Transcription of Formulas for gear calculation - internal gears
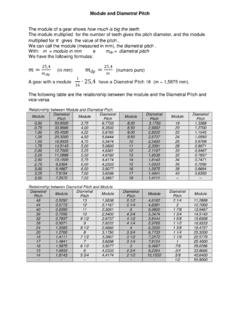
1 Formulas for gears calculation internal gears Contens internal spur gears with normal profile internal spur gears with corrected profile Without center distance variation With center distance variation internal helical gears with normal profile internal helical gears with corrected profile Without center distance variation With center distance variation Length of contact and contact radius Ra Interference Dimension over pins and balls Meaning of symbols a Center distance m Module Pressure angle Q Dimension over pins or balls Helix angle r Radius d Diameter Ra Radius to start of active profile g Length of contact s Tooth thickness on diameter d g1 Legth of recession os Chordal thickness g2 Length of approach t Pitch hf Dedendum w Chordal thickness over z teeth ( spur gears ) hk Addendum W Chordal thickness over z teeth (helical gears )
2 H0 Corrected addendum z Number of teeth hr Whole depth x Profile correction factor l Tooth space Meaning of indices b Reffered to rolling diameter n Reffered to normal section c Referred to roll diameter of basic rack o Reffered to pitch diameter f Reffered to root diameter q Reffered to the diameter throug balls center g Reffered to base diameter r Reffered to balls k Refferred to outside diameter s Reffered to transverse section i Refferred to equivalent w Reffered to tool internal spur gears with normal profile = = + = = 2 = cos = + 2 = cos = = = or = 1 internal spur gears with corrected profile a)- Without center distance variation = = + or = + = 2 2 tan b)- with center distance variation $%& '= $%& + 2 tan ()*(+,)*,+ -'= 13 '= 13 '= 6'7 6 28$%& $%& '9: = 8 2 + 2 9 internal helical gears with normal profile = ; ;=.
3 = cos ; ;= ; cos ; <= ; cos = tan <= tan ; cos = <= < <= < cos < = < = < or = < = + = 2 = + 2 <= > ;= ? internal helical gears with corrected profile a)- Without center distance variation = < < = <+ < or = <+ < < = < 2 2 < tan < ; = ; 2 2 < tan ; b)- With center distance variation $% = $% + 2 tan <()*(+,)*,+ -'= 12?
4 /0 13? '= 13? ';= 6'7 ; 6 28$% $% 9: = <@ cos = 2 + 2 A Contact length calculation B C=D6 C 6 C B =D6 6 E = B C B C+ -' sin ' EC= B C 6'C sin ' E = B + 6' sin ' Contact radius Ra calculation GH =D8B + E9 + 6 In the case of helical gears use transverse section values '; instead of ' . Fig. N 3 Interference Primary interference Minimum internal diameter without interference IJKLMN=DIOK+8 KPQ RST UQ9K Secondary interference (figure N 4) cos V = 5) W) X = $%& V $%& ' cos Y = W++ZH3+* W)+ W+ H3 cos [ = W++*H3+* W)+ W) H3 When the points K1 and K2 on the pinion and gear move to K 1 and K 2 in time t1 and t2 , the respective angles are: for the gear : Y \ ; =]* ^_+ for the pinion: [ + X.]
5 C=`Z a_) To avoid interference, the points K1 and K2 should not coincide at K1 and K2 and should satisfy the condition: C> or `Z a_) > ]* ^_+ The diagram of figure N 5 is used to determine the largest difference z2 z1 , which is a function of the pressure angle and the ratio cW , where not interference exist. When the gears are corrected hk becomes: =cW3+ZcW3) Fig. N 5 Dimension over pins and balls (figure N 6) spur gear with even number of teeth $%& d= $%& 4e 2 ./0 12+f2 2 from which we have d 6d= 6 ./0 1g h = K ij Ii spur gear with odd number of teeth d and 6d are the same as for even teeth, but h = K ij klRmKn Ii Helical gear with even number of teeth $% = $% 4e 2?
6 /0 12>+f2? 2? 6d;= 6 ;./0 12?./0 1g? h = K ijp Ii Helical gear with odd number of teeth d; and 6d; are the same as for even teeth, but h = K ijp klRmKn Ii 6