charged
chap26 - Physics & Astronomy
physics.gsu.edu3/22/2016 4 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. For charged particles, what is the quantity q/m called? A. Linear charge density. B. Charge-to-mass ratio. C. Charged mass ...
Synchrotron Radiation - NASA
asd.gsfc.nasa.govMagnetic field We now split v into components parallel and perpendicular to the uniform magnetic field, v k and v⊥ respectively. The pitch angle θ of the particle’s path is given by tanθ = v⊥/v k, that is, θ is the angle between the vectors v and B. Since v k × B = 0, v k = constant. The acceleration is perpendicular to the magnetic ...