Search results with tag "Discrete"
Table of Discrete-Time Fourier Transform Pairs
pfister.ee.duke.eduTable of Discrete-Time Fourier Transform Pairs: Discrete-Time Fourier Transform : X() = X1 n=1 x[n]e j n Inverse Discrete-Time Fourier Transform : x[n] = 1 2ˇ Z 2ˇ X()ej td: x[n] X() condition anu[n] 1 1 ae j jaj<1 (n+ 1)anu[n] 1 (1 ae j)2 jaj<1 (n+ r 1)! n!(r 1)! anu[n] 1 (1 ae j)r jaj<1 [n] 1 [n n 0] e j n 0 x[n] = 1 2ˇ X1 k=1 (2ˇk) u[n ...
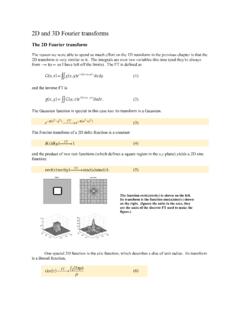
2D and 3D Fourier transforms - Yale University
cryoemprinciples.yale.eduThe discrete Fourier transform The Fourier transform is defined as an integral over all of space. How could we evaluate this on a computer? We will have to take a finite number of discrete samples both in the real (x,y) space and in the (u,v) frequency space. Let’s first do this in one dimension, and we’ll model discrete samples by multiplying
Chapter 3 Data and Signals - Kasetsart University
www.cpe.ku.ac.thto information that is continuous; digital data refers to informationinformation that that hashas discretediscrete statesstates.. AnalogAnalog datadata taketake onon continuous values.. Digital data take on discrete values.. Analog and Digital Data ... Time and Frequency Domain Composite Signals Bandwidth 3.8. Figure 3.2 A sine wave 3.9.
Fundamentals of Dynamical Systems / Discrete-Time …
people.uncw.eduDr. Dylan McNamara people.uncw.edu/ mcnamarad . Fundamentals of Dynamical Systems / Discrete-Time Models
Fourier Transform of continuous and discrete signals
www.complextoreal.comthe Fourier series coefficients (FSC). After we discuss the continuous-time Fourier transform (CTFT), we will then look at the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT). We write the Fourier series coefficients of a continuous-time signal once again as 0 1 n T t n x t dt j T Ce (1.3) Where Z n is the n th harmonic or is equal to n times the ...
Wavelet Transforms in Time Series Analysis
www2.atmos.umd.edu• The Fourier Transform converts a time series into the frequency domain: Continuous Transform of a function f(x): fˆ(ω) = Z∞ −∞ f(x)e−iωxdx where fˆ(ω) represents the strength of the function at frequency ω, where ω is continuous. Discrete Transform of a function f(x): fˆ(k) = Z∞ −∞ f(x)e−ikxdx where kis a discrete ...
1 Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
www.ee.iitb.ac.in1 Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) We have seen some advantages of sampling in the last section. We showed that by choosing the sampling rate wisely, the samples will contain …
Lecture 2: Signals and systems: part I - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.eduSignals and Systems: Part I In this lecture, we consider a number of basic signals that will be important building blocks later in the course. Specifically, we discuss both continuous-time and discrete-time sinusoidal signals as well as real and complex expo-nentials. Sinusoidal signals for both continuous time and discrete time will be-
Chapter 4 - THE DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM
web.mit.eduHST582J/6.555J/16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2005 Chapter 4 - THE DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM c Bertrand Delgutte and Julie Greenberg, 1999
Reading 6a: Expectation, Variance and Standard Deviation ...
ocw.mit.eduDe nition: Let X be a continuous random variable with range [a;b] and probability density function f(x). The expected value of Xis de ned by E(X) = Z b xf(x)dx: a Let’s see how this compares with the formula for a discrete random variable: n E(X) = X x ip(x i): i=1 The discrete formula says to take a weighted sum of the values x iof X, where ...
LECTURE NOTES ON DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
www.mrecacademics.comDISCRETE MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY. Prerequisites: NIL Course Objectives: This course provides the concepts of mathematical logic demonstrate predicate logic and Binary Relations among different variables, discuss different type of functions and ... Algebraic structures - Algebraic systems Examples and general properties ...
