Transcription of Pathophysiology of Respiratory Failure and Use of ...
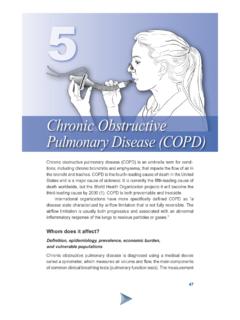
1 Pathophysiology of Respiratory Pathophysiology of Respiratory Failure and Failure and Use of Mechanical Ventilation Use of Mechanical Ventilation Puneet Katyal, MBBS, MSHI Puneet Katyal, MBBS, MSHI Ognjen Gajic Ognjen Gajic, MD , MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USAD efinition Definition n n Chest wall (including Chest wall (including pleura and pleura and diaphragm) diaphragm) n n Airways Airways n n Alveolar Alveolar capillary capillary units units n n Pulmonary circulation Pulmonary circulation n n Nerves Nerves n n CNS or Brain Stem CNS or Brain Stem n n Respiratory Failure is a syndrome of inadequate Respiratory Failure is a syndrome of inadequate gas exchange due to dysfunction of one or more gas exchange due to dysfunction of one or more essential components of the Respiratory system: essential components of the Respiratory system: Respiratory System Respiratory System Lung: Alveolar Unit Brain Spinal cord Nerves Intercostal muscles Chest wall Airway Pleura DiaphragmEpidemiology Epidemiology n n Incidence.
2 About 360,000 cases per year in the Incidence: about 360,000 cases per year in the United States United States n n 36% die during hospitalization 36% die during hospitalization n n Morbidity and mortality rates increase with age Morbidity and mortality rates increase with age and presence of comorbidities and presence of comorbiditiesClassification Classification n n Type I or Hypoxemic (PaO2 <60 at sea level): Type I or Hypoxemic (PaO2 <60 at sea level): Failure of Failure of oxygen exchange oxygen exchange n n Increased shunt fraction (Q Increased shunt fraction (Q S S /Q /Q T T ) ) n n Due to alveolar flooding Due to alveolar flooding n n Hypoxemia refractory to supplemental oxygen Hypoxemia refractory to supplemental oxygen n n Type II or Type II or Hypercapnic Hypercapnic (PaCO2 >45): (PaCO2 >45).
3 Failure to Failure to exchange or remove carbon dioxide exchange or remove carbon dioxide n n Decreased alveolar minute ventilation (V Decreased alveolar minute ventilation (V A A ) ) n n Often accompanied by hypoxemia that corrects with Often accompanied by hypoxemia that corrects with supplemental oxygen supplemental oxygenClassification Classification n n Type III Respiratory Failure : Type III Respiratory Failure : Perioperative Perioperative Respiratory Respiratory Failure Failure n n Increased Increased atelectasis atelectasis due to low functional residual capacity due to low functional residual capacity ( (FRC FRC) in the setting of abnormal abdominal wall mechanics )
4 In the setting of abnormal abdominal wall mechanics n n Often results in type I or type II Respiratory Failure Often results in type I or type II Respiratory Failure n n Can be ameliorated by anesthetic or operative technique, Can be ameliorated by anesthetic or operative technique, posture posture, , incentive incentive spirometry spirometry, post , post- -operative analgesia, attempts to lower operative analgesia, attempts to lower intra intra- -abdominal pressure abdominal pressure n n Type IV Respiratory Failure : S Type IV Respiratory Failure : Shock hock n n Type IV describes patients who are Type IV describes patients who are intubated intubated and ventilated and ventilated in the process of resuscitation for shock in the process of resuscitation for shock n n Goal of ventilation is to stabilize gas exchange and to unload t Goal of ventilation is to stabilize gas exchange and to unload the he Respiratory muscles, lowering their oxygen consumption Respiratory muscles, lowering their oxygen consumptionClassification Classification n n Respiratory Failure may be Respiratory Failure may be n n Acute Acute n n Chronic Chronic n n Acute on chronic Acute on chronic n n.
5 Acute exacerbation of advanced COPD : acute exacerbation of advanced COPDP athophysiology: Pathophysiology : Mechanisms Mechanisms n n Hypoxemic Failure Hypoxemic Failure n n Ventilation/Perfusion (V/Q) mismatch Ventilation/Perfusion (V/Q) mismatch n n Shunt Shunt n n Exacerbated by low mixed venous O2 (SvO2) Exacerbated by low mixed venous O2 (SvO2) n n Hypercapnic Hypercapnic Failure Failure n n Decreased minute ventilation (MV) relative to Decreased minute ventilation (MV) relative to demand demand n n Increased dead space ventilation Increased dead space ventilationPathophysiology: Pathophysiology : Etiologic Categories Etiologic Categories n n Nervous system Nervous system Failure (Type II) Failure (Type II) n n Central Central hypoventilation hypoventilation n n Neuropathies Neuropathies n n Muscle (pump) Muscle (pump) Failure (Type II) Failure (Type II) n n Muscular dystrophies Muscular dystrophies n n Myopathies Myopathies n n Neuromuscular Neuromuscular transmission Failure transmission Failure (Type II) (Type II) n n Myasthenia gravis Myasthenia gravis n n Airway Failure Airway Failure (Type II) (Type II) n n Obstruction Obstruction n n Dysfunction DysfunctionPathophysiology: Pathophysiology .
