Transcription of Organic Reactions Summary For Use as a Study Guide ... - CPP
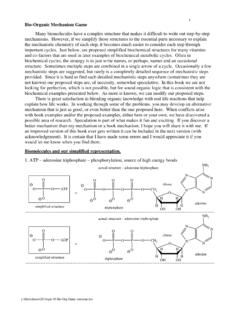
1 Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 1 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with Organic Reactions Summary For Use as a Study Guide Beauchamp Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 2 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with Important acid/base Reactions used in the examples below. Write out every one of these easy mechanisms. OHNathiolates are good nucleophiles,SN2>E2atMe,1oand 2oRX,and strong bases, E2 > hydroxideRH2 CSHthiolsRH2 CSNaKeq=Ka(RSH)Ka(H2O)10-810-16=10+8 Keq= n-BuLiLDA is a very strong base thatis also very sterically hindered,it always acts as a base in = lithium diisopropylamidediisopropylamineLiKeq=Ka (HNR2)Ka(H-C4H9)10-3710-50=10+13 Keq=NHn-butyl lithiumN Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 3 y.
2 \files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with NR2 Naenolates are good nucleophiles, SN2 > E2 at Me, 1o and 2o RX, and strong bases, E2 > SN2 at = lithium diisopropylamideestersNaKeq =Ka(ROCOCH3)Ka(HNR2)10-2510-37=10+12 Keq =ester enolatesOCOCR2 HOCOCR2RR NR2 Naenolates are good nucleophiles, SN2 > E2 at Me, 1o and 2o RX, and strong bases, E2 > SN2 at = lithium diisopropylamidecarboxylic acidsNaKeq =Ka( O2 CCH3)Ka(HNR2)10-2510-37=10+12 Keq =acid dianionOCOCR2 HOCOCHR2H2 NR2 Naenolates are good nucleophiles, SN2 > E2 at Me, 1o and 2o RX, and strong bases, E2 > SN2 at = lithium diisopropylamidenitrilesKeq =Ka( O2 CCH3)Ka(HNR2)10-3010-37=10+7 Keq =nitrile enolateCCR2H2 n-BuLin-butyl lithium removes proton from sulfur salt and makes a good nucleophile at ketones and aldehydes, forming =Ka(HCR2 SPh2)Ka(H-C4H9)10-3310-50=10+17 Keq =n-butyl lithiumsulfur salt = ylidRCSPh2 XHRRCSPh2R n-BuLin-butyl lithium removes proton from dithiane and makes a good nucleophile at all of our electrophiles.
3 It can react once or twice in SN2 Reactions . Sulfur acetal forms carbonyl group after hydrolysis using Hg+2. Makes aldehydes and =Ka(dithiane)Ka(H-C4H9)10-3310-50=10+17 Keq =n-butyl lithiumdithianeSCSHH dithiane carbanionSCSH Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 4 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with Arrow-Pushing schemes for the above Reactions HONacarboxylatesRCOOHRCOON acarboxylic acidsHNaalkoxidessodium hydoxideRH2 COHalcoholsRH2 CONasodium hydrideHOHHH thiolatesRH2 CSHthiolsRH2 CSNaHONaHOHNR2 Nasodium amideterminal alkynesCRCH terminal acetylidesCRCNaLDAlithium diisopropylamidediisopropylamineLiNHn-bu tyl lithiumNCH2H2CH2 CCH3 Liketones / aldehydesNaketone enolatesRCOCH2 HRCOCH2 LDANR2 NaestersNaester enolatesOCOCR2 HOCOCR2 RRLDANR2 Nacarboxylic acidsNaacid dianionOCOCR2 HOCOCHR2H2 enolateCCR2 HNaNCCR2 NbetaineWittig salt = ylidRCPPh3 XHRRCPPh3 Rbetainesulfur salt = ylidRCSPh2 XHRRCSPh2 RLidithianeSCSHH dithiane carbanionSCHSHLDANR2 NaLDANR2 Nan-butyl lithiumCH2H2CH2 CCH3 Lin-butyl lithiumCH2H2CH2 CCH3 Lin-butyl lithiumCH2H2CH2 CCH3 Lisodium hydoxide Organometallics used in our course (Mg.)
4 Li and Cu) RBrLiRBrRBrLiLiRLiorganolithium reagentsbromohydrocarbonsdiscardLi RBrRBrRBrRGrignard reagents(organomagnesium reagents)bromohydrocarbonsMgMgMgMg+2 BrR(MgBr) CuBrRLiRCuRLiRCuRLireacts with RBr (SN2)reacts with acid chloridesreacts with , -unsaturated C=Odialkyl cuprates Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 5 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with SN2 versus E2 choices at 2oRX. At secondary RX (X= OTs, I, Br, Cl) SN2 and E2 products are in close competition with each other. Anions whose conjugate acids have higher pKa s (stronger bases have weaker acids) generally produce more E2 relative to SN2. The examples that we will emphasize at 2oRX centers are carboxlyates (SN2 > E2) vs hydroxide and alkoxides (E2 > SN2), and cyanide (SN2 > E2) vs terminal acetylides (E2 > SN2), azide (SN2 > E2) vs dialkylamides (E2 > SN2) and metal hydrides (SN2 > E2) vs simple hydride (E2 > SN2).