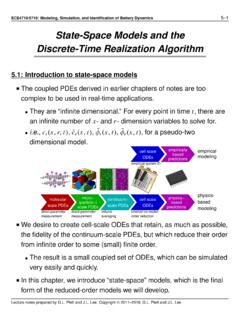
State-Space Models and the Discrete-Time Realization …
mocha-java.uccs.eduDiscrete-Time Realization Algorithm 5.1: Introduction to state-space models The coupled PDEs derived in earlier chapters of notes are too complex to be used in real-time applications. •They are “infinite dimensional.” For every point in time t, there are an infinite number of x- and r- dimension variables to solve for. •i.e., c s(x,r ...
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM SENIOR HIGH …
negorlrmds.weebly.comvariables and probability distributions. The learner is able to apply an appropriate random variable for a given real-life problem (such as in decision making and games of chance). The learner … 1. illustrates a random variable (discrete and continuous). M11 /12 SP-IIIa -1 2. distinguishes between a discrete and a continuous random variable.
9.6 Correlation of Discrete-Time Signals - Rutgers University
eceweb1.rutgers.edu9.6 Correlation of Discrete-Time Signals A signal operation similar to signal convolution, but with completely different physical meaning, is signal correlation.
SECOND EDITION SIMULATION MODELING ANALYSIS
fac.ksu.edu.sa./ 1.3 Discrete-Event Simulation ' , 7 1.3.1 Time-Advance Mechanisms S 1.3.2 Components and 'Organization of a Discrete-Event Simulation Model 10 J 1.4 Simulation of a Single-Server Queueing System 13 1.4.1 Problem Statement 13 1.4.2 Intuitive Explanation . 19 1.4.3 Program Organization and Logic 29 ...
Statistics for Spatio-Temporal Data
download.e-bookshelf.de3.2 Introduction to Deterministic Dynamical Systems, 59 3.2.1 Linear Discrete Dynamical Systems, 60 3.2.2 Nonlinear Discrete Dynamical Systems, 70 3.2.3 Bifurcation, 72 3.2.4 Chaos, 75 3.2.5 State-Space Reconstruction, 79 3.2.6 The Need for Statistical Models for Dynamical Processes, 80 3.3 Time Series Preliminaries, 80 3.4 Basic Time Series ...
2017-10-17 14-13 - Cabarrus County Schools
www.cabarrus.k12.nc.usDiscrete Probability Distributions Worksheet 1. You flip four coins. Let X, the random variable, be all four coins. a. List the sample space for the experiment. b. What are the possible values for x? c. Is the random variable, x, continuous or discrete? d. Construct a probability distribution for this experiment. pc X) e.
EC6303 Signals and Systems Department of ECE 2016-2017 ...
dscet.ac.inSignals are classified as Continuous Time (CT) and Discrete Time(DT) signals. Both CT and DT signals are further classified as Deterministic and Random signals, Even and Odd signals, Energy and Power signals, Periodic and Aperiodic signals 2. With suitable examples distinguish a deterministic signal from a random signal.
Math 55: Discrete Mathematics
math.berkeley.eduicates, quanti ers and logical connectives. Let C(x) denote the predi-cate \x is in the correct place", let E(x) denote the predicate \x is in excellent condition", and let T(x) denote the predicate \x is a tool". and suppose that the domain consists of all tools. a) Something is not in the correct place. 9x :C(x).
