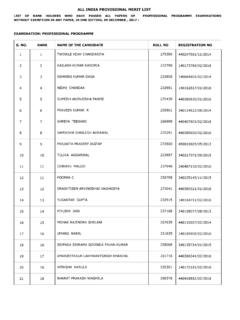
Transcription of ECONOMIC, BUSINESS AND COMMERCIAL LAWS - ICSI
1 ISTUDY MATERIAL EXECUTIVE PROGRAMMEECONOMIC, BUSINESS AND COMMERCIAL LAWSMODULE 2 PAPER 7 ii THE INSTITUTE OF COMPANY SECRETARIES OF INDIATIMING OF HEADQUARTERSM onday to FridayOffice Timings to Dealing TimingsWithout financial transactions to financial transactions to Typesetting by AArushi Graphics, Prashant Vihar, New Delhi, and Printed at HT Media Ltd., Greater Noida/September 2020iiiiiEXECUTIVE PROGRAMMEECONOMIC, BUSINESS AND COMMERCIAL LAWSI ndia redrafted its economic policy to usher in a new era of deregulation, liberalisation and global integration. Since then significant policy initiatives have been introduced, to provide stimulus for accelerated growth, industrial efficiency and international competitiveness. As part of reform process, the Government has also initiated legislative reforms in the area of economic , BUSINESS and COMMERCIAL laws . The Government enacted Foreign Exchange Management Act, The Competition Act, 2002, Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 and amended Benami Transaction Prohibitions Act.
2 Further, the Prevention of Money Laundering Act to deal with new categories of economic offences, has also been enacted. Similarly, in the area of consumer protection and BUSINESS laws , the process of reforms is going the light of above developments, this study material has been prepared to provide an understanding of certain economic , BUSINESS and COMMERCIAL legislations which have direct bearing on the functioning of companies. The study material has been divided into three parts consisting of twenty four study lessons. Part I dealing with Foreign Exchange Management & NBFCs consists of Study Lessons I to XI, whereas Part II dealing with Competition laws consists of Study Lesson XIIand Part III dealing with BUSINESS & COMMERCIAL laws consists of Study Lessons XIII to study material has been published to aid the students in preparing for the economic , BUSINESS and COMMERCIAL laws paper of the CS Executive Programme. It has been prepared to provide basic understanding of some of the economic , BUSINESS and COMMERCIAL laws thereunder, which have a bearing on the conduct of corporate affairs.
3 It is part of the educational kit and takes the students step by step through each phase of preparation stressing key concepts, principle, pointers and procedures. Company Secretaryship being a professional course, the examination standards are set very high, with emphasis on knowledge of concepts, applications, procedures and case laws , for which sole reliance on the contents of this study material may not be enough. Besides, as per the Company Secretaries Regulations, 1982, students are expected to be conversant with the amendments to the laws made upto six months preceding the date of examination. The material may, therefore, be regarded as the basic material and must be read alongwith the original Bare Acts, Rules, Regulations, Case Law, Chartered Secretary Journal published by the Institute every month. The legislative changes made upto June, 2020 have been incorporated in the study materialThe subject of economic , BUSINESS and COMMERCIAL laws is inherently complicated and is subjected to constant refinement through new primary legislations, rules and regulations made thereunder and court decisions on specific legal issues.
4 It, therefore becomes necessary for every student to constantly update himself with the various legislative changes made as well as judicial pronouncements rendered from time to time by referring to the Institute s journal Chartered Secretary and e-bulletin as well as other law/professional the event of any doubt, students may write to the Directorate of Professional Development, Perspective Planning & Studies of the Institute for clarification at care has been taken in publishing this study material yet the possibility of errors, omissions and/or discrepancies cannot be ruled out. This publication is released with an understanding that the Institute shall not be responsible for any errors, omissions and/or discrepancies or any action taken in that there be any discrepancy, error or omission noted in the study material, the Institute shall be obliged if the same is brought to its notice for issue of corrigendum in the PROGRAMMEMODULE 2 PAPER 7 economic , BUSINESS AND COMMERCIAL laws (MAX MARKS 100)ObjectivePart I : To provide expert knowledge in Foreign Exchange Management and II : To provide expert knowledge in Competition III : To provide working knowledge in BUSINESS and COMMERCIAL I: Foreign Exchange Management &NBFCs (40 Marks)Detailed Contents 1.
5 Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934: Central Banking functions; Monetary policy; Penalties. 2. Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999: Introduction 3. Foreign Exchange Transactions & Compliances: Current and Capital Account Transactions; Acquisition &Transfer ofImmovable Property in India and Abroad; Realization and Repatriation of Foreign Exchange; Brief information of other FEMA Regulations. 4. Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010: Introduction and Object, Eligible Contributor, Eligible Receiver, Registration,Offences and Penalties. 5. Foreign Direct Investments Regulations & FDI Policy: Automatic and Approval Route of FDI; Setting up of Subsidiary/Joint Venture/Liaison Office/ Branch Office by Non-residents; Foreign Portfolio Investments. 6. Overseas Direct Investment: ODI Policy, foreign currency remittances, Setting up of Subsidiary/Joint Venture/Branch Office. 7. Liberalized Remittance Scheme: Investment Outside India by Indian Residents.
6 8. External COMMERCIAL Borrowings (ECB): An Overview. 9. Foreign Trade Policy & Procedure: Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS); Service Exports from India Scheme(SEIS); Duty exemption / remission schemes; Export oriented units (EOUS); Electronics Hardware Technology Parks (EHTPS); Software Technology Parks (STPS); Bio-Technology Parks (BTPS).Imports and related policies. 10. Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs): Definition; Types; Requirement of Registration as NBFC and exemptions from registration as NBFC; Micro Finance Institutions, Activities of NBFCs; Compliances by the NBFCs and requirements of approvals of RBI; Deposit Accepting and Non-deposit vAccepting NBFCs; Deemed NBFC; Core Investment Company and Systemically Important Core Investment Companies; Peer to Peer Lending; Defaults, Adjudication, prosecutions and penalties. 11. Special economic Zones Act, 2005: Establishment of Special economic Zones; Approval and Authorization to Operate SEZ; Setting up of Unit; Special economic Zone laws , Case Studies & Practical AspectsPart II: Competition Law (25 Marks) 12.
7 Competition Act, 2002: Competition Policy ; Anti-Competitive Agreements; Abuse of Dominant Position; Overview of Combination and Regulation of Combinations; Competition Advocacy; Competition Commission of India; Appellate laws , Case Studies & Practical AspectsPart III: BUSINESS & COMMERCIAL laws (35 Marks)Consumer Protection 13. Consumer Protection Act, 1986: Consumer Protection in India; Rights of Consumers; Consumer Dispute Redressal Forums; Nature and Scope of Remedies. 14. Essential Commodities Act, 1955: Essential Commodities; Powers of Central Government; Authorities responsible to administer the Act; Delegation of powers; Nature of Order passed under the Act; Seizure and Confiscation of Essential Commodities; Offences by Companies. 15. Legal Metrology Act, 2009: Standard weights and measures; Power of inspection, seizure; Declarations on pre-packaged commodities; Offences and Law 16. Transfer of Property Act, 1882: Types of Properties; Properties which cannot be Transferred; Rule Against Perpetuities; Lis Pendens; Provisions Relating to Sale; Mortgage, Charge, Lease, Gift and Actionable Claim; Specific Performance.
8 17. Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016: Registration of Real Estate Project; Real Estate Agents; Real Estate Regulatory Authority; Central Advisory Council; The Real Estate Appellate Tribunal; Offences, Penalties and Adjudication. Specimen Agreement for Sale between the Promoter and the Allottee; Due Diligence laws 18. Benami Transaction Prohibitions (Act): Benami Property; Benami Transaction, Prohibition of Benami Transaction; Authority, Adjudication of Benami property. 19. Prevention of Money Laundering: Problem and adverse effect of money laundering; Methods of money laundering; Offence of money laundering; Attachment, adjudication and laws 20. Indian Contracts Act, 1872: Essential elements of a Valid contract ; Indemnity and Guarantee; Bailment and Pledge; Law of Agency; E- contract ; Landmark judgments. 21. Specific Relief Act, 1963: Specific reliefs and defense; specific performance and defense; viunenforceable contracts; Rescission of Contracts; Cancellation of Instruments; Declaratory Decrees; Preventive Reliefs.
9 22. Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Essentials of a contract of Sale; Sale Distinguished from Agreement to Sell, Bailment, contract for Work and Labour and Hire-Purchase; Conditions and Warranties; Doctrine of Caveat Emptor; Performance of the contract of Sale; Landmark judgments. 23. Partnership Act, 1932: Rights and Liabilities of Partners; Registration of Firms; Dissolution of Firms and Partnership; Landmark judgments 24. Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881: Negotiable Instruments and Parties; Material Alteration; Crossing and bouncing of Cheques; Dishonour of Cheques & its Remedies; Presumption of Law as to Negotiable Instruments; Landmark laws , Case Studies & Practical AspectsviiLESSON WISE SUMMARYECONOMIC, BUSINESS AND COMMERCIAL laws PART I - FOREIGN EXCHANGE MANAGEMENT & NBFCSL esson 1 - Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 The Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935 in accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The purposes for which the Reserve Bank of India was established as India s central bank have been spelt out in the preamble to the Reserve Bank of India Act, which states as follows: (i) to regulate the issue of banknotes and the keeping of reserves with a view to securing monetary stability in India and generally to operate the currency and credit system of the country to its advantage; and (ii) that it is essential to have a modern monetary policy framework to meet the challenge of an increasingly complex economy ; the primary objective of the monetary policy is to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth and the monetary policy framework in India shall be operated by the Reserve Bank of objective of the lesson is to introduce the students regarding: l Origins of the Reserve Bank of India; l Banking Functions.
10 L Issue bank notes; l Monetary Policy Functions; l Public Debt Functions; l Foreign Exchange Management; l Banking Regulation & Supervision; l Regulation and Supervision of NBFCs; l Regulation & Supervision of Co-operative banks; l Regulation of Derivatives and Money Market Instruments; l Payment and Settlement Functions; l Consumer Protection Functions; l Financial Inclusion and Development Functions;Lesson 2 - Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 IntroductionThe Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) is an Act of the Parliament of India to consolidate and amend the law relating to foreign exchange with the objective of facilitating external trade and payments and for promoting the orderly development and maintenance of foreign exchange market in India. The Act extends to the whole of India and it also applies to all branches, offices and agencies outside India owned or controlled by a person resident in India and also to any contravention thereunder committed outside India by any person to whom this Act is expected that, at the end of this lesson, students will, inter alia, be in a position to: l Understand the Concept of FEMA; l Structure and Overall Schemes of FEMA; l Rules and Regulations framed by RBI under FEMA;Lesson 3 - Foreign Exchange Transactions & CompliancesThe management of foreign exchange is very important in the present day BUSINESS .