Transcription of Naming Ionic & Covalent Compounds
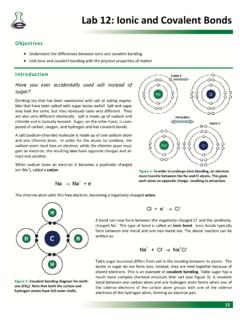
1 Name Lab Day Naming Ionic & Covalent Compounds Introduction: The symbols, formulas, and names of chemical Compounds are important to know for a clear understanding of chemistry. The nomenclature system takes a logical approach to Naming Compounds and writing formulas. Compounds that consist of two nonmetal atoms bonded together are known as Covalent Compounds . Nonmetal elements are located on the right side of the periodic table. An example of a Covalent Compounds is N2O3. To name these Compounds , prefixes are used to indicate the number of each element involved. The name of the second nonmetal element is modified with an ide ending. So N2O3 is named dinitrogen trioxide. Sometimes the prefix mono is dropped from the name of the first nonmetal element and simply understood to be one as in CO, carbon monoxide. Ionic Compounds consist of a metal cation bonded to a nonmetal anion or a polyatomic anion. In order to attain a full octet, metal elements in group IA lose one electron to form a +1 charge.
2 Groups IIA and IIIA metal elements form +2 and +3 ions respectively, for the same reason. Metals that form only one common charge in Ionic Compounds are called type I cations. A few of the transition elements form one common charge also and they include Ag+, Zn+2, and Cd+2. Many metal elements exist with more than one common Ionic charge. Most of these metals elements are the transition elements which are those found in the B groups on the periodic table. These metals are called type II cations. In Naming these ions, the charge must be given as part of the name. For example, Cu+ is named as copper(I) in the IUPAC Naming system or cuprous in the old Latin system. To name copper without the Roman numeral designation or the Latin name is incorrect. Therefore CuCl is named copper(I) chloride or cuprous chloride but not just copper chloride. (Don t mix systems either cuprous(I) chloride is incorrect also). Acids can be identified as having a hydrogen atom shown first in the chemical formula.
3 For example HCl, H2SO4, or HNO3 in water (aqueous) are acids. NH3 is written with the hydrogens to the right because it is a base. Binary acids are made up of two elements. The first of the two elements must be hydrogen and the second is a nonmetal. Examples include HBr(aq), H2S(aq), and HF(aq). Notice that these Compounds are followed by an (aq) designation to represent the aqueous solution in which they ionize. When these Compounds are found in the gaseous state they are not acids and are more correctly named as simple binary 2 Compounds , , from above, hydrogen bromide (HBr(g)), hydrogen sulfide H2S(g)), and hydrogen fluoride (HF(g)). To name binary acids, the prefix hydro is used to indicate hydrogen, followed by the name of the other nonmetal element. An ic suffix is attached to the nonmetal element and the word acid follows. So then HCl(aq) is named hydrochloric acid, H3P(aq) is named hydrophosphoric acid, and HI(aq) is named hydroiodic acid. Oxyacids are acids that have oxygen as part of a polyatomic anion as well as beginning with hydrogen.
4 Polyatomic anions ending in ate use an ic suffix followed by the word acid. H2SO4 contains the sulfate ion, SO4 2, and is named sulfuric acid and H3PO4 contains the phosphate ion, PO4 3, and is named phosphoric acid. Polyatomic anions ending in ite use an ous suffix followed by the word acid. HNO2 contains the nitrite ion, NO2 , and is named nitrous acid and HBrO2 contains the bromite ion, BrO2 , and is named bromous acid. It should also be noted that if a prefix is involved in the name of the polyatomic ion, it is kept when Naming the acid. For example, HBrO4 is perbromic acid since the polyatomic ion perbromate, BrO4 is in it. Procedure: Name the following type I Ionic Compounds (metals with only one common charge hydrogen & ammonium are included in this category): 1. NaCl 2. AgNO3 3. BaCrO4 4. Ca(OH)2 5. ZnCO3 6. Na2SO4 7. Al2O3 8. CdBr2 9. KNO2 10. (NH4)3PO4 11.
5 KClO3 3 12. MgS 13. (NH4)2S 14. K2Cr2O7 15. HCl (g) 16. KBrO3 17. Cd(ClO2)2 18. H2O2 19. KCN 20. BaH2 21. NaHSO3 22. KSCN 23. Ag2CO3 Name the following type II Ionic Compounds (metals with two common charges): 1. Fe(NO3)3 Latin name IUPAC name 2. Cu2C2O4 Latin name IUPAC name 3. NiF2 IUPAC name 4. HgCl2 Latin name IUPAC name 5. CrBr3 Latin name IUPAC name 4 6. Cu2CO3 Latin name IUPAC name 7. FeSO4 Latin name IUPAC name 8. Ni(MnO4)2 IUPAC name 9. Co3(PO4)2 Latin name 10. CrF3 Latin name IUPAC name 11. SnS2 Latin name IUPAC name 12. HgC2O4 Latin name IUPAC name 13. Pb(HCO3)2 Latin name IUPAC name 14. Cu(OH)2 Latin name IUPAC name Name the following Covalent Compounds : 1.
6 CO2 2. N2O 3. PCl5 4. CCl4 5. SO2 5 6. N2O4 7. P2O5 8. OF2 9. NF3 10. CS2 11. NO 12. SO3 Name the following acids: 1. H2SO4(aq) 2. HCl(aq) 3. H3PO4(aq) 4. H2CO3(aq) 5. HIO3(aq) 6. HClO(aq) 7. HNO3(aq) 8. HI(aq) 9. HClO4(aq) 10. HC2H3O2(aq) 11. H2C2O4(aq) 12. H2S(aq)