Transcription of Basic Network Design - Cisco
1 CHAPTER 3-1 Ethernet-to-the-Factory Design and Implementation GuideOL-14268-013 Basic Network DesignOverviewThe main function of the manufacturing zone is to isolate critical services and applications that are important for the proper functioning of the production floor control systems from the enterprise Network (or zone). This separation is usually achieved by a demilitarized zone (DMZ). The focus of this chapter is only on the manufacturing zone. This chapter provides some guidelines and best practices for IP addressing, and the selection of routing protocols based on the manufacturing zone topology and server farm access layer Design .
2 When designing the manufacturing zone Network , Cisco recommends that future growth within the manufacturing zone should be taken into consideration for IP address allocation, dynamic routing , and building server chapter has the following starting assumptions: Systems engineers and Network engineers have IP addressing, subnetting, and Basic routing knowledge. Systems engineers and Network engineers have a Basic understanding of how Cisco routers and switches work. IP AddressingAn IP address is 32 bits in length and is divided into two parts.
3 The first part covers the Network portion of the address and the second part covers the host portion of the address. The host portion can be further partitioned (optionally) into a subnet and host address. A subnet address allows a Network address to be divided into smaller IP AddressingIn the manufacturing zone, the level 3 workstations and servers are static. Additionally, it is recommended to statically configure level 2 and level 1 control devices. These servers send detailed scheduling, execution, and control data to controllers in the manufacturing zone, and collect data from the controllers for historical data and audit purposes.
4 Cisco recommends manually assigning IP addresses to all the devices including servers and Cisco networking equipment in the manufacturing 3-2 Ethernet-to-the-Factory Design and Implementation GuideOL-14268-01 Chapter 3 Basic Network Design IP Addressingzone. For more information on IP addressing, see IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users at the following URL: In addition, Cisco recommends referencing devices by their IP address as opposed to their DNS name, to avoid potential latency delays if the DNS server goes down or has performance issues.
5 DNS resolution delays are unacceptable at the control Dynamic Host Configuration protocol and DHCP Option 82 Dynamic Host Configuration protocol (DHCP) is used in LAN environments to dynamically assign host IP addresses from a centralized server, which reduces the overhead of administrating IP addresses. DHCP also helps conserve limited IP address space because IP addresses no longer need to be permanently assigned to client devices; only those client devices that are connected to the Network require IP addresses. The DHCP relay agent information feature (option 82) enables the DHCP relay agent (Catalyst switch) to include information about itself and the attached client when forwarding DHCP requests from a DHCP client to a DHCP server.
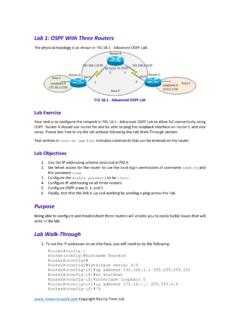
6 This basically extends the standard DHCP process by tagging the request with the information regarding the location of the requestor. (See Figure 3-1.)Figure 3-1 DHCP Option 82 Operation The following are key elements required to support the DHCP option 82 feature: Clients supporting DHCP Relay agents supporting option 82 DHCP server supporting option 82 The relay agent information option is inserted by the DHCP relay agent when forwarding the client-initiated DHCP request packets to a DHCP server. The servers recognizing the relay agent information option may use the information to assign IP addresses and to implement policies such as restricting the number of IP addresses that can be assigned to a single circuit ID.
7 The circuit ID in relay agent option 82 contains information identifying the port location on which the request is details on DHCP features, see the following URL: #wp1070843 DHCP ClientDHCP ClientDHCP ServerClients generates aDHCP request Relay agent fills in Option 82 (Remote ID and Circuit ID) along with gateway IP address and unicast to DHCP server DHCP server Option 82 capable, use the appended information Based on appendedinformation, returns with proper IP address and policiesRemoves Option 82, implement policy and IP address assignment 12354221076 3-3 Ethernet-to-the-Factory Design and Implementation GuideOL-14268-01 Chapter 3 Basic Network Design IP Addressing General Best PracticesNoteThe DHCP option 82 feature is supported only when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and on the VLANs to which subscriber devices using this feature are and the DHCP option 82 feature have not been validated in the lab for EttF version At this time.
8 Cisco recommends considering only DHCP with option 82 for the application servers at level Addressing General Best Practices IP Address ManagementIP address management is the process of allocating, recycling, and documenting IP addresses and subnets in a Network . IP addressing standards define subnet size, subnet assignment, Network device assignments, and dynamic address assignments within a subnet range. Recommended IP address management standards reduce the opportunity for overlapping or duplicate subnets, non-summarization in the Network , duplicate IP address device assignments, wasted IP address space, and unnecessary Space PlanningWhen planning address space, administrators must be able to forecast the IP address capacity requirements and future growth in every accessible subnet on the Network .
9 This is based on many factors such as number of end devices, number of users working on the floor, number of IP addresses required for each application or each end device, and so on. Even with plentiful availability of private address space, the cost associated with supporting and managing the IP addresses can be huge. With these constraints, it is highly recommended that administrators plan and accurately allocate the addressing space with future growth into consideration. Because the control traffic is primarily confined to the cell/area zone itself, and never crosses the Internet, Cisco recommends using a private, non-Internet routable address scheme such as , where x is a particular site, y is a function, and z is the host address.
10 These are guidelines that can be adjusted to meet the specific needs of a manufacturing operation. For more information on private IP addresses, see RFC 1918 at the following URL: AddressingHierarchical addressing leads to efficient allocation of IP addresses. An optimized address plan is a result of good hierarchical addressing. A hierarchical address plan allows you to take advantage of all possible addresses because you can easily group them contiguously. With random address assignment, there is a high possibility of wasting groups of addresses because of addressing benefit of hierarchical addressing is a reduced number of routing table entries.