6 Etiologic Categories Etiologic Categories n n Chest wall and pleural Chest wall and pleural space Failure (Type II) space Failure (Type II) n n Kyphoscoliosis Kyphoscoliosis n n Morbid obesity Morbid obesity n n Pneumothorax Pneumothorax n n Hydrothorax Hydrothorax n n Hemothorax Hemothorax n n Alveolar unit Failure Alveolar unit Failure (Type I) (Type I) n n Collapse Collapse n n Flooding: edema, blood, Flooding: edema, blood, pus, aspiration pus, aspiration n n Fibrosis Fibrosis n nPulmonary vasculature Failure (Type I) Pulmonary vasculature Failure (Type I) n nPulmonary embolism Pulmonary embolism n nPulmonary hypertension Pulmonary hypertensionCauses Causes n n Type I Respiratory Failure Type I Respiratory Failure n n Pneumonia Pneumonia n n Cardiogenic Cardiogenic pulmonary edema pulmonary edema n n Pulmonary edema due to increased hydrostatic pressure Pulmonary edema due to increased hydrostatic pressure n n Non Non- -cardiogenic pulmonary edema cardiogenic pulmonary edema n n Pulmonary edema due to increased permeability Pulmonary edema due to increased permeability n n Acute lung injury (ALI) Acute lung injury (ALI) n n Acute Respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Acute Respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
7 N n Pulmonary embolism (see also type IV Respiratory Failure ) Pulmonary embolism (see also type IV Respiratory Failure ) n n Atelectasis (see also type III Respiratory Failure ) Atelectasis (see also type III Respiratory Failure ) n n Pulmonary fibrosis Pulmonary fibrosisCauses Causes n n Type II Respiratory Failure Type II Respiratory Failure n n Central hypoventilation Central hypoventilation n n Asthma Asthma n n Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) n n Hypoxemia and Hypoxemia and hypercapnia hypercapnia often occur together often occur together *Neuromuscular and chest wall disorders Neuromuscular and chest wall disorders n n Myopathies Myopathies n n Neuropathies Neuropathies n n Kyphoscoliosis Kyphoscoliosis n n Myasthenia gravis Myasthenia gravis n n Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome Obesity Hypoventilation SyndromeCauses Causes n n Type III Respiratory Failure Type III Respiratory Failure n n Inadequate post Inadequate post- -operative analgesia, upper abdominal operative analgesia, upper abdominal incision incision n n Obesity, Obesity.
8 Ascites ascites n n Pre Pre- -operative tobacco smoking operative tobacco smoking n n Excessive airway secretions Excessive airway secretions n n Type IV Respiratory Failure Type IV Respiratory Failure n n Cardiogenic Cardiogenic shock shock n n Septic shock Septic shock n n Hypovolemic Hypovolemic shock shockDiagnosis: History Diagnosis: History n n Sepsis suggested by fever, chills Sepsis suggested by fever, chills n n Pneumonia suggested by cough, sputum production, Pneumonia suggested by cough, sputum production, chest pain chest pain n n Pulmonary embolus suggested by sudden onset of Pulmonary embolus suggested by sudden onset of shortness of breath or chest pain shortness of breath or chest pain n n COPD exacerbation suggested by history of heavy COPD exacerbation suggested by history of heavy smoking, cough, sputum production smoking, cough, sputum production n n Cardiogenic pulmonary edema suggested by chest pain, Cardiogenic pulmonary edema suggested by chest pain.
9 Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and orthopnea paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and orthopneaDiagnosis: History Diagnosis: History n n Noncardiogenic edema suggested by the Noncardiogenic edema suggested by the presence of risk factors including sepsis, presence of risk factors including sepsis, trauma, aspiration, and blood transfusions trauma, aspiration, and blood transfusions n n Accompanying sensory abnormalities or Accompanying sensory abnormalities or symptoms of weakness may suggest symptoms of weakness may suggest neuromuscular Respiratory Failure as would the neuromuscular Respiratory Failure as would the history of an ingestion or administration of history of an ingestion or administration of drugs or toxins.
10 Drugs or toxins. n n Additional exposure history may help diagnose Additional exposure history may help diagnose asthma, aspiration, inhalational injury and some asthma, aspiration, inhalational injury and some interstitial lung diseases interstitial lung diseasesDiagnosis: Physical Findings Diagnosis: Physical Findings n n Hypotension usually with signs of poor perfusion Hypotension usually with signs of poor perfusion suggests severe sepsis or massive pulmonary embolus suggests severe sepsis or massive pulmonary embolus n n Hypertension usually with signs of poor perfusion Hypertension usually with signs of poor perfusion suggests cardiogenic pulmonary edema suggests cardiogenic pulmonary edema n n Wheezing suggests airway obstruction: Wheezing suggests airway obstruction: n n Bronchospasm Bronchospasm n n Fixed upper or lower airway pathology Fixed upper or lower airway pathology n n Secretions Secretions n n Pulmonary edema ( Pulmo)