Search results with tag "Euclidean"
500 - OCLC
www.oclc.org.9 Non-Euclidean geometries Including Bolyai, elliptic, Gauss, hyperbolic, inversive, Lobachevski geometries; imbeddings of non-Euclidean spaces in other geometries Class a specific type of non-Euclidean geometry with the type, e.g., non-Euclidean analytic geometries 516.3 [517] [Unassigned] Most recently used in Edition 9 518 Numerical analysis
The Euclidean Algorithm - Rochester Institute of Technology
www.rit.eduWhy does the Euclidean Algorithm work? The example used to find the gcd(1424, 3084) will be used to provide an idea as to why the Euclidean Algorithm works. Let d represent the greatest common divisor. Since this number represents the largest divisor that evenly divides both numbers, it is obvious that d 1424 and d 3084. Hence d 3084 –1424
Projective Geometry: A Short Introduction
morpheo.inrialpes.frence, one can infer theorems. The Euclidean geometry is based on mea-sures taken on rigid shapes, e.g. lengths and angles, hence the notion of shape invariance (under rigid motion) and also that (Euclidean) geometric properties are invariant under rigid motions. 15th century: the Euclidean geometry is not su cient to model perspec-tive ...
LECTURES IN BASIC COMPUTATIONAL NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
web.engr.uky.eduIn the case of Euclidean spaces, we can define another useful object related to the Euclidean norm, the inner product (often called the “dot product” when applied to finite-dimensional vectors). Definition 1.3 Let S be a N-dimensional Euclidean space with v,w ∈ S. Then hv,wi ≡ XN i=1 viwi (1.4) is called the inner product.
Chapter 4 Measures of distance between samples: Euclidean
www.econ.upf.edutwo- or three-dimensional space to multidimensional space, is called the Euclidean distance (but often referred to as the ‘Pythagorean distance’ as well). Standardized Euclidean distance Let us consider measuring the distances between our 30 samples in Exhibit 1.1, using just the three continuous variables pollution, depth and temperature.
The Euclidean Algorithm and Multiplicative Inverses
www.math.utah.eduThe Euclidean Algorithm is a set of instructions for finding the greatest common divisor of any two positive integers. Its original importance was probably as a tool in construction and measurement; the algebraic problem of finding gcd(a,b) is equivalent to the following
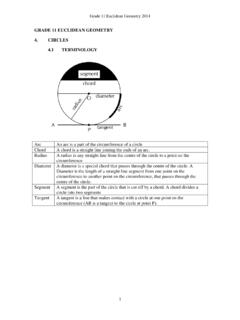
GRADE 11 EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY 4. CIRCLES 4.1 …
holycrosshigh.co.za1 GRADE 11 EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY 4. CIRCLES 4.1 TERMINOLOGY Arc An arc is a part of the circumference of a circle Chord A chord is a straight line joining the ends of an arc. Radius A radius is any straight line from the centre of the circle to a point on the circumference ...
Introduction to Vectors and Tensors Volume 1
oaktrust.library.tamu.eduVolume II begins with a discussion of Euclidean Manifolds which leads to a development of the analytical and geometrical aspects of vector and tensor fields. We have not included a discussion of general differentiable manifolds. However, we have included a chapter on vector and tensor fields defined on Hypersurfaces in a Euclidean Manifold.
A Guide to Euclidean Geometry - Mindset Learn
learn.mindset.africaAsk learners to watch a particular video lesson for homework (in the school library or on the website, depending on how the material is available) as preparation for the next days lesson; if desired, learners can be given specific questions to answer in preparation for the next day’s lesson The Basics of Euclidean Geometry 1.
Chapter 1 Euclidean space - Rice University
www.owlnet.rice.eduEuclidean space 5 PROBLEM 1{4. In the triangle depicted above let L1 be the line determined by x and the midpoint 1 2 (y + z), and L2 the line determined by y and the midpoint 12 (x + z).Show that the intersection L1 \L2 of these lines is the centroid. (This proves the theorem which states that the medians of a triangle are concurrent.) PROBLEM 1{5.
Multivariable Calculus Lectures - Mathematics
math.jhu.eduAs an introduction to the course, I thought to play with the structure of Euclidean space and linear algebra just to establish notation and begin the conversation. I also used a bit of Mathematica for visualization. Helpful Documents. Mathematica: IntersectingPlanes. 1.1. Real Euclidean Space Rn. Figure 1. The plane R2. 1.1.1. The plane. The ...
The Foundations of Geometry - University of California ...
math.berkeley.edument of the euclidean geometry is clearly shown; for example, it is shown that the whole of the euclidean geometry may be developed without the use of the axiom of continuity; the signifi-cance of Desargues’s theorem, as a condition that a given plane geometry may be regarded as a part of a geometry of space, is made apparent, etc. 5.
Gr 10 Maths – Euclidean Geometry GR 10 MATHS - The …
theanswer.co.zaGr 10 Maths – Euclidean Geometry: Exercise_Questions Copyright © The Answer 3 Converse Facts e.g. 1 The original statement (see FACT 1) is: If ABC is a straight ...
MATHEMATICS WORKSHOP EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY
allcopypublishers.co.za1 tangent s e c a n t d i a m e t e r c h or d arc r a d i u s sector.. seg ment CHAPTER 8 EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY BASIC CIRCLE TERMINOLOGY THEOREMS INVOLVING THE CENTRE OF A CIRCLE THEOREM 1 A The line drawn from the centre of a circle perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord.
Coordinate Geometry - University of Wisconsin–Madison
people.math.wisc.eduC0 = (0;1) (see Theorem 3.13) and in Euclidean geometry every triangle is congruent to the triangle whose vertices are of form A = ( a; 0), B = ( b; 0), C = (0 ;c ) (see Corollary 4.14).
Higher Geometry - University of Colorado Denver
www-math.ucdenver.eduIntroduction Brief Historical Sketch Greeks (Thales, Euclid, Archimedes) Parallel Postulate Non-Euclidean Geometries Projective Geometry Revolution
NON-EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY - University of Washington
sites.math.washington.eduThe first four postulates, or axioms, were very simply stated, but the Fifth Postulate was quite different from the others. Postulates I-IV I. A straight line segment can be drawn ... into subtleties of basic geometry. Here are some theorems, that if proved, imply V: The distance between two parallel lines is finite. (Proclus, 410-485)
MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: REAL ANALYSIS - t n
trb.tn.nic.inMATHEMATICS UNIT 1: REAL ANALYSIS Ordered sets – Fields – Real field – The extended real number system – The complex field- Euclidean space - Finite, Countable and uncountable sets - …
PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONSINS EUCLIDEAN
www.isinj.com1.2. If the sum of two adjacent angles is two right angles, their non-coincident arms are in the same straight line. 1.3. If two straight lines intersect, the vertically opposite angles are equal. 1.4. If a straight line cuts two other straight lines so as to make the alternate angles equal, the two straight lines are parallel. 1.5.
IBM SPSS Statistics 19 Statistical Procedures Companion
www.norusis.com380 Chapter 17 Proximity Matrix To get the squared Euclidean distance between each pair of judges, you square the differences in the four scores that they assign ed to each of the four top-rated pairs.
Problems and Solutions in Matrix Calculus
issc.uj.ac.zaMatrix Calculus by Willi-Hans Steeb ... Rn n-dimensional Euclidean space space of column vectors with nreal components ... of M have Hamming distance n=2. The Hamming distance between two vectors is the number of entries at which they di …
An Invitation to 3-D Vision - University of Delaware
www.eecis.udel.eduThe theory culminates in Chapter 10 with a uni ed theorem on a rank condition for arbitrarily mixed point, line and plane features. It captures all possible constraints among multiple images of these geometric ... 2.1 Three-dimensional Euclidean space . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Algorithms for Non-negative Matrix Factorization
proceedings.neurips.ccusing some measure of distance between two non-negative matrices A and B . One useful measure is simply the square of the Euclidean distance between A and B [13], IIA -BI12 = L(Aij - Bij)2 ij This is lower bounded by zero, and clearly vanishes if and only if A = B . Another useful measure is D(AIIB) = 2: ( Aij log k· B:~ - Aij + Bij ) "J (2) (3)
Introduction to Kernel Methods - University of Pittsburgh
people.cs.pitt.eduHilbert Spaces Vector Space A set V endowed with the addition operation and the scalar multiplication operation such that these operations satisfy certain rules It is trivial to verify that the Euclidean space is a real vector space Inner Product (on a real vector space) A real function such that for all x, y, z in V and all c in we have
INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL TOPOLOGY
people.math.ethz.chthree chapters of this book di er from [14]. The rst is that our exposition uses the intrinsic notion of a smooth manifold. The basic de nitions are included in Section 1.1 and the proofs of some foundational theorems such as the existence of partitions of unity and of embeddings in Euclidean space are relegated to the appendix.
Introduction to Differential Geometry
www.math.toronto.eduChapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Some history In the words of S.S. Chern, ”the fundamental objects of study in differential geome- ... 1.Embeddings of simple manifolds in Euclidean space can look quite complicated. The following one-dimensional manifold8 is intrinsically, ‘as a manifold’, just a closed curve, that is, a circle. The problem
17. Inner product spaces - MIT Mathematics
math.mit.eduEuclidean distance. De nition 17.3. Let V be a real vector space. A norm on V is a function k:k: V ! R; what has the following properties kkvk= jkjkvk; for all vectors vand scalars k. positive that is kvk 0: non-degenerate that is if kvk= 0 then v= 0. satis es the triangle inequality, that is ku+ vk kuk+ kvk: Lemma 17.4. Let V be a real inner ...
Derivation of the Lorentz Transformation
www2.physics.umd.eduThe derivation can be compactly written in matrix form. However, for those not familiar with matrix notation, I also write it without matrices. ... (24) and (25) describe a Euclidean space-time and preserve the space-time distance: (x0) 2+ (˙t0)2 = x + (˙t)2. 4.
Graduate Texts in Mathematics
www.maths.ed.ac.ukflatness (local equivalence to Euclidean space). Chapter 8 departs some-what from the traditional order of presentation, by investigating subman-ifold theory immediately after introducing the curvature tensor, so as to define sectional curvatures and give the curvature a more quantitative ge-ometric interpretation.
Rotation matrix - BrainMaster Technologies Inc.
brainm.comAug 04, 2011 · Rotation matrix From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In linear algebra, a rotation matrix is a matrix that is used to perform a rotation in Euclidean space. For example the matrix rotates points in the xy-Cartesian plane counterclockwise through an angle θ about the origin of the Cartesian coordinate system. To perform the rotation, the position of each point must be …
Solution 1. Solution 2. Solution 3.
math.berkeley.eduMath 140. Solutions to homework problems. Homework 1. Due by Tuesday, 01.25.05 1. Let Dd be the family of domains in the Euclidean plane bounded by the smooth curves ∂Dd equidistant to a bounded convex domain D0.How does the perimeter Length(∂Dd) depend on the distance d between ∂Dd and D0? Solution 1.
EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY - BRETTONWOOD HIGH SCHOOL
brettonwoodhighschool.co.zaEuclidean Geometry ...Grades 10-12 Compiled by Mr N. Goremusandu (UThukela District) SECTION B GRADE 11 : EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY THEOREMS 1. The line drawn from the centre of a circle perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord. 2. The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the centre of the circle. 3.
Euclidean Distance Matrix - Stanford University
ccrma.stanford.eduEuclidean Distance Matrix These results [(1068)] were obtained by Schoenberg (1935), a surprisingly late date for such a fundamental property of Euclidean geometry. −John Clifford Gower [190, § 3] By itself, distance information between many points in …
Euclidean Geometry Notes - Florida Atlantic University
math.fau.eduYIU: Euclidean Geometry 3 3. ABC is a triangle with a right angle at C. If the median on the side a is the geometric mean of the sidesb and c, show that c =3b. 4. (a)Supposec = a+kbfor a righttriangle with legs a, b, and hypotenuse c.Showthat0<k<1, and a : b : c =1−k2:2k :1+k2. (b) Find two right triangles which are not similar, each ...
Euclidean Distance - Paul Barrett's Homepage
www.pbarrett.netSeptember, 2005 Euclidean Distance raw, normalized, and double‐scaled coefficients
EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY MATHEMATICS GRADE 10
tongaatsecondary.co.zaeuclidean geometry mathematics grade 10 revision pack past papers january 1, 2018 by: ayanda dladla cell no: 074 994 7970
EUCLIDEAN PARALLEL POSTULATE
web.ma.utexas.eduFeb 05, 2010 · EUCLIDEAN PARALLEL POSTULATE 2.1 INTRODUCTION. There is a well-developed theory for a geometry based solely on the five Common Notions and first four Postulates of Euclid. In other words, there is a geometry in which neither the Fifth Postulate nor any of its alternatives is taken as an axiom. This
Euclidean Space and Metric Spaces - UCI Mathematics
www.math.uci.eduDe nition 8.2.2. (Open Sets) (i) O M is called open or, in short O o M , i 8 x 2 O 9 r > 0 s.t. x 2 B( x;r ) O: (ii) Any set U M containing a ball B( x;r ) about x is called neighborhood of x . The collection of all neighborhoods of a given point x is denoted by U (x ).
Similar queries
EUCLIDEAN, NON-EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY, Rochester Institute of Technology, Projective Geometry, Euclidean Geometry, Dimensional, Dimensional Euclidean, Distance, Euclidean Distance, Introduction to, Chapter, Guide, Lesson, Euclidean Geometry 1, Chapter 1 Euclidean space, Multivariable Calculus, INTRODUCTION, Space, Gr 10 Maths – Euclidean Geometry, Coordinate Geometry, Geometry, Postulates, Theorems, MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: REAL ANALYSIS, SPSS Statistics 19 Statistical Procedures, Matrix, Euclidean space, Algorithms for Non-negative Matrix Factorization, Spaces, Three, Chapter 1, 17. Inner product spaces, Derivation of the Lorentz Transformation, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, Euclidean Distance Matrix, Between, Points, Euclidean Space and Metric Spaces, Nition