5 Higher basicity and steric hindrance in either RX or the electron pair donor also favors E2 > SN2. The following examples show similar looking base/nucleophiles (used in our course) that react differently with 2oRX structures. (They all react by SN2 at methyl and 1oRX and they all react by E2 at 3oRX.) It is the Reactions at 2o RX centers that are ambiguous. 2o RX structures are the most basic, so SN2 > basic, so E2 > of conjugate acid = 9pKa of conjugate acid = 25pKa of conjugate acid = 5pKa of conjugate acid = 16-19 RCOOOHOR cyanideterminal acetylidescarboxylateshydroxide and alkoxidesMore basic, so E2 > basic, so SN2 > E2. Less basic, so SN2 > basic, so E2 > of conjugate acid = 5pKa of conjugate acid = 37pKa of conjugate acid = ?pKa of conjugate acid = 37azidedialkyl amidessodium borohydridelithium aluminum hydridehydridesMore basic, so E2 > basic, so SN2 > Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 6 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with 1.
6 Making RBr from alkane and alkene hydrocarbons and alcohols a. RBr from alkanes - mechanism using Br2 / h for free radical substitution of alkane sp3 C-H bonds to form sp3 C-Br bonds at the weakest C-H bond. H3CH2 CCH3H3 CCHCH3 BrBrBroverall reactionh BrH1. initiationBrBrh BrBr H = 46 kcal/moleweakest bond ruptures first2b propagationH3 CCCH3 HBrBrH3 CCCH3 HBrBr H = -22 kcal/mole (overall)BE = +46 kcal/moleBE = -68 kcal/mole2a propagationH3 CCCH3 HHBrBrHH3 CCCH3H H = +7 kcal/mole (overall)BE = +95 kcal/moleBE = -88 kcal/mole H = -15both steps3. termination = combination of two free radicals - relatively rare because free radicals are at low concentrationsBrH3 CCCH3HH3 CCCH3 HBrH3 CCCH3 HCH3CH3 CHCHCH3H3 CCHCH3CH3 H = -68 kcal/mole H = -80 kcal/molevery minor product Example Reactions BrBr2 / h CH4Br2 / h BrH3 Cachiralachiral Brenantiomers (R and S)Br2 / h BrachiralBr2 / h can do E2 twice,to make alkynes2 Br2 / h BrBr Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 7 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with Brallylic substitutionBr2 / h b.
7 RBr from alkenes (anti-Markovnikov addition of HBr using free radical chemistry ): mechanism using HBr / ROOR / h for free radical addition to alkane pi bonds (anti-Markovnikov addition = Br adds to less substituted position to form most stable free radical intermediate, and then H adds to more substituted position) H3CH2 CCH2 BrH3 CHCCH2 HBrR2O2 (cat.)h overall reaction1. initiation (two steps)ROORh ROORBrHROROHBr H = 40 kcal/mole H = -23 kcal/moleBE = +88 kcal/moleBE = -111 kcal/mole(cat.)reagent2a propagationH3 CHCCH2 BrH3 CCCH2 BrH H = -5 kcal/moleBE = +63 kcal/mole BE = -68 kcal/mole H = -15both steps(2a + 2b)2b propagationH3 CCCH2 BrHBrHH3CH2 CCH2 BrBr H = -10 kcal/moleBE = +88 kcal/mole BE = -98 kcal/mole3. termination = combination of two free radicals - relatively rare because free radicals are at low concentrationsBrH3 CCCH2 HBrCH2 CCH3 HCH2CH3 CHCHCH3H2 CCHCH2CH3 H = -68 kcal/mole H = -80 kcal/molevery minor productsH3 CCCH2 BrHBrBrBrBrBr Example Reactions H-Br / h ROOR (cat.)