Manual for SOA Exam MLC. - Binghamton University
people.math.binghamton.edu2/90 Chapter 6. Benefit premiums. Actuarial problems. (#4, Exam M, Spring 2005) For a fully discrete whole life insurance of 100,000 on (35) you are given:
ECE438 - Laboratory 1: Discrete and Continuous-Time …
engineering.purdue.eduINLAB REPORT: Each student on the team must write by hand the following statement in the lab report, sign and date. “I have read and understood the Laboratory Ethics section (Section 2) of Laboratory 1. I pledge to behave ethically and with honesty in ECE438 this semester. The reports I …
MATH 2P82 MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS (Lecture Notes)
spartan.ac.brocku.caDiscrete Random Variables A random variable yields a number , for every possible outcome of a random experiment. A table (or a formula, called probability function) summarizing the in-formation about 1. possible outcomes of the RV (numbers, arranged from the smallest to the largest) 2. the corresponding probabilities
ECE 314 { Signals and Systems Fall 2012
ece-research.unm.eduProblem 1.4 Determine the fundamental frequency of the discrete-time square wave shown in Fig. 1.16. Solution: As the graph shows, x[n] = x[n+8] = x[n+16] =:::; 8n 2 Z: Therefore, the fundamental period is No = 8, and, consequently,!o = 2ˇ=No = ˇ=4 rad/sample. Problem 1.5 a) First note that x(t) = cos2(2ˇt) = 0:5 (1 + cos(4ˇt)). Hence, if x is
ECE 301: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #2
web.ics.purdue.eduAly El Gamal ECE 301: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #2 Problem 4 Problem 4 One of the important properties of convolution, in both continuous and discrete time, is the associativity property. In this problem, we will check and illustrate this property. (a)Prove the equality 2 2 2 2 and 2
Correlation and Convolution - UMD
www.cs.umd.educorrelation and convolution do not change much with the dimension of the image, so understanding things in 1D will help a lot. Also, later we will find that in some cases it is enlightening to think of an image as a continuous function, but we will begin by considering an image as discrete , meaning as composed of a collection of pixels. Notation
Circular Convolution - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.edu6.341: Discrete-Time Signal Processing OpenCourseWare 2006 Lecture 16 Linear Filtering with the DFT Reading: Sections 8.6 and 8.7 in Oppenheim, Schafer & Buck (OSB). Circular Convolution x[n] and h[n] are two finite sequences of length N with DFTs denoted by X[k] and H[k], respectively. Let us form the product W [k] = X[k]H[k],
Convolution - Rutgers University
eceweb1.rutgers.eduthat is, it is applicable to both continuous-and discrete-timelinear systems. In this chapter, we study the convolution concept in the time domain. The slides contain the copyrighted material from Linear Dynamic Systems and Signals, Prentice Hall, …
2-D Fourier Transforms - New York University
eeweb.engineering.nyu.edu• Li C l tiLinear Convolution – 1D, Continuous vs. discrete signals (review) – 2D • Filter Design • Computer Implementation Yao Wang, NYU-Poly EL5123: Fourier Transform 2. What is a transform? • Transforms are decompositions of a function f(x)
EMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN
www.bharathuniv.ac.inDiscrete Cosine Transformations (DCT) and inverse DCT (IDCT) functions fast. The latter are a must for fast execution of the algorithms for signal analyzing, coding, filtering, noise cancellation, echo-elimination, compressing and decompressing, etc. Figure 2.6 shows the block diagram for a digital signal processor
What is Discrete Mathematics? - Washington University in ...
research.engineering.wustl.eduTheory, Abstract Algebra, Combinatorics, Graph Theory, Game Theory, Network Optimization, … •The concepts learned will also be helpful in continuous areas
Chapter 2: Probability - Auckland
www.stat.auckland.ac.nz• conditional probability, and what you can and can’t do with conditional expressions; ... • calculating probabilities for continuous and discrete random variables. 2.1 Sample spaces and events Definition: A sample space, Ω, is a set of possible outcomes of a random experiment. Definition: An event, A, is a subset of the sample space.
Date JST [Tutorial] Joe Suzuki (Osaka University, Japan ...
iasc-ars2022.orgDivided Differences, Falling Factorials, and Discrete Splines: Another Look at Trend Filtering and Related Problems Chair: Wataru Sakamoto (Okayama University, Japan) [Tutorial] Joe Suzuki (Osaka University, Japan) Solve 100 Problems of Math and R/Python for Statistical Learning Chair: Koji Yamamoto (Yokohama City University, Japan)
Lecture Notes on Discrete Mathematics - IIT Kanpur
home.iitk.ac.in3.De ning a set of rules which generate its members (recursive notation), e.g., let X= fx: xis an even integer greater than 3g: Then, Xcan also be speci ed by (a)4 2X, (b)whenever x2X, then x+ 2 2X, and (c)every element of Xsatis es the above two rules.
Discrete Mathematics for Computer Science
people.cs.pitt.eduDiscrete mathematics • Discrete mathematics – study of mathematical structures and objects that are fundamentally discrete rather than continuous. • Examples of objectswith discrete values are – integers, graphs, or statements in logic. • Discrete mathematics and computer science. – Concepts from discrete mathematics are useful for
Discrete uniform distribution (from X - William & Mary
www.math.wm.eduThe shorthand X ∼ discrete uniform(a,b)is used to indicate that the random variable X has the discrete uniform distribution with integer parameters a and b, where a <b. A discrete uniform random variable X with parameters a and b has probability mass function f(x)= 1 b−a+1
Discrete Fourier Transform
sigproc.mit.eduDiscrete Fourier Transform: discrete frequencies for aperiodic signals. Discrete Fourier Transform De nition and comparison to other Fourier representations. analysis synthesis DFT: X[k] = 1 N NX−1 n=0
Discrete Structures for Computer Science: Counting ...
cglab.cacourse COMP 2804 (Discrete Structures II). Students are assumed to have taken COMP 1805 (Discrete Structures I), which covers mathematical rea-soning, basic proof techniques, sets, functions, relations, basic graph theory, asymptotic notation, and countability. During a 12-week term with three hours of classes per week, I cover most
Discrete-Time FourierTransform - Pearson
www.pearsonhighered.comto discrete-time signals x[n] obtained by sampling x(t). In the discrete-time case, the line spectrum is plotted as a function of normalized frequency ωˆ. In Chapter 6, we developed the frequency response H(ejωˆ)which is the frequency-domain representation of an FIR filter. Since an FIR filter can also be characterized in the time domain ...
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
home.engineering.iastate.eduDiscrete Fourier Transform (DFT) Recall the DTFT: X(ω) = X∞ n=−∞ x(n)e−jωn. DTFT is not suitable for DSP applications because •In DSP, we are able to compute the spectrum only at specific discrete values of ω, •Any signal in any DSP application can be measured only in a finite number of points. A finite signal measured at N ...
Discrete-Time Signal Processing - Second Edition
entsphere.comDiscrete-Time Signal Processing - Second Edition Author: Alan V. Oppenheim Keywords: 1998 Prentice Hall ISBN: 0-13-754920-2 Created Date: 10/28/2005 5:12:18 AM ...
Discrete Fourier Series & Discrete Fourier Transform
www.ee.cityu.edu.hkThe DFS is derived from the Fourier series as follows. Let be a periodic sequence with fundamental period where is a positive integer. Analogous to (2.2), we have: (7.1) for any integer value of . H. C. So Page 3 Semester B 2011-2012 ... Given two periodic sequences and with period : and Compute .
Similar queries
Discrete-Time Fourier Transform, Discrete, Continuous, Time, Fundamentals of Dynamical Systems / Discrete-Time, Fundamentals of Dynamical Systems / Discrete-Time Models, Fourier, Fourier series, Time Fourier, Time series, Signals and Systems, MIT OpenCourseWare, Signals, Discrete time, Expectation, Variance and Standard Deviation, A continuous, Course, Structures, Discrete-Time, Variables, 9.6 Correlation of Discrete-Time Signals, Simulation, Event Simulation, Dynamical Systems, Discrete Dynamical Systems, Dynamical, Cabarrus County Schools, Discrete Probability, Probability, Math 55: Discrete Mathematics, Predi-cate, Predicate, Fully discrete, ECE438 - Laboratory 1: Discrete and Continuous-Time, Report, Write, Laboratory, MATH, Convolution, Circular Convolution, Systems, Chapter, Discrete Cosine, What is Discrete Mathematics, Theory, Combinatorics, Graph Theory, Lecture Notes on Discrete Mathematics, Rules, Discrete uniform distribution from, Random, Discrete uniform distribution, Discrete Structures, Discrete-time signals, Discrete Fourier, Discrete Fourier Series & Discrete Fourier Transform, Series, Sequences




























![Date JST [Tutorial] Joe Suzuki (Osaka University, Japan ...](/cache/preview/6/b/9/b/f/1/4/7/thumb-6b9bf14717ece6b6327c843c03842851.jpg)








