Chapter 12 Alternating Current Circuits
Found 12 free book(s)Fundamentals of Alternating Current - Engineering
www.site.uottawa.ca12 Fundamentals of Alternating Current In this chapter, we lead you through a study of the mathematics and physics of alternating current (AC) circuits. After completing this chapter you should be able to: Develop a familiarity with sinusoidal functions. Write the general equation for a sinusoidal signal based on its amplitude,
Chapter 12 Alternating-Current Circuits
web.mit.eduAlternating-Current Circuits 12.1 AC Sources In Chapter 10 we learned that changing magnetic flux can induce an emf according to Faraday’s law of induction. In particular, if a coil rotates in the presence of a magnetic field, the induced emf varies sinusoidally with time and leads to an alternating current (AC), and provides a source of AC ...
Chapter 24: Alternating-Current Circuits
www.csun.eduChapter 24: Alternating-Current Circuits 2. The voltage in the European wall socket oscillates between the positive and negative peak voltages, resulting in an rms voltage of 240 V. Multiply the rms voltage by the square root of two to calculate the peak voltage. Calculate the peak voltage: VV max rms 2 2 240 V 340 V 6.
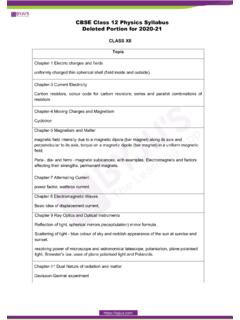
CBSE Class 12 Physics Deleted Syllabus Portion for 2020-21
cdn1.byjus.comChapter-7 Alternating Current power factor, wattless current. Chapter 8 Electromagnetic Waves Basic idea of displacement current, Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Reflection of light, spherical mirrors,(recapitulation) mirror formula , Scattering of light - blue colour of sky and reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset.
Chapter 31 Alternating Current Circuits
www.austincc.eduMFMcGraw-PHY 2426 Chap31-AC Circuits-Revised: 6/24/2012 24 Average Power - Inductors Inductors don’t dissipate energy, they store energy. The voltage and the current are out of phase by 90 o. As we saw with Work, energy changed only when a portion of the force was in the direction of the displacement. In electrical circuits energy is
Alternating Voltage and Current
www.oakton.eduTopics Covered in Chapter 15 15-7: Period 15-8: Wavelength 15-9: Phase Angle 15-10: The Time Factor in Frequency and Phase 15-11: Alternating Current Circuits with Resistance 15-12: Nonsinusoidal AC Waveforms 15-13: Harmonic Frequencies 15-14: The 60-Hz AC Power Line 15-15: Motors and Generators 15-16: Three-Phase AC Power
Chapter 21: RLC Circuits - Department of Physics
www.phys.ufl.eduPHY2054: Chapter 21 2 Voltage and Current in RLC Circuits ÎAC emf source: “driving frequency” f ÎIf circuit contains only R + emf source, current is simple ÎIf L and/or C present, current is notin phase with emf ÎZ, φshown later sin()m iI t I mm Z ε =−=ωφ ε=εω m sin t ω=2πf sin current amplitude() m iI tI mm R R ε ε == =ω
Chapter 21: RLC Circuits
www.phys.ufl.eduPHY2054: Chapter 21 2 Voltage and Current in RLC Circuits ÎAC emf source: “driving frequency” f ÎIf circuit contains only R + emf source, current is simple ÎIf L and/or C present, current is notin phase with emf ÎZ, φshown later sin()m iI t I mm Z ε =−=ωφ ε=εω m sin t …
Chapter Seven ALTERNATING CURRENT
www.ncert.nic.inIn fact, the I or rms current is the equivalent dc current that would produce the same average power loss as the alternating current. Equation (7.7) can also be written as P = V2 / R = I V (since V = I R) Example 7.1 A light bulb is rated at 100W for a 220 V supply. Find (a) the resistance of the bulb; (b) the peak voltage of the source; and
Abstract Algebra Theory and Applications
abstract.ups.eduAug 16, 2013 · theoretical results could be assumed or omitted. A chapter dependency chart appears below. (A broken line indicates a partial dependency.) Chapter 23 Chapter 22 Chapter 21 Chapter 18 Chapter 20 Chapter 19 Chapter 17 Chapter 15 Chapter 13 Chapter 16 Chapter 12 Chapter 14 Chapter 11 Chapter 10 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Chapter 7 Chapters 1{6
Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance
physics.wm.eduChapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance - 21 - To study a constant supply voltage on an RC circuit, we set the left side of equation 3.12 equal to a constant voltage. Then we have a simple homogeneous differential equation with the simple solution for the current of a decaying exponential, I I e /(t RC) 0
Holt Physics Section Reviews
doboshphysics.weebly.comHolt Physics Section Reviews To jump to a location in this book 1. Click a bookmark on the left. To print a part of the book 1. Click the Print button.