Euclidean Distance Matrix
Found 10 free book(s)Problems and Solutions in Matrix Calculus
issc.uj.ac.zaMatrix Calculus by Willi-Hans Steeb ... Rn n-dimensional Euclidean space space of column vectors with nreal components ... of M have Hamming distance n=2. The Hamming distance between two vectors is the number of entries at which they di …
Derivation of the Lorentz Transformation
www2.physics.umd.eduThe derivation can be compactly written in matrix form. However, for those not familiar with matrix notation, I also write it without matrices. ... (24) and (25) describe a Euclidean space-time and preserve the space-time distance: (x0) 2+ (˙t0)2 = x + (˙t)2. 4.
Algorithms for Non-negative Matrix Factorization
proceedings.neurips.ccusing some measure of distance between two non-negative matrices A and B . One useful measure is simply the square of the Euclidean distance between A and B [13], IIA -BI12 = L(Aij - Bij)2 ij This is lower bounded by zero, and clearly vanishes if and only if A = B . Another useful measure is D(AIIB) = 2: ( Aij log k· B:~ - Aij + Bij ) "J (2) (3)
Euclidean Distance Matrix - Stanford University
ccrma.stanford.eduEUCLIDEAN DISTANCE MATRIX Wıκımization [439].) Having found equivalent matrix criteria, we will see there is a bridge from bounded convex polyhedra to EDMs in § 5.9.5.6 Now we develop some invaluable concepts, moving toward a link of the Euclidean metric properties to matrix criteria. 5.4 EDM definition
Rotation matrix - BrainMaster Technologies Inc.
brainm.comAug 04, 2011 · Rotation matrix From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In linear algebra, a rotation matrix is a matrix that is used to perform a rotation in Euclidean space. For example the matrix rotates points in the xy-Cartesian plane counterclockwise through an angle θ about the origin of the Cartesian coordinate system. To perform the rotation, the position of each point must be …
Solution 1. Solution 2. Solution 3.
math.berkeley.eduMath 140. Solutions to homework problems. Homework 1. Due by Tuesday, 01.25.05 1. Let Dd be the family of domains in the Euclidean plane bounded by the smooth curves ∂Dd equidistant to a bounded convex domain D0.How does the perimeter Length(∂Dd) depend on the distance d between ∂Dd and D0? Solution 1.
17. Inner product spaces - MIT Mathematics
math.mit.eduEuclidean distance. De nition 17.3. Let V be a real vector space. A norm on V is a function k:k: V ! R; what has the following properties kkvk= jkjkvk; for all vectors vand scalars k. positive that is kvk 0: non-degenerate that is if kvk= 0 then v= 0. satis es the triangle inequality, that is ku+ vk kuk+ kvk: Lemma 17.4. Let V be a real inner ...
k-Shape: Efficient and Accurate Clustering of Time Series
www1.cs.columbia.edu2.3 Time-Series Distance Measures The two state-of-the-art approaches for time-series com-parison first z-normalize thesequences andthen use adis-tance measure to determine their similarity, and possibly capture more invariances. The most widely used distance metricisthesimpleED[20]. EDcomparestwotimeseries
MATH 304 Linear Algebra
www.math.tamu.eduThat is, the nullspace of a matrix is the orthogonal complement of its row space. Proof: The equality Ax = 0 means that the vector x is orthogonal to rows of the matrix A. Therefore N(A) = S⊥, where S is the set of rows of A. It remains to note that S⊥= Span(S)⊥= R(AT)⊥. Corollary Let V be a subspace of Rn. Then dimV +dimV⊥ = n.
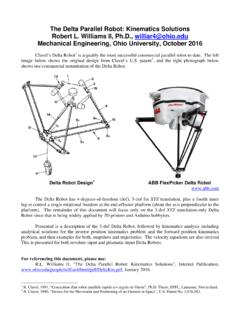
The Delta Parallel Robot: Kinematics Solutions Robert L ...
www.ohio.edu4 The three-dof Delta Robot is capable of XYZ translational control of its moving platform within its workspace. Viewing the three identical RUU chains as legs, points Bii,1,2,3 are the hips, points Aii,1,2,3 are the knees, and points Pii,1,2,3 are the ankles.The side length of the base equilateral triangle is sB and the side length of the moving platform equilateral triangle is sP.