8 Brachiral Br2 / h ROOR (cat.)Brachiral Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 8 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with Br2 / h ROOR (cat.)BrR/Senantiomers BrBr2 / h ROOR (cat.)cis and trans c. RBr from alkenes (anti-Markovnikov addition of HBr using borane chemistry ): mechanism using 1. BH3 2. Br2 / CH3O-- for anti-Markovnikov addition of H-Br to alkane pi bonds (concerted, syn addition of H-BH2 to alkene pi bond, followed by complex with Br2 and migration of R group to Br) H3CH2 CCH2 BrH3 CHCCH2overall reactionstep 1 BHRR1. (BH3)22. Br2, CH3OH2 CCCHH2 CCH2CH2CH3H2 CCCH2 CCH2CH2H3 CHHBRRsyn addition, with H at more substituted position and B at less substituted 2H2 CCCH2 CCH2CH2H3 CHHBRRBrBrH2 CCCH2 CCH2CH2H3 CHBRRBrBrHH2 CCCH2 CCH2CH2H3 CHBRRBrHBrOH3CH2 CCCH2 CCH2CH2H3 CHBRRBrHOCH3H2 CCCH2 CCH2CH2H3 CHBRRBrHOCH3 Example Reactions Brachiral1.
9 (BH3)22. Br2, CH3O Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 9 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with Brachiral1. (BH3)22. Br2, CH3O BrR/Senantiomers1. (BH3)22. Br2, CH3O Br( ) or (dl) enantiomers1. (BH3)22. Br2, CH3O d. RBr from alcohols: i. mechanism using HBr SN2 at methyl and 1o ROH; SN1 at 2o and 3o ROH, with possibility of rearrangements H3CH2 CCH2 OHBrHH3CH2 CCH2 OHHBrH3CH2 CCH2 BrHOHacidbaseSN2 CHCCH3H3 CCH3CH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 OHHBrHacidbaseCHCCH3H3 CCH3 OHHHCCCH3H3 CCH3 Hsp2 = flatHrearrangementBrtopbottomCHCCH3H3 CCH3 BrHCHCCH3H3 CCH3 HBrS (top)R (bottom)BrCH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 BrachiralSN1 Example Reactions OHIHISN2 OHClHClSN2R/SenantiomersOHBrHBrSN1achira lTypical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 10 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with OHHBrBrRSachiralSN1rearrangementOHClSN2 or SN1 HClachiralCHCCH3 HBrH3 CCH3CH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 CHCHCH3 BrH3 CCH3 BrHOHmajorachiralrearrangementminorR/Sen antiomersHBrOHCH3 BrCH3CH3 Brachiral (cis and trans) ii.
10 Mechanism using PBr3 : SN2 at methyl and 1o ROH; SN1 at 2o and 3o ROH, with possibility of rearrangements H3CH2 CCH2 OCHCCH3H3 CCH3CH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 OHHH3CH2 CCH2 OPBr2 HBrH3CH2 CCH2 BrHOPBr2 HCHCCH3H3 CCH3 OHHPBr2 CCCH3H3 CCH3 HHBrCHCCH3H3 CCH3 BrHCHCCH3H3 CCH3 HBrBrCH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 BrachiralBrPBrBrBrPBrBrrearrangementSN2S N1 SRadds to both faces Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 11 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with Example Reactions OHISN2P/I2 = PI3 OHClSN2R/SenantiomersPCl3 OHBrSN1achiralPBr3 OHBrRSachiralSN1rearrangementPBr3 OHClSN2 or SN1achiralPCl3 CHCCH3H3 CCH3CH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 CHCHCH3 BrH3 CCH3 BrHOHmajorachiralrearrangementminorR/Sen antiomersPBr3SN1 OHCH3 BrCH3CH3 Brachiral (cis and trans)PBr3SN1 iii. mechanism using SOBr2 SN2 at methyl and 1o ROH; SN1 at 2o and 3o ROH, with possibility of rearrangements H3CH2 CCH2 OHH3CH2 CCH2 OHSBrBrSBrOOBrBrH3CH2 CCH2 OHSOBrSN2H3CH2 CCH2 BrOHSOBrOHSOBrOSOBrH Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 12 y:\files\classes\ Organic chemistry Tool Chest\ Reactions Lists\Org rxns Summary , SN-E, C=O, epoxides chem, with CHCCH3H3 CCH3CH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 OHHCHCCH3H3 CCH3 OHHSCCCH3H3 CCH3 HHBrCHCCH3H3 CCH3 BrHCHCCH3H3 CCH3 HBrBrCH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 BrachiralrearrangementSRadds to both facesBrSBrOOBrBrCHCCH3H3 CCH3 OHHSOBrOHSOBrOHSOBrOSOBrHSN1 Example Reactions OHClSOCl2SN2 OHClSN2R/SenantiomersSOCl2 OHBrSN1achiralSOBr2 OHBrRSachiralSN1rearrangementSOBr2 OHBrSN2 or SN1achiralSOBr2 CHCCH3H3 CCH3CH2 CCH3H3 CCH3 CHCHCH3 BrH3 CCH3 BrHOHmajorachiralrearrangementminorR/Sen antiomersSN1 SOBr2 Typical First Year Organic Reactions Beauchamp 13 y.