Transcription of LESSON PLAN: Place Value - Mindset Learn
1 LESSON PLAN: Place Value Dear Teacher I hope that the following LESSON description will help to improve your teaching strategy in your classroom. It was particularly designed with you the teacher in mind. The methods used are fun, easy and cost effective. I hope you will find it useful and apply the methodology with a positive and enthusiastic approach. Before we can begin any LESSON we must understand the following: What is Mathematics? Mathematics is a language that makes use of symbols and notations for describing numerical, geometric and graphical relationships. It is a human activity that involves observing, representing and investigating patterns and qualitative relationships in physical and social phenomena and between mathematical objects themselves. It helps to develop mental processes that enhance logical and critical thinking, accuracy and problem-solving that will contribute to decision-making. ( quoted from the CAPS document) Every Mathematics LESSON should be hour 24 minutes per day for Grades 1 to 3.
2 Specific Skills To develop essential mathematical skills the learner should: develop the correct use of the language of Mathematics; develop number vocabulary , number concept and calculation and application skills; Learn to listen, communicate, think, reason logically and apply the mathematical knowledge gained; Learn to investigate, analyse, represent and interpret information (quoted from the CAPS document) Subject Mathematics Content Area Numbers, operations and relationships Topic Place Value Concept Number Concept Development Educator Rose Siasa School Walter Sisulu Primary Grade 3 Weighting of Content Areas in Foundation Phase Weighting of Content Area Time Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Time per week Numbers, Operations and Relationships 65% 60% 58% 120 minutes Patterns, Functions and Algebra 10% 10% 10% 80 minutes Space and Shape (Geometry) 11% 13% 13% 80 minutes Measurement 9% 12% 14% 80 minutes Data Handling (Statistics) 5% 5% 5% 60 minutes Note: This LESSON plan is only part of an entire daily Mathematics LESSON .
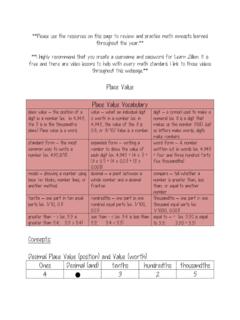
3 You should include as part of this LESSON plan: Counting Mental Mathematics Consolidation of concepts Problem Solving Group work Independent Activities Content Area Topic Concept and skills for the year Grade 1 Concept and skills for the year Grade 2 Concept and skills for the year Grade 3 Numbers, Operations and Relationships Place Value Begin to recognise the Place Value of at least two-digit numbers to 20 Decompose two-digit numbers into multiples of 10 and ones/units Recognise the Place Value of at least two-digit numbers to 99 Decompose two-digit numbers up to 99 into multiples of 10 and ones/units Identify and state the Value of each digit Recognise the Place Value of three digit numbers to 999 Decompose three-digit numbers up to 999 into multiples of 100, multiples of 10 and ones/units Identify and state the Value of each digit Apparatus 1. Flard Cards 2. DBE workbooks Definition Place Value : The Value of a number Flash card: Cards used to work with Place Value .
4 Teaching Method Introduce the vocabulary Hundreds, Tens and Units Begin with showing a number and asking learners what the number is. The learner reads out the number. Ask the learner how many digits the number has. In this case the number is 221 and it has 3 digits. Teach the learners to read the Hundreds, tens and units from left to right. Let them see how this is done by standing in front of the class with your back to the class. Show them from side to side. A clear understanding of the position of the hundred, the tens and the units is needed. Hand out envelopes with all the Place Value cards in them. Each learner should have her own set of these flard cards. 1. 10 100 2. 20 200 3. 30 300 4. 40 400 5. 50 500 6. 60 600 7. 70 700 8. 80 800 9. 90 900 Ask the learners to pick up one card. Ask them if it's a unit , ten or a hundred. Ask the learners to pick up a unit. Allow them to say what the unit is.
5 Ask the learners to pick up a ten. Allow them to tell you the Value of the ten. Ask the learners to pick up the hundred. Allow them to tell you what the Value of the hundred is. Write a number on the board and break it down. 298 = 200 + 90 + 8 546 = 500 + 40 +6 Allow the learners to build up and break down the numbers they have on their desks. For fun do a Place Value calculation 400 + 30 + 6 300 + 50 + 3 700 + 80 + 9 Application: Do the activity in the DBE book. References.