Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
Found 9 free book(s)AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews ...
www.bmj.comreviews, which led to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement.3 The reporting guide for systematic reviews of observational (non-randomised) studies is MOOSE (Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology).4 The quality of reporting of a systematic review may, however, more accurately ...
The Systematic Review: An Overview
alliedhealth.ceconnection.comconducted systematic review. Reporting standards similar to those produced for primary research de-signs have been created for systematic reviews. The PRISMA statement, or Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses, pro-vides a checklist for review authors on how to re-port a systematic review.10 Ultimately, the quality
The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for ...
hbg.cochrane.orgThe Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement published in 2009 (hereafter referred to as PRISMA 2009) (4-7) is a reporting guideline designed to address poor reporting of systematic reviews (8). The PRISMA 2009 statement comprised a checklist
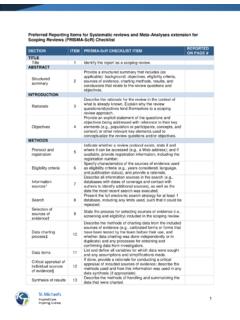
PRISMA 2009 checklist
www.prisma-statement.orgFunding 27 Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (e.g., supply of data); role of funders for the systematic review. From: Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med 6(7): e1000097.
The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for ...
www.bmj.comThe Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement, published in 2009, was designed to help systematic reviewers transparently report why the review was done, what the authors did, and what they found. Over the past decade, advances in systematic review methodology and terminology have
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta ...
prisma-statement.orglished guideline for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies evaluating health care interventions —the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA, www.prisma-statement. org) [12,13]—we have developed PRISMA for Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2014. Table 1 summarizes the difference
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and …
www.prisma-statement.orgJBI = Joanna Briggs Institute; PRISMA-ScR = Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews. * Where sources of evidence (see second footnote) are compiled from, such as bibliographic databases, social media platforms, and Web sites.
Systematic and Non-Systematic Literature Review ...
www.evidera.comMoher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Steward LA, and PRISMA-P Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement.
Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
ajot.submit2aota.orgSystematic reviews should be conducted and published by a team of two or more reviewers. Having only one reviewer is a risk-of-bias indicator for systematic reviews, and best practice methodology requires a multiple-reviewer approach to decrease risk of bias in the review. TITLE Provide a descriptive title for the systematic review.