Of Polymers
Found 11 free book(s)Identification of Polymers
www.chymist.comrecycling of these polymers easier, the plastics industry has adopted the codes shown. Since compliance in labeling is voluntary, not all plastics are labeled for identification. Identification, simply by appearance, is difficult, however, there are a few types that are readily identifiable. Clear, colorless
Understanding Rheology of Thermoplastic Polymers
www.tainstruments.compolymers’ flow behavior at temperatures above the glass transition temperature (for an amorphous material) or the melting point (for a semi-crystalline polymer). Melt viscosity is a constant at low shear rates or frequencies. The viscosity in this region is known as the zero shear, or Newtonian, viscosity ho. For low molecular weight polymers
5.33 Lecture Notes: Introduction To Polymer Chemistry
web.mit.eduPolymers are formed by linking monomers through chemical reaction — called polymerization. You don’t end up with a unique molecule. i monomers chain of monomers i A → — (A-A-A )i/3— Homopolymer: all A identical • The most produced/used polymers are homopolymers of terminal alkenes. • Produced by radical polymerization.
Medical Device Polymers - University of Minnesota
saliterman.umn.eduProf. Steven S. Saliterman Medical Device Polymers Polyolefins Polyethylene (PE ) Polypropylene (PP) Cyclic Olefin Copolymers ( COCs) Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC ) Polystyrene/styrenics Polystyrene Poly(acrylonitrile-co-butadiene-co-styrene) (ABS) Polyacrylate (Acrylic, PMMA) Polycarbonate (PC) Polyurethanes Polyformaldehyde (POM) (Delrin or Acetal )
PVP Polymers Brochure - | Brenntag
www.brenntag.comPVP polymers are supplied in various viscosity grades as a powder and/or aqueous solution. The full line of PVP polymers are also available for personal care applications such as film forming, emulsion stabilization and colorant dispersion. Ashland also
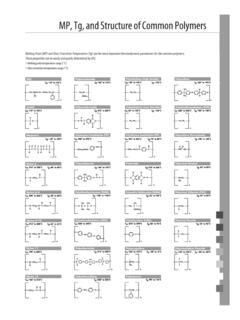
MP, TG, and Structure of Common Polymers
www.perkinelmer.comMP, Tg, and Structure of Common Polymers Melting Point (MP) and Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) are the most important thermodynamic parameters for the common polymers. These properties can be easily and quicky determined by DSC. Melting point temperature range (0 C) Glass transition temperature range (0 C) Polyethylene (High Density) ABS
MASS SPECTROMETRY FOR POLYMERS
www.waters.comPolymers can form a range of structures and possibly contain more than one type of repeat unit. The order and connectivity of a polymer backbone affect the fragmentation pattern that is observed. Figure 5 shows some possible polymer structures. Figure 5 . Examples of polymer structures. Block copolymer Star polymer Comb polymer Brush polymer ...
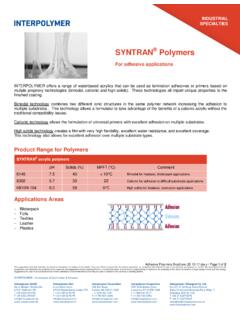
SYNTRAN Polymers - JNS-Smithchem
jns-smithchem.comBimodal Polymers Brochure US 08-17.docx / Page 1 of 2 The suggestions and data included are based on information we believe to be reliable. They are offered in good faith, but without guarantee, as conditions and methods of use of our products are beyond our control.
TECHNICAL WHITEPAPER Low Temperature Properties of …
www.appstate.eduPolymers that have a Tg greater than room temperature are in the glassy state at room temperature and examples of these are plastics such as PS, PMMA and PET. These plastics tend to be brittle and easy to break at room temperature. PVC is in the glassy state at room temperature but is a special case
CHAPTERS 14/15: POLYMER STRUCTURES, APPLICATIONS, & …
www3.nd.eduPOLYMERS • A polymer is a macromolecule (long molecules) built of small covalently bonded units called monomers (“mer” from the Greek word meros meaning part). • These small units are repeated throughout the macromolecule chain. • The macromolecules are bonded together by weak Van der Waals
POLYMERS - Btech College in Tirupati
aits-tpt.edu.in1 POLYMERS Polymers are the high molecular weight compounds obtained by repeated union of simple molecules. (Monomers). Ex: Starch, Polyvinyl chloride, Polyethylene, Nylon 6, 6 and etc. The word ‘ Polymer’ is coined from two Greek words: poly means many and mer means unit or part. The term polymer is defined as very large molecules having high molecular